Abstract
Rats born of egg albumin immunized mothers have a diminished capacity to produce IgE antibody to egg albumin persisting for at least 13-14 weeks after birth. At the same time the primary IgG response to the antigen is usually enhanced. Previous studies indicated that these effects were mediated by factors transferred in maternal milk. The phenomenon can be duplicated by the administration of small quantities of immune serum to rats during the first 3 weeks of life. The active component of immune serum is shown to be specific antibody. Suckling rats acquire egg-albumin-specific IgG from the immune mother via the milk. Their serum level approaches that of the mother by 20 days but declines rapidly after weaning to become undetectable by 6-8 weeks. As maternal influence on the immune responsiveness of the offspring persists for several weeks beyond this time, it is unlikely that the mechanism involves a simple blocking by circulating antibody of the access of antigen to cellular receptors. Alternative mechanisms are briefly discussed. Attention is drawn to the possibility that the suppression of IgE antibody responsiveness by maternal IgG may represent a physiological regulatory process with a role in inhibiting the development of infantile allergies.
Full text
PDF

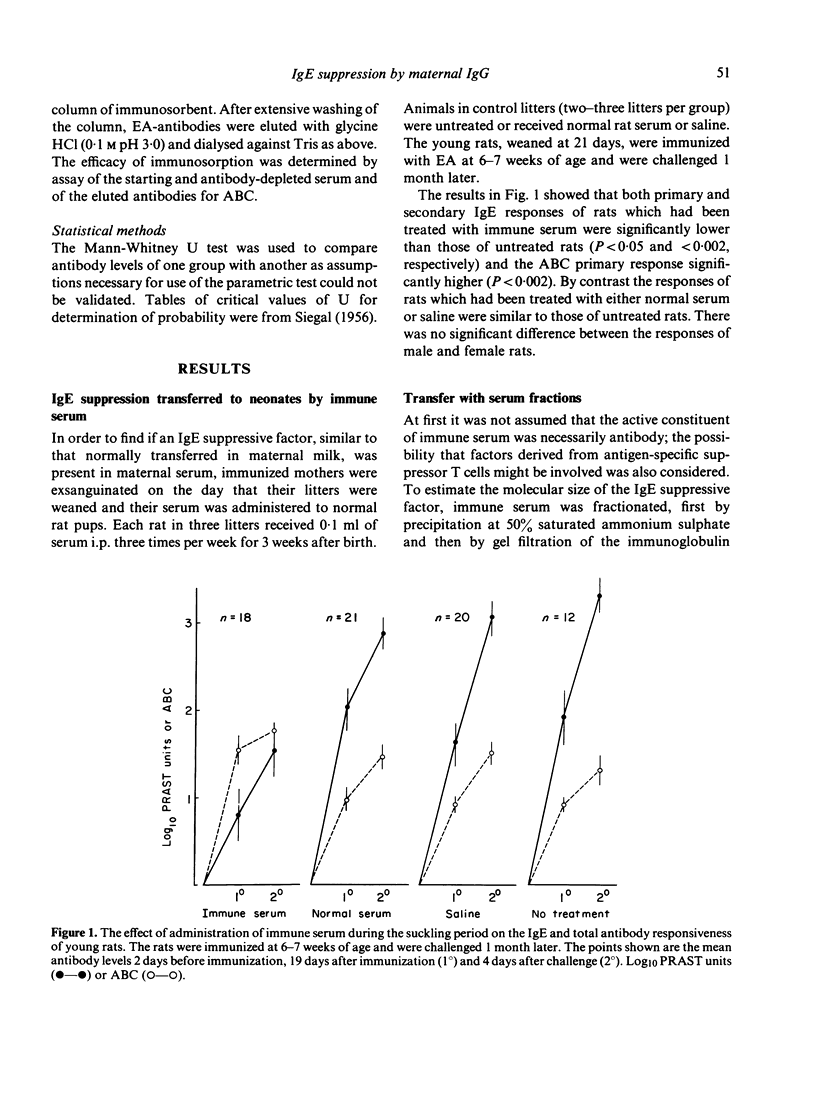
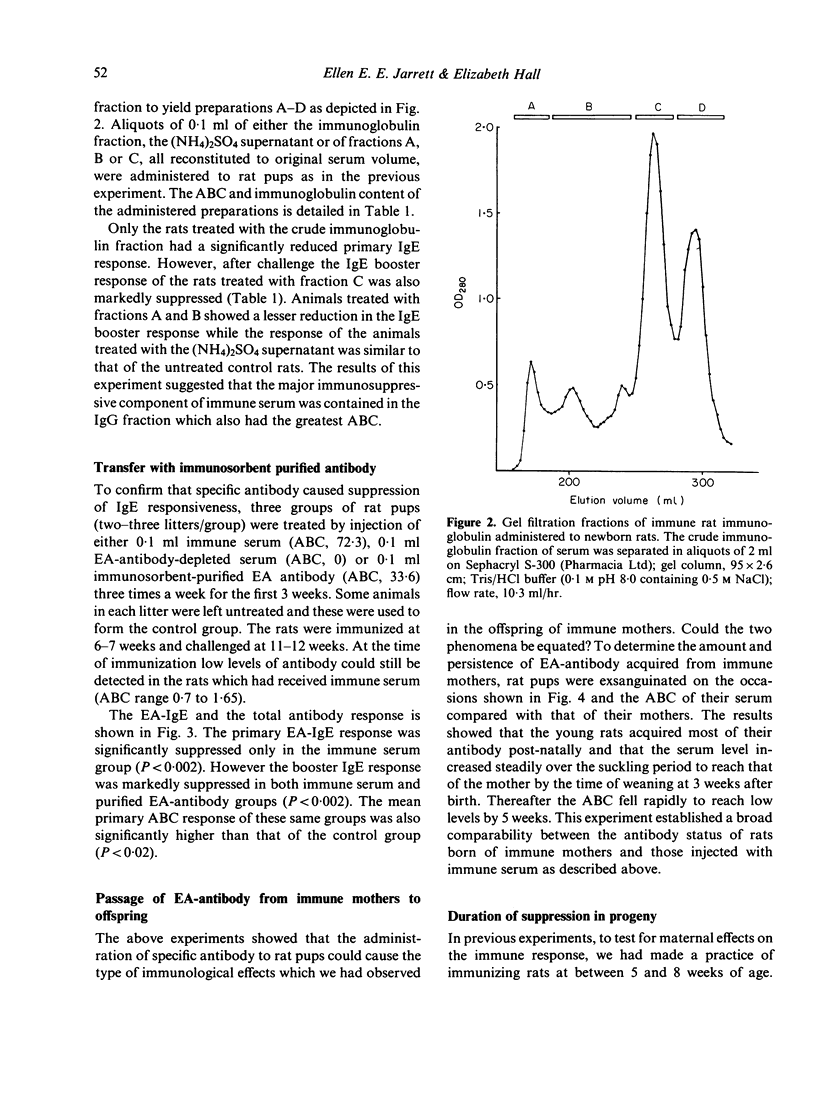
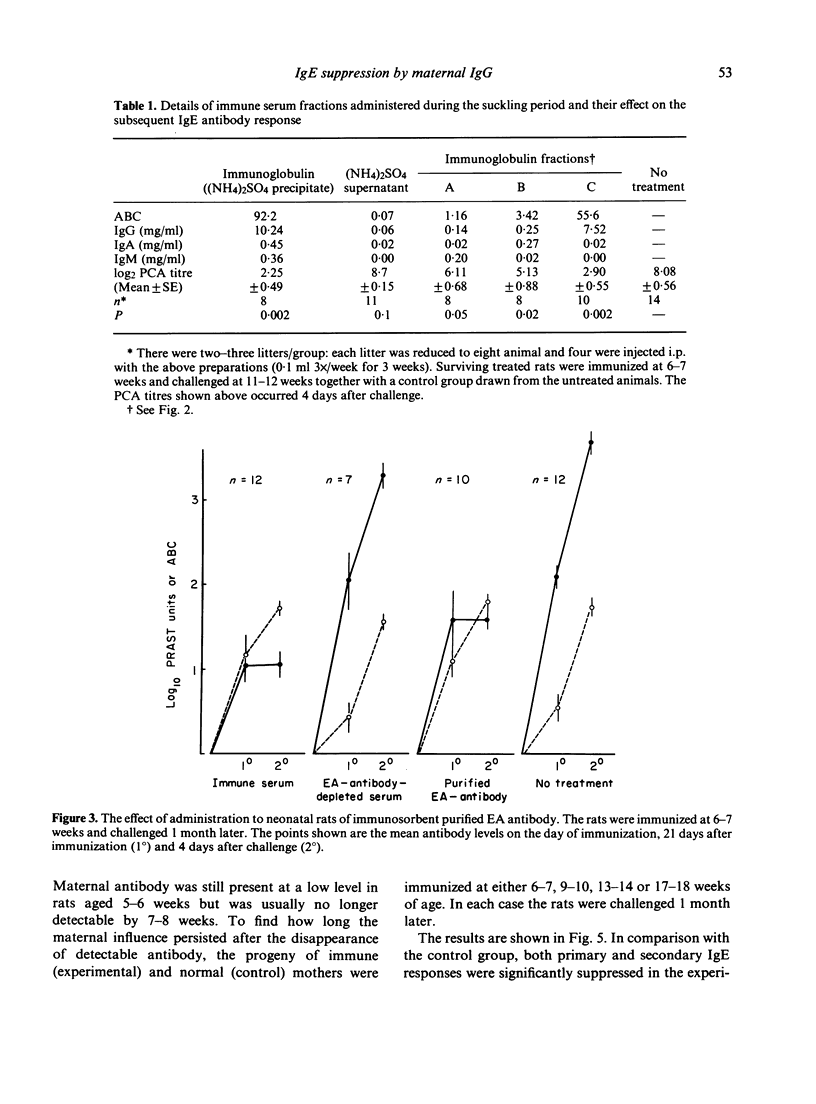
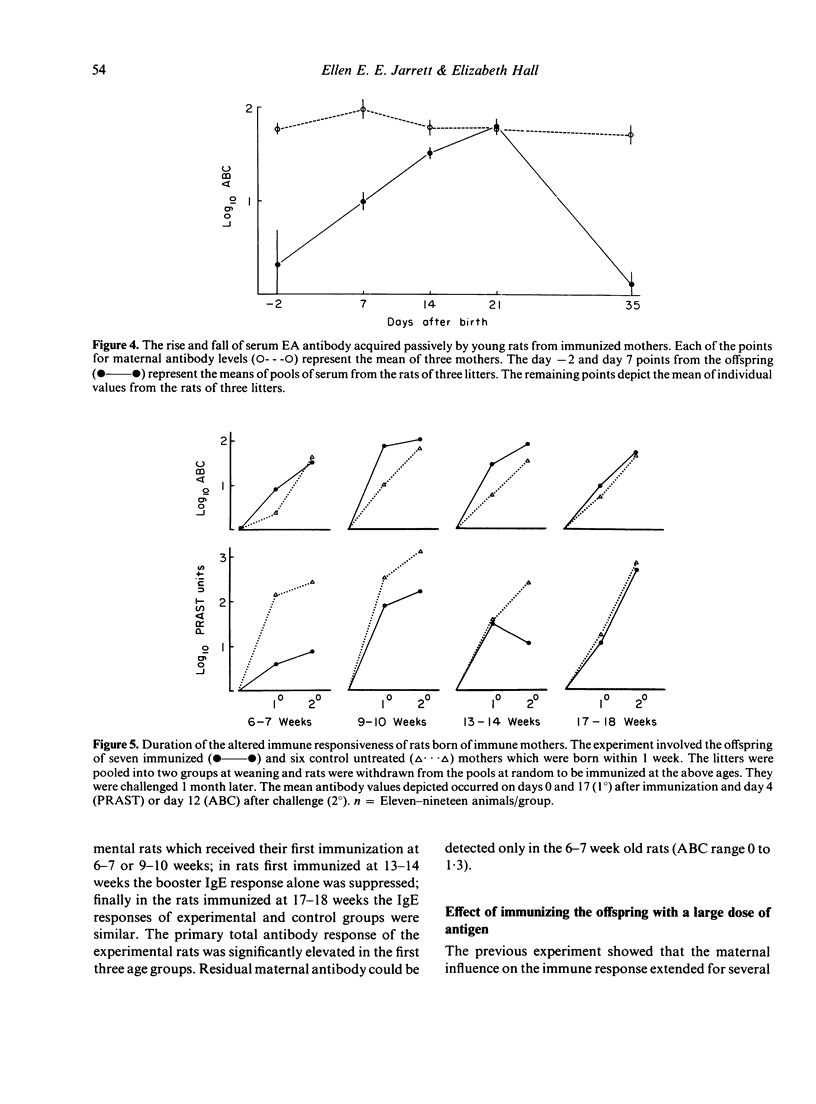



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht P., Ennis F. A., Saltzman E. J., Krugman S. Persistence of maternal antibody in infants beyond 12 months: mechanism of measles vaccine failure. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):715–718. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM D. R., TERRY R. J. The survival of globulins absorbed from the gut in suckling rats. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):584–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0660584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Relationships between immunoglobulins and the intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):129–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer D. V., Kunz H. W., Gill T. J., 3rd Immunologic sensitization prior to birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Oct 10;120(3):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannaeus A., Inganäs M. A follow-up study of children with food allergy. Clinical course in relation to serum IgE- and IgG-antibody levels to milk, egg and fish. Clin Allergy. 1981 Nov;11(6):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1981.tb02171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannaeus A., Johansson S. G., Foucard T. Clinical and immunological aspects of food allergy in childhood. II. Development of allergic symptoms and humoral immune response to foods in infants of atopic mothers during the first 24 months of life. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978 Jul;67(4):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1978.tb16360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY R. The termination of the capacity of young rats to absorb antibody from the milk. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 May 29;145(919):179–185. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E. Activation of IgE regulatory mechanisms by transmucosal absorption of antigen. Lancet. 1977 Jul 30;2(8031):223–225. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92837-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Hall E. Regulation of ongoing IgE antibody responses with minute doses antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):520–523. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Stewart D. C. Rat IgE production. I. Effect of dose of antigen on primary and secondary reaginic antibody responses. Immunology. 1974 Sep;27(3):365–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E. Stimuli for the production and control of IgE in rats. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:52–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E., Hall E. Selective suppression of IgE antibody responsiveness by maternal influence. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):145–147. doi: 10.1038/280145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson T., Ellerson J. R., Haig D. M., Jarrett E. E., Bennich H. A radioimmunoassay for evaluation of the IgE and IgG antibody responses in the rat. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHISON N. A. INDUCTION OF IMMUNOLOGICAL PARALYSIS IN TWO ZONES OF DOSAGE. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Dec 15;161:275–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. The carrier effect in the secondary response to hapten-protein conjugates. I. Measurement of the effect with transferred cells and objections to the local environment hypothesis. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):10–17. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard J. V., Orlans E. The biological half-lives of four rat immunoglobulin isotypes. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):683–686. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair N. R. Modulation of immunity by antibody, antigen-antibody complexes and antigen. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;4(2):355–432. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B., Riddell G. S., Whyte D. F. Specific immunosuppressive delay of the plaque-forming response by trace amounts of antibody of maternal origin in young rats injected with mouse or sheep erythrocytes. Immunology. 1972 Feb;22(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


