Abstract
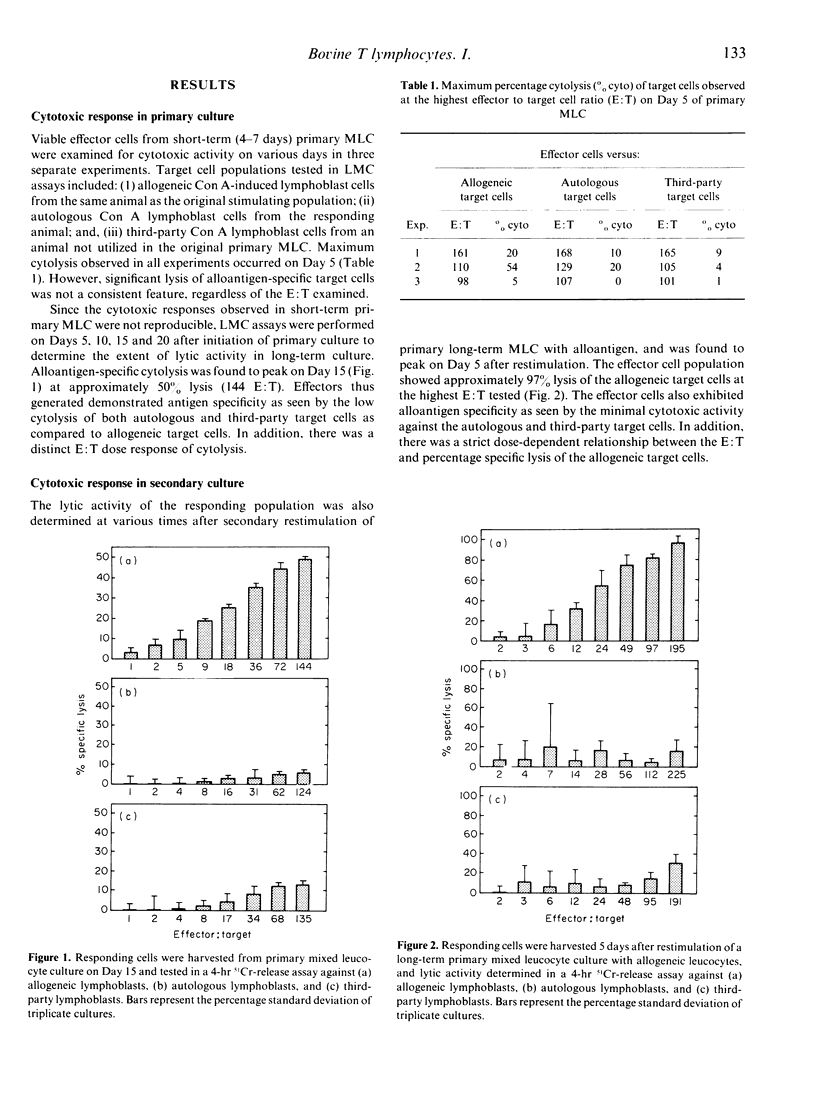
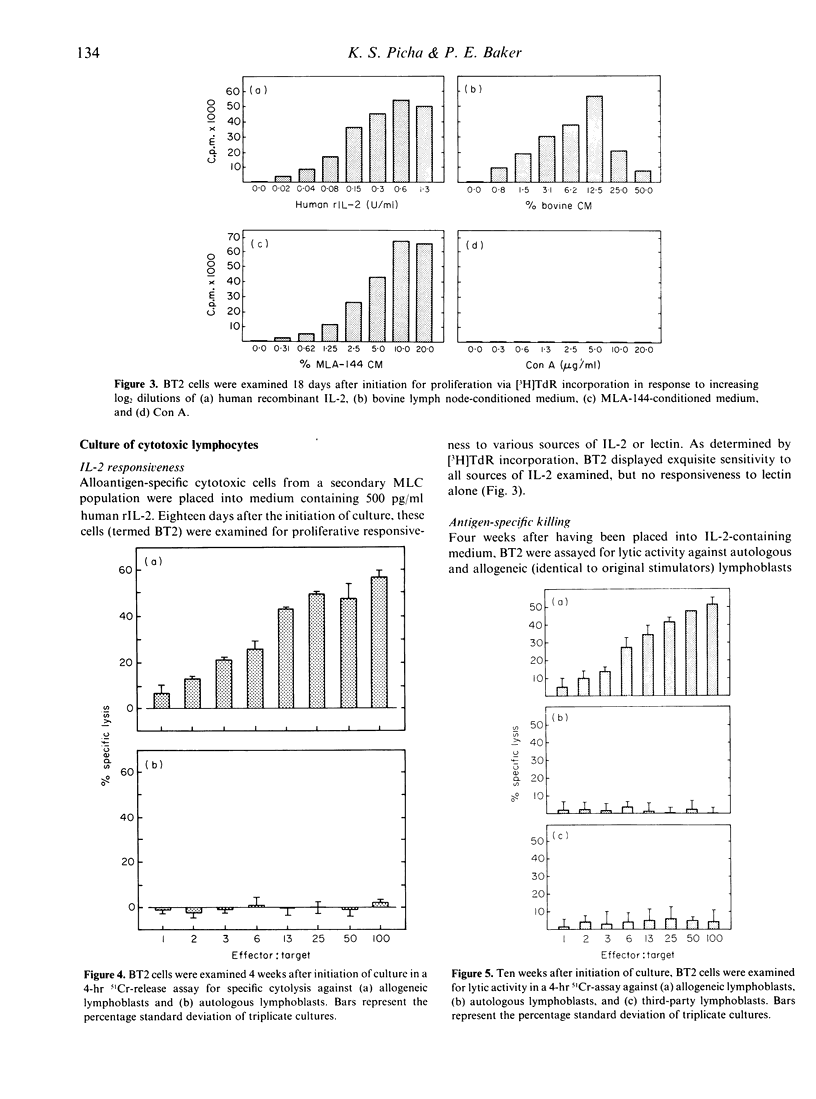
Primary and secondary bovine allogeneic mixed leucocyte cultures were examined for the generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic leucocytes. While optimal generation of murine and human cytotoxic T lymphocytes typically requires 4-8 days, alloantigen-specific cytotoxic bovine leucocytes were demonstrated consistently only after prolonged incubation periods, optimally found to be about 15 days. Restimulation of long-term bovine mixed leucocyte cultures with the original stimulator population revealed responder cells demonstrating augmented alloantigen-specific lytic activity. When placed into human recombinant interleukin-2, responder cells expanded and required passaging every 3-4 days. The same was not true of cells placed into interleukin-2-free medium. Cells cultured in interleukin-2-containing medium retained alloantigen specificity after 10 weeks of culture. Moreover, they continued to display total dependence on human, simian or bovine interleukin-2 for growth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. E., Gillis S., Smith K. A. Monoclonal cytolytic T-cell lines. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):273–278. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Knoblock K. F. Bovine costimulator. I. Production kinetics, partial purification, and quantification in serum-free Iscove's medium. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jul;3(4):365–379. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blecha F., Minocha H. C. Suppressed lymphocyte blastogenic responses and enhanced in vitro growth of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in stressed feeder calves. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Nov;44(11):2145–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlie J., Stott E. J. The response of bovine lymphocytes from lymph and blood to phytohaemagglutinin. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Nov;1(1):5–13. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(79)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmann H., Pawlas S. Characterization and separation of bovine lymphocyte populations. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1980;3(3):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(80)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Engers H. D., Macdonald H. R., Brunner T. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. I. Response of normal and immune mouse spleen cells in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):703–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. In vitro generation of tumor-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes. Secondary allogeneic mixed tumor lymphocyte culture of normal murine spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):468–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Union N. A., Baker P. E., Smith K. A. The in vitro generation and sustained culture of nude mouse cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1460–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. W., Greenfield R. E., Evermann J. F., Parish S. M., Perryman L. E. Delayed-type hypersensitivity, contact sensitivity, and phytohemagglutinin skin-test responses of heat- and cold-stressed calves. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Sordat B., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. IV. Functional activation of memory cells in the absence of DNA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):622–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser J. E., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes in vitro. IX. induction of secondary CTL responses in primary long-term MLC by supernatants from secondary MLC. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondel P. M., Bach F. H. Recognitive specificity of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. I. Antigen-specific inhibition of human cell-mediated lympholysis. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1339–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausser J. L., Rosenberg S. A. In vitro growth of cytotoxic human lymphocytes. I. Growth of cells sensitized in vitro to alloantigens. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1491–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



