Abstract
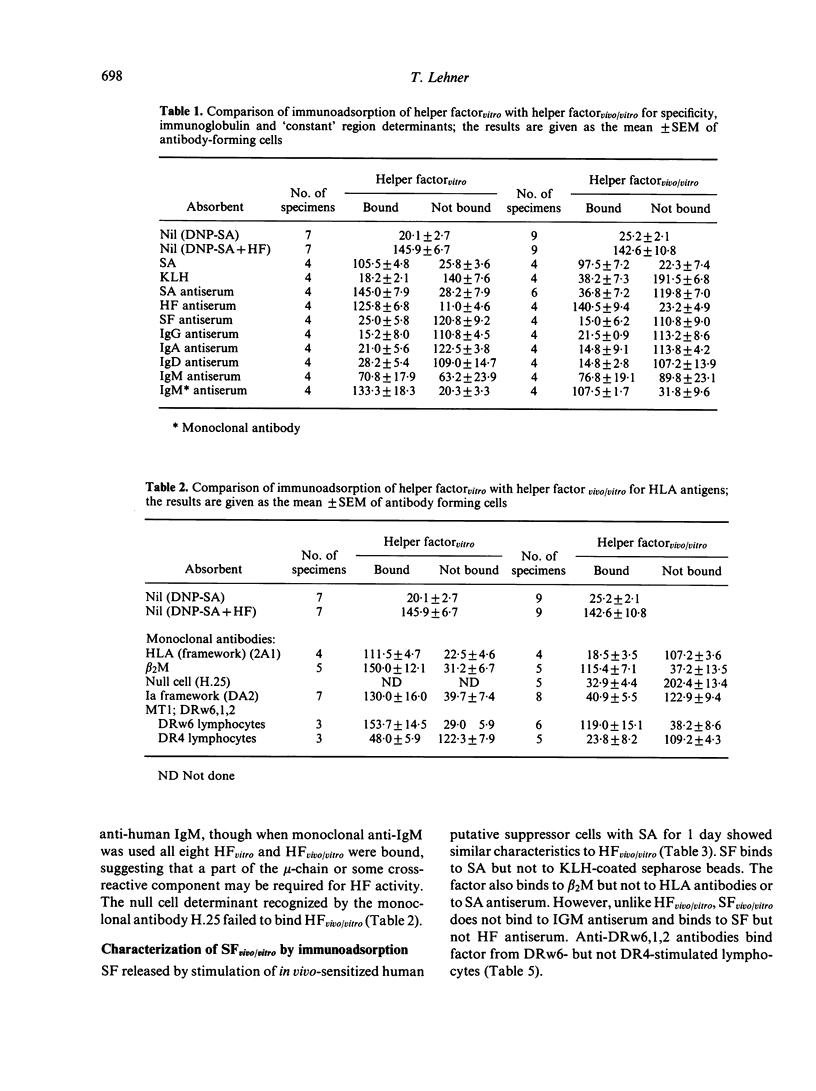
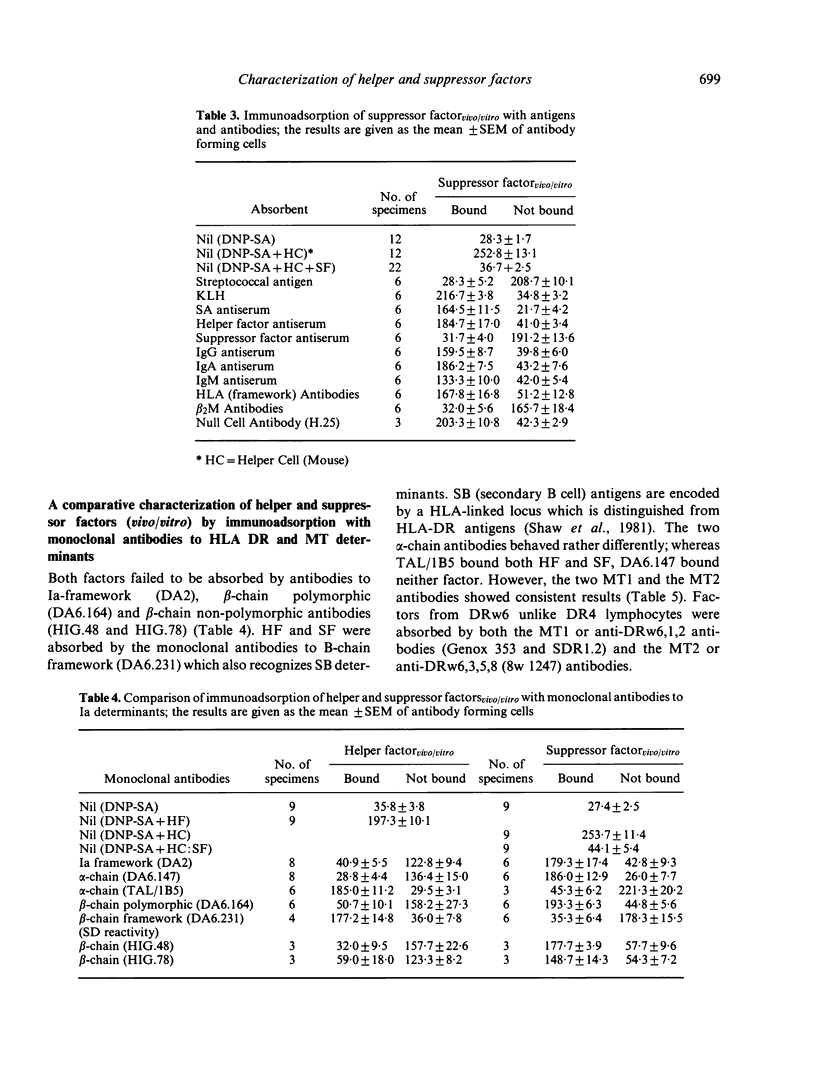
Human helper and suppressor cells can be induced entirely in vitro, by culturing lymphocytes with a small or large dose of antigen for 4 days in a Marbrook—Diener system. The corresponding helper or suppressor factor (vitro) can then be released by a second pulse of antigen for 1 day. However, if sensitization has taken place in vivo by a naturally encountered antigen, then helper or suppressor factor (vivo/vitro) can be released by a single pulse of antigen for 1 day from putative in vivo-induced helper or suppressor cells. Helper factorvitro was compared with helper factorvivo/vitro, stimulated by a streptococcal protein antigen derived from Streptococcus mutans. The results of affinity chromatography suggest that both helper factors have an antigen-specific binding site and bind to monoclonal antibodies directed against HLA-DR, MT, β2M and μ chain and a `constant' part on helper factor (HF) determinants. The HFvivo/vitro unlike HFvitro may reflect in vivo-sensitization and thus assay putative in vivo-sensitized antigen specific helper cells. Similarly, suppressor factor vivo/vitro might be a measure of in vivo-induced suppressor cells. Like HF, suppressor factor (SF) has an antigen-specific binding site, HLA-DR, MT and β2M determinants and a `constant' portion of SF. The DR determinants were further characterized by immunoadsorption, using monoclonal antibodies to the α- and β-chain of DR antigen. The results suggest that helper and suppressor factorvivo/vitro express similar Ia determinants. Both expressed an α-chain determinant, recognized by one of the two anti-α-chain antibodies (TAL/1B5), and a β-chain non-polymorphic determinant recognized by one of the four anti-β chain antibodies used (DA6.231). However, both HF and SF derived from DRw6- but not from DR4-typed lymphocytes expressed MT1 (DRw6,1,2) or MT2 (DRw6,3,5,8) determinants. As DR and MT determinants can be expressed on the same molecule, it is possible that both are involved in helper and suppressor activities.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armerding D., Kubo R. T., Grey H. M., Katz D. H. Activation of T and B lymphocytes in vitro: presence of beta2-microblobulin determinants on allogeneic effect factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch H-M, Gelfand E. W. Generation of human plaque-forming cells in culture: tissue distribution, antigenic and cellular requirements. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Basten A. Specific collaboration between T and B lymphocytes across a cell impermeable membrane in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 3;237(70):13–15. doi: 10.1038/newbio237013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Mudawwar F., Schneeberger E. The specificity of T-cell helper factor in man. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1436–1448. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie S., Feldmann M., Mozes E., Maurer P. H. In vitro studies on H-2 linked unresponsiveness. 1. Normal helper cells to (T,G)-A-L and GAT in low and non-responder mice. Immunology. 1977 Mar;32(3):291–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr R. W., Kannapell C. C., Stein J. A., Gebel H. M., Mann D. L., Duquesnoy R. J., Fuller T. C., Rodey G. E., Schwartz B. D. Molecular relationships of the human B cell alloantigens, MT2, MB3, MT4, and DR5. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1809–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Tung A. S. Regulation of IgE antibody production by serum molecules. VI: Preliminary biochemical and immunological characterization of serum molecules active in suppressing IgE antibody production. Immunopharmacology. 1979 Mar;1(2):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(79)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Woody J. N., Rees A., Feldmann M. Induction of human antigen-specific suppressor factors in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):517–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Kontiainen S., Lehner T. A comparative investigation of the generation of specific T cell-helper function induced by Streptococcus mutans in monkeys and mice. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2384–2389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Kontiainen S., Lehner T. Generation of specfic T-cell suppressor function induced by Streptococcus mutans in monkeys and mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):903–909. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.903-909.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Zanders E. D., Sanderson A. R., Ward P. J., Feldmann M., Kontiainen S., Lehner T., Woody J. N. Antigen-specific helper factor reacts with antibodies to human beta 2 microglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Lamb J. R., Kontiainen S. Cell-bound helper and suppressor factors in primate lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):706–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Lamb J. R., Welsh K. L., Batchelor R. J. Association between HLA-DR antigens and helper cell activity in the control of dental caries. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):770–772. doi: 10.1038/292770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. The relationship between human helper and suppressor factors to a streptococcal protein antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M. L., Cresswell P. Human B cell alloantigens: expression of MB and MT determinants. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2004–2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudawwar F. B., Yunis E. J., Geha R. S. Antigen-specific helper factor in man. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1032–1043. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Kavathas P., Pollack M. S., Charmot D., Mawas C. Family studies define a new histocompatibility locus, SB, between HLA-DR and GLO. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):745–747. doi: 10.1038/293745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M. M., Stocker J. W., Caeppellini R. Monoclonal antibodies against human lymphocyte antigens. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):666–668. doi: 10.1038/273666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UytdeHaag F., Heynen C. J., Ballieux R. E. Induction of antigen-specific human suppressor T lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):556–557. doi: 10.1038/271556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanders E. D., Lamb J. R., Kontiainen S., Lehner T. Partial characterization of murine and monkey helper factor to a streptococcal antigen. Immunology. 1980 Nov;41(3):587–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kretser T. A., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F. Demonstration of two distinct light chains in HLA-DR-associated antigens by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):214–221. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


