Abstract
Suppression of systemic immunity after the feeding of antigen was investigated in mice by means of serum transfer experiments. Serum collected from mice 1 hr after a single intragastric dose of 25 mg OVA induced suppression of systemic DTH when injected intraperitoneally into recipient mice. This suppression was found to be restricted to the cell-mediated limb of immunity and was antigen-specific. A postulated function of the intestine, conversion of antigen into tolerogenic form by means of intestinal antigen processing, was studied by attempting to mimic intestinal alteration of OVA by chemical modification of the antigen. Parenteral injection of mice with either deaggregated or denatured OVA did not produce the typical pattern of unresponsiveness seen in animals given intestinally processed OVA. Intestinal processing was also shown to be distinct from systemic antigen processing. Mice injected with serum containing systemically 'filtered' OVA did not become tolerant to OVA in the manner of recipients of serum from OVA-fed mice.
Full text
PDF
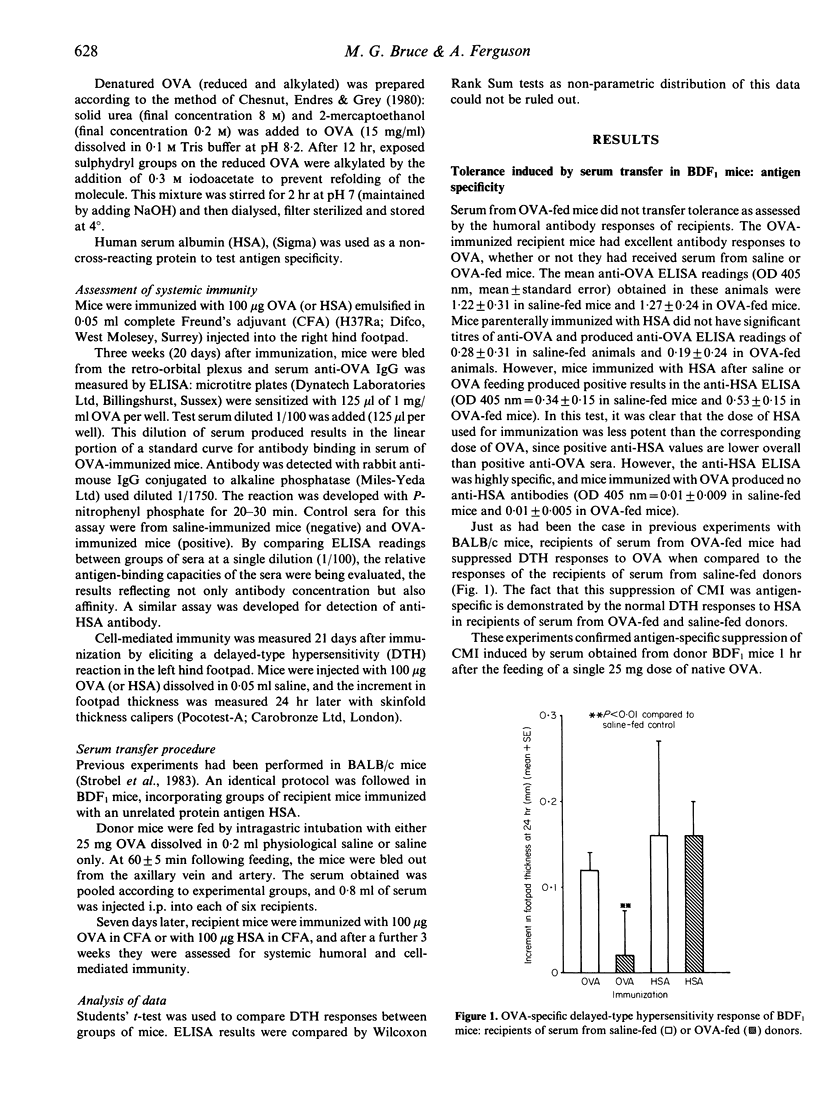
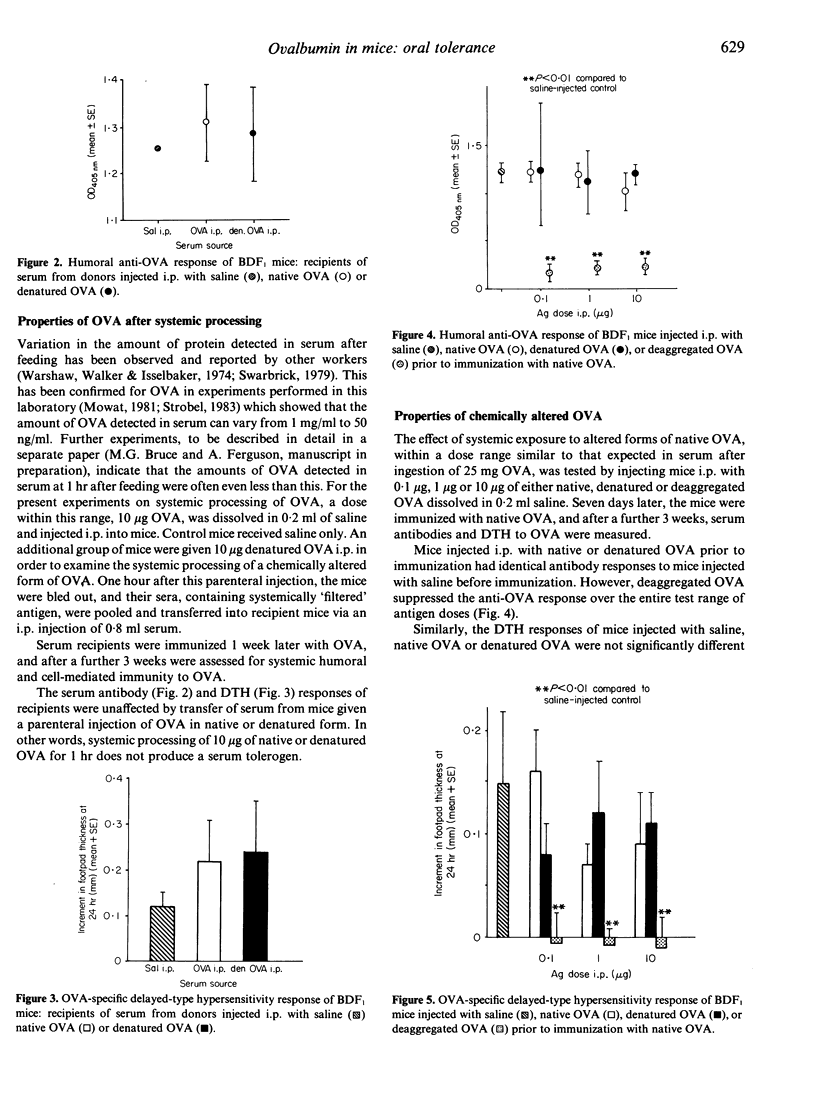

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chesnut R. W., Endres R. O., Grey H. M. Antigen recognition by T cells and B cells: recognition of cross-reactivity between native and denatured forms of globular antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. D., Strejan G. H. Immunological tolerance of the mouse IgE system: dissociation between T cell tolerance and suppressor cell activity. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):602–608. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREI P. C., BENACERRAF B., THORBECKE G. J. PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE ANTIGEN, A CRUCIAL STEP IN THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY RESPONSE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:20–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Weigle W. O. Studies on the induction of immunologic unresponsiveness. 3. Antigen form and mouse strain variation. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukić M. L., Cowing C., Leskowitz S. Strain differences in ease of tolerance induction to bovine gamma-globulin: dependence on macrophage function. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):503–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity in the small intestinal mucosa. V. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to a dietary antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):574–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Strobel S., Drummond H. E., Ferguson A. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. I. Reversal of oral tolerance to ovalbumin by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):105–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Mowat A. M., Drummond H. E., Pickering M. G., Ferguson A. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. II. Oral tolerance for CMI is due to activation of cyclophosphamide-sensitive cells by gut-processed antigen. Immunology. 1983 Jul;49(3):451–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Ishizaka K. Reaginic antibody formation in the mouse. VI. Suppression of IgE and IgG antibody responses to ovalbumin following the administration of high dose urea-denatured antigen. Cell Immunol. 1975 Dec;20(2):276–289. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J. Protein uptake by the intestine: evidence for absorption of intact macromolecules. Gastroenterology. 1974 May;66(5):987–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


