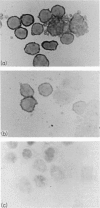
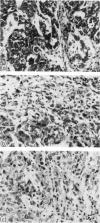
Abstract
The murine monoclonal antibody CI-panHu reacts strongly with the cell surface of all human cells, including erythrocytes, tumour cells and HLA-A,B,C-negative cell lines. As such, this antibody defines the first pan-human cell-surface antigen reported. The antigenic determinant detected is associated with a protein doublet of 16,000 MW whose expression is restricted to cells from humans, apes and some species of Old World monkeys. Antibody reactivity is not diminished by routine fixation procedures, nor by paraffin-embedding, and the antigenic determinant is relatively protease-resistant. The use of this antibody as a positive control in immunoassays of human cells is discussed.
Full text
PDF

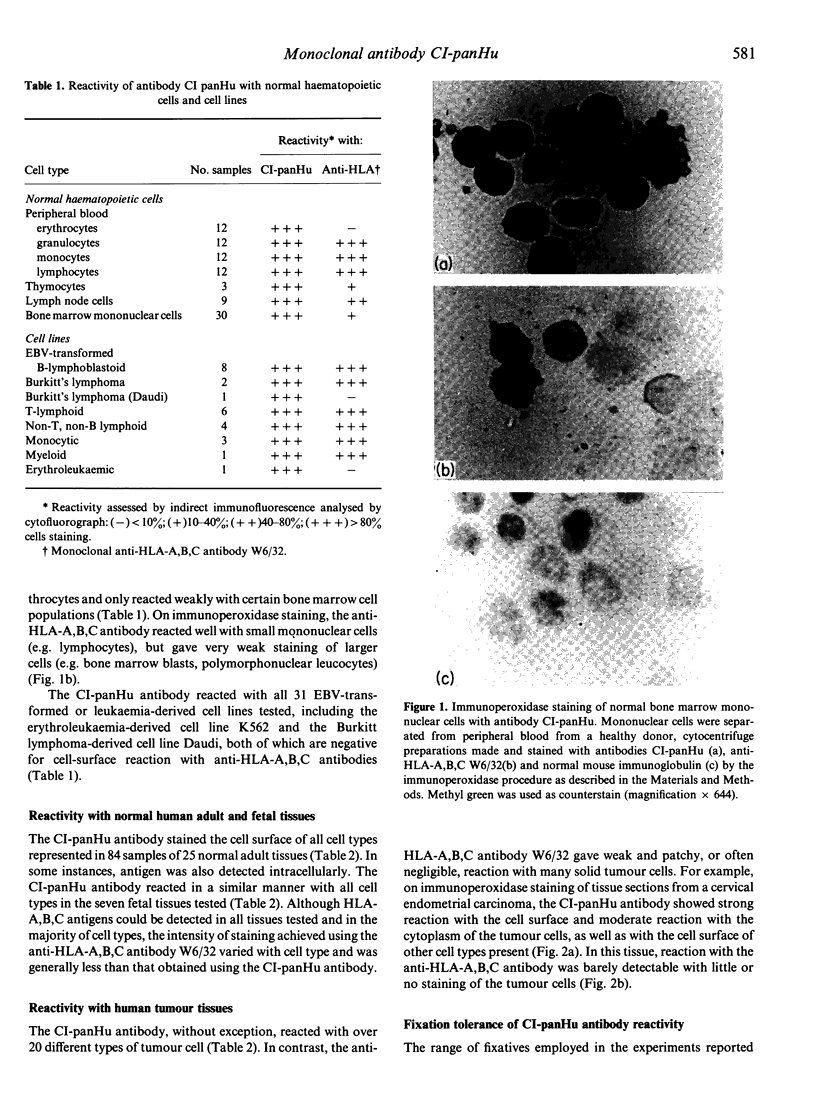
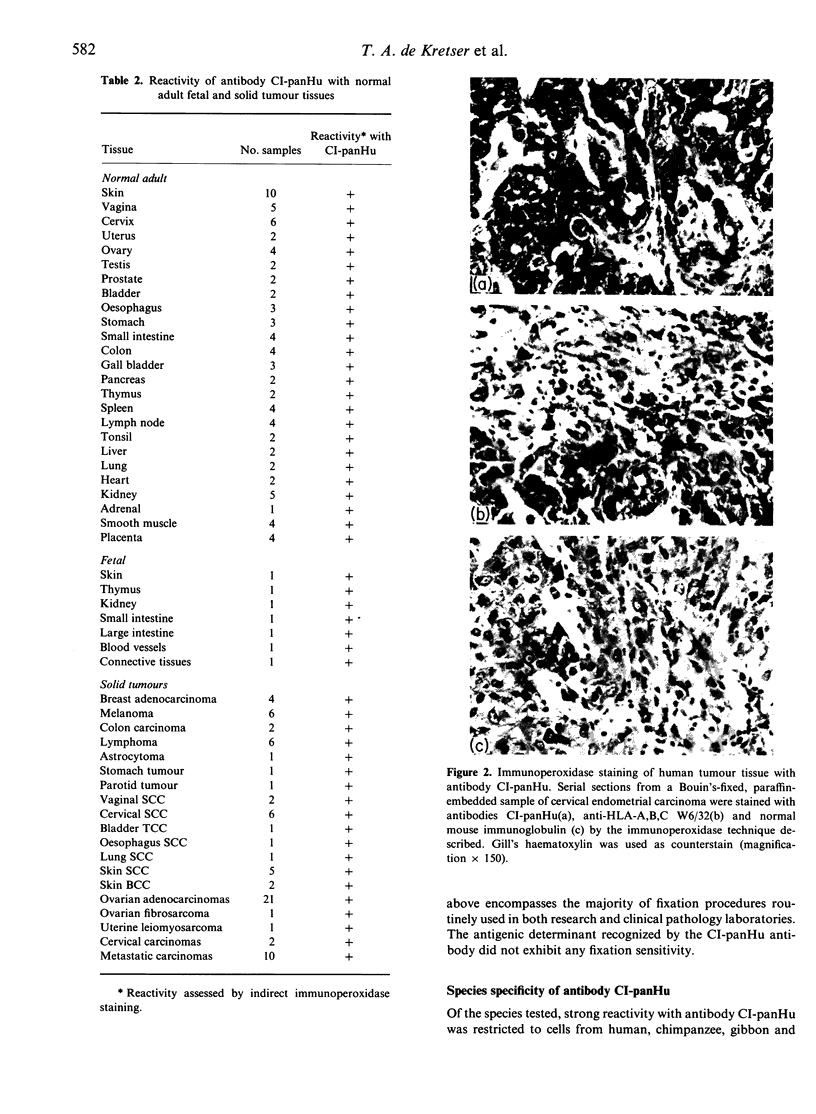
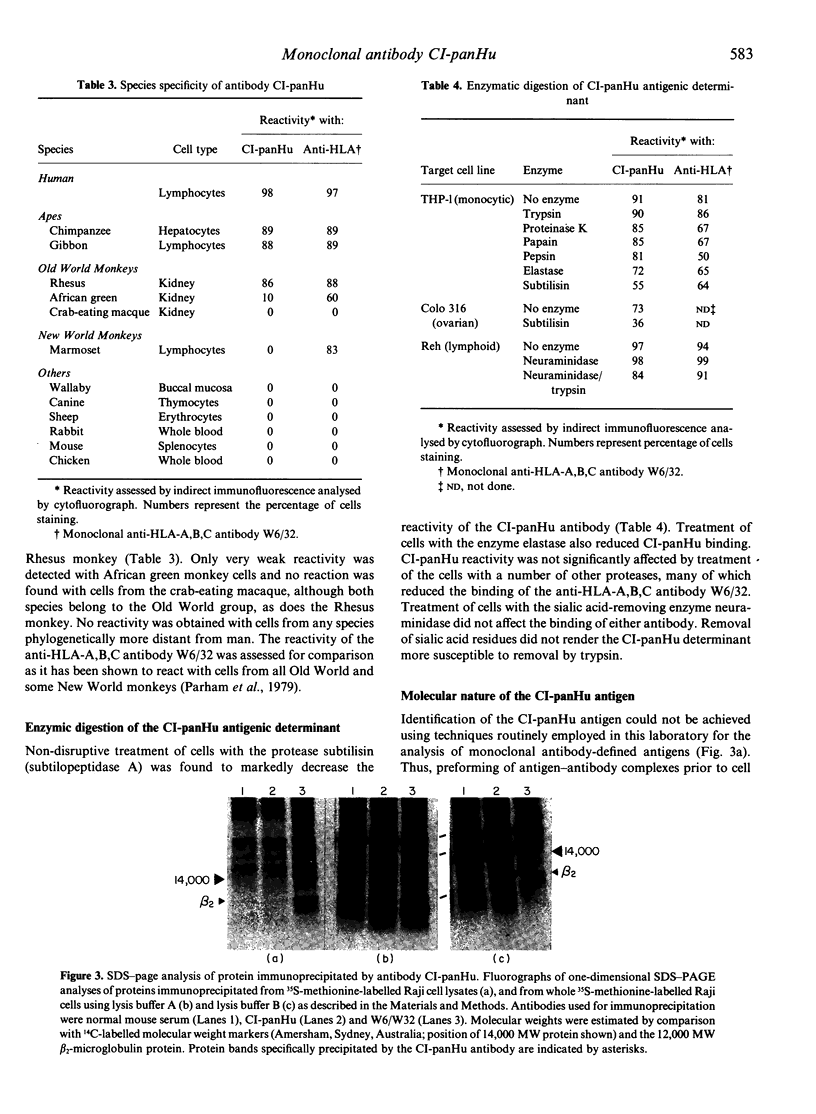


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Kraft N., Atkins R. C. The immunohistochemical demonstration of major histocompatibility antigens in the human kidney using monoclonal antibodies. Pathology. 1982 Oct;14(4):409–414. doi: 10.3109/00313028209092120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Sehgal P. K., Brodsky F. M. Anti-HLA-A,B,C monoclonal antibodies with no alloantigenic specificity in humans define polymorphisms in other primate species. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):639–641. doi: 10.1038/279639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. J., Beverley P. C. Characterisation of breast cancer infiltrates using monoclonal antibodies to human leucocyte antigens. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):149–159. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kretser T. A., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F. Demonstration of two distinct light chains in HLA-DR-associated antigens by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):214–221. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kretser T. A., Thorne H. J., Jacobs D. J., Jose D. G. The sebaceous gland antigen defined by the OM-1 monoclonal antibody is expressed at high density on the surface of ovarian carcinoma cells. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1985 Sep;21(9):1019–1035. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(85)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]