Abstract
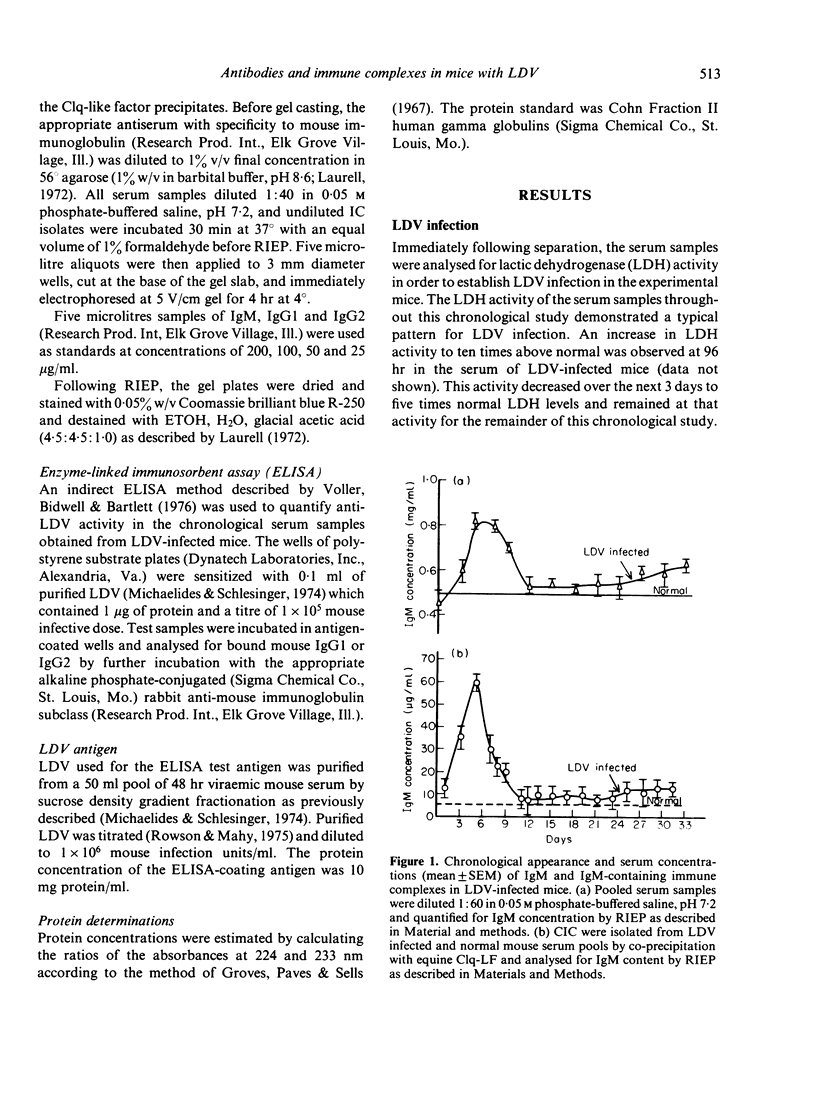
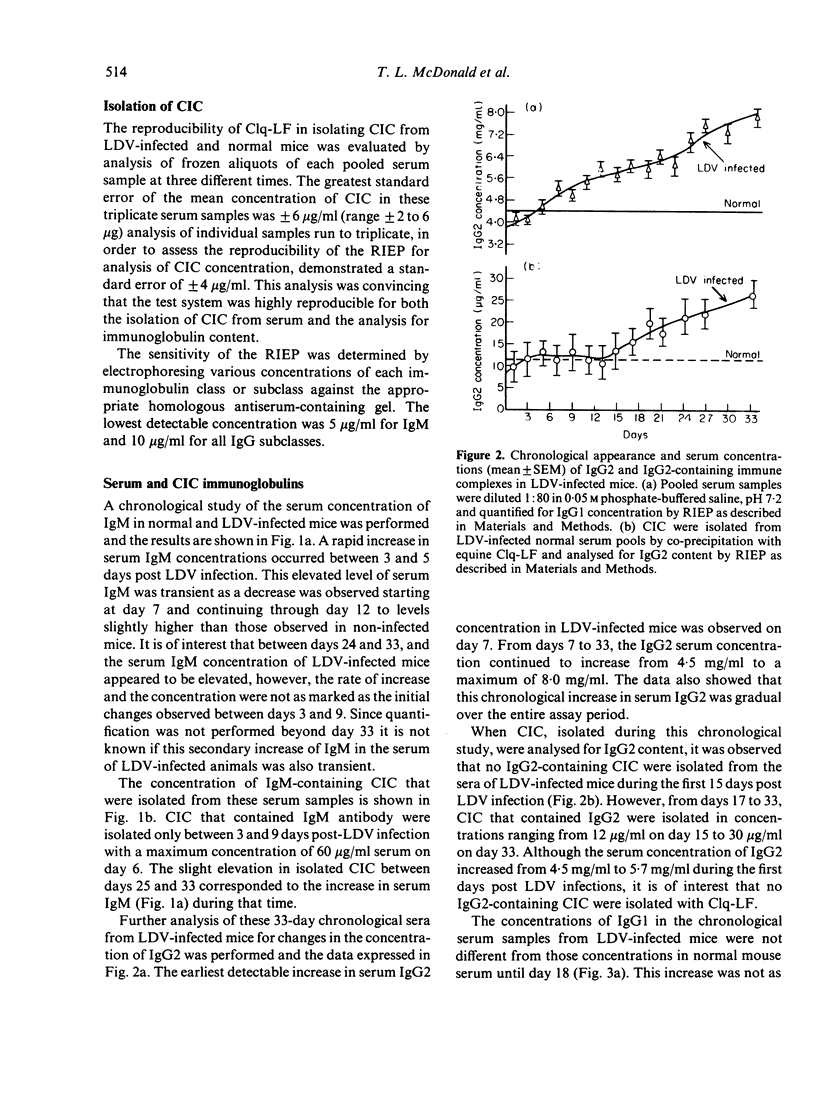
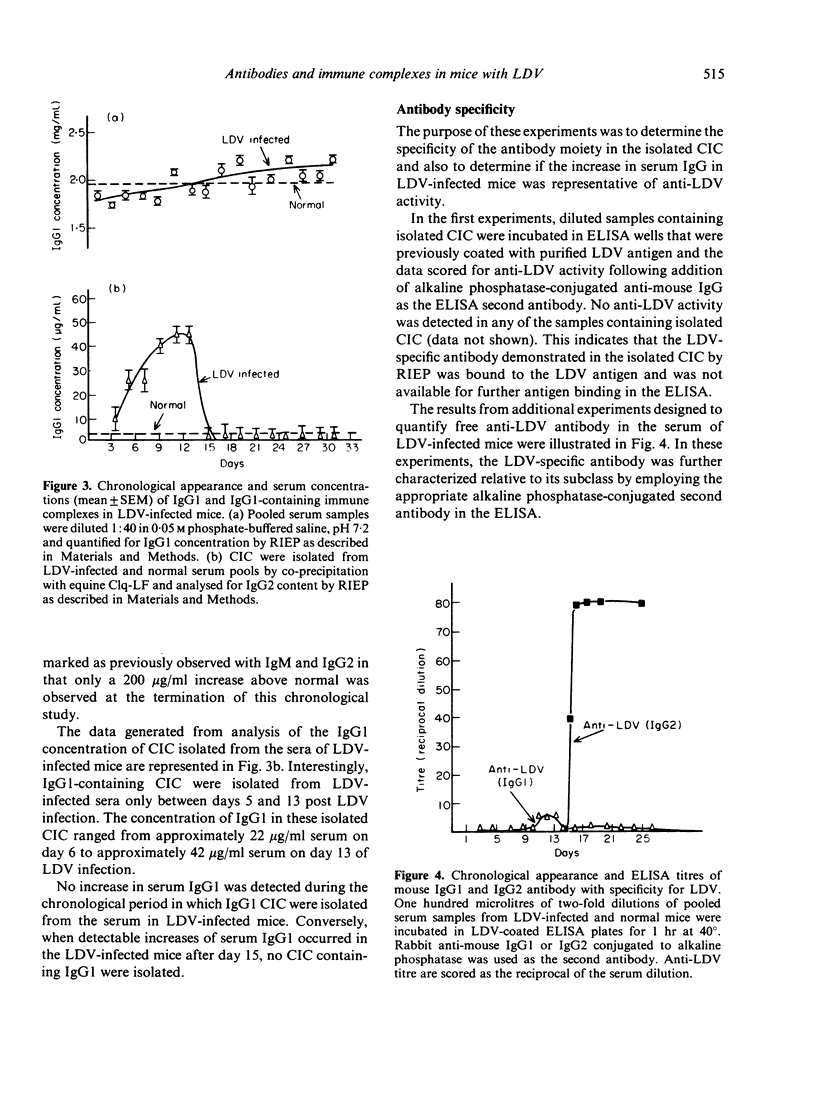
A chronological study of circulating immune complexes (CIC) in lactic dehydrogenase virus (LDV)-infected mice has been performed. The results demonstrate that CIC containing immunoglobulin of the IgM class were isolated between days 3 and 9 post-LDV infection and corresponded to an increase in serum IgM. IgG1-containing CIC were also transient in the serum of LDV-infected mice in that they were isolated only between days 5 and 13. The occurrence of IgG1 CIC did correlate with an increase in total IgG1 in the serum, however, it did correlate with a small (1:10) increase in IgG1 anti-LDV activity. In contrast, CIC containing immunoglobulin of the serum IgG2 subclass were not isolated from LDV-infected serum until 15 days post infection. This chronological appearance of IgG2 CIC did not correlate with the observed increase in total IgG2 concentration in LDV-infected mice on day 7, however, was analogous to the rapid increase in free serum LDV-specific antibody. We propose that the non-specific suppression of the immune response and tumour enhancement during the acute phase of LDV infection could be due to the immunoregulatory properties of IgG1 CIC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonventre P. F., Bubel H. C., Michael J. G., Nickol A. D. Impaired resistance to bacterial infection after tumor implant is traced to lactic dehydrogenase virus. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):316–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.316-319.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc H. T., Kinsky R. G., Kanellopoulos J., Voisin G. A. Biologic properties of transplantation immune sera. IV. Influence of the course of immunization, dilution and complexing to antigen on enhancing activity of Ig classes. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1143–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves W. E., Davis F. C., Jr, Sells B. H. Spectrophotometric determination of microgram quantities of protein without nucleic acid interference. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. N., Harris S., Henri E. M., Farber M. B. Enhancement of growth of allogeneic mouse tumor by the IgG1 fraction of alloantibody preparations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jan;60(1):167–172. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and blocking serum activity to tumor antigens. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:209–277. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. C., Chang R. W., Turk J. L. Infection with LDH virus alters host response to tumours. Br J Cancer. 1979 Apr;39(4):453–456. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. C., Tosta C. E., Wedderburn N. Exacerbation of murine malaria by concurrent infection with lactic dehydrogenase-elevating virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Aug;33(2):357–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Notkins A. L., Mergenhagen S. E. Inhibition of cellular immune reactions in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):873–874. doi: 10.1038/221873a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakov N., Feldman M., Segal S. Effect of lactic dehydrogenase virus infection on tumor induction and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):667–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahy B. W., Rowson K. E., Parr C. W., Salaman M. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of Riley virus. I. Action of substances affecting the reticuloendothelial system on plasma enzyme levels in mice. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):967–981. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. L. Isolation of Clq-binding virus-antibody immune complexes from lactic dehydrogenase virus (LDV)-infected mice. Immunology. 1982 Feb;45(2):365–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. L. Isolation of immune complexes by an equine Clq-like factor. Immunol Commun. 1981;10(8):741–752. doi: 10.3109/08820138109051960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides M. C., Schlesinger S. Effect of acute or chronic infection with lactic dehydrogenase virus (LDV) on the susceptibility of mice to plasmacytoma MOPC-315. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1560–1564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides M. C., Schlesinger S. Structural proteins of lactic dehydrogenase virus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides M. C., Simms E. S. Immune responses in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. I. Antibody response to DNP-BGG and hyperglobulinaemia in BALB/c mice. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):981–988. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides M. C., Simms E. S. Immune responses in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. II. Contact sensitization to DNFB and characterization of lymphoid cells during acute LDV infection. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 15;29(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides M. C., Simms E. S. Immune responses in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. III. Antibody response to a T-dependent and a T-independent antigen during acute and chronic LDV infection. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 15;50(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mahar S., Scheele C., Goffman J. Infectious virus-antibody complex in the blood of chronically infected mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Inhibition of antibodies to nuclear antigen and to DNA in New Zealand mice infected with lactate dehydrogenase virus. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):784–786. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Lactic dehydrogenase virus-induced immune complex type of glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1260–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G. Deposition of immune complexes in the kidneys of mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1264–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley V. Persistence and other characteristics of the lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus (LDH-virus). Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):198–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren H. O., Hellström I., Bansal S. C., Hellström K. E. Suggestive evidence that the "blocking antibodies" of tumor-bearing individuals may be antigen--antibody complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1372–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- StC Sinclair N. R. Mechanisms of immunoregulation. Immunoregulation by antibody and antigen-antibody complexes. Transplant Proc. 1978 Jun;10(2):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner W., Ebert P. S., Spahn G., Bassin R., Chirigos M. A. Potentiation of murine sarcoma virus (Harvey) (Moloney) oncogenicity in lactic dehydrogenase-elevating virus-infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1314–1318. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisin G. A. Role of antibody classes in the regulatory facilitation reaction. Immunol Rev. 1980;49:3–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


