Abstract
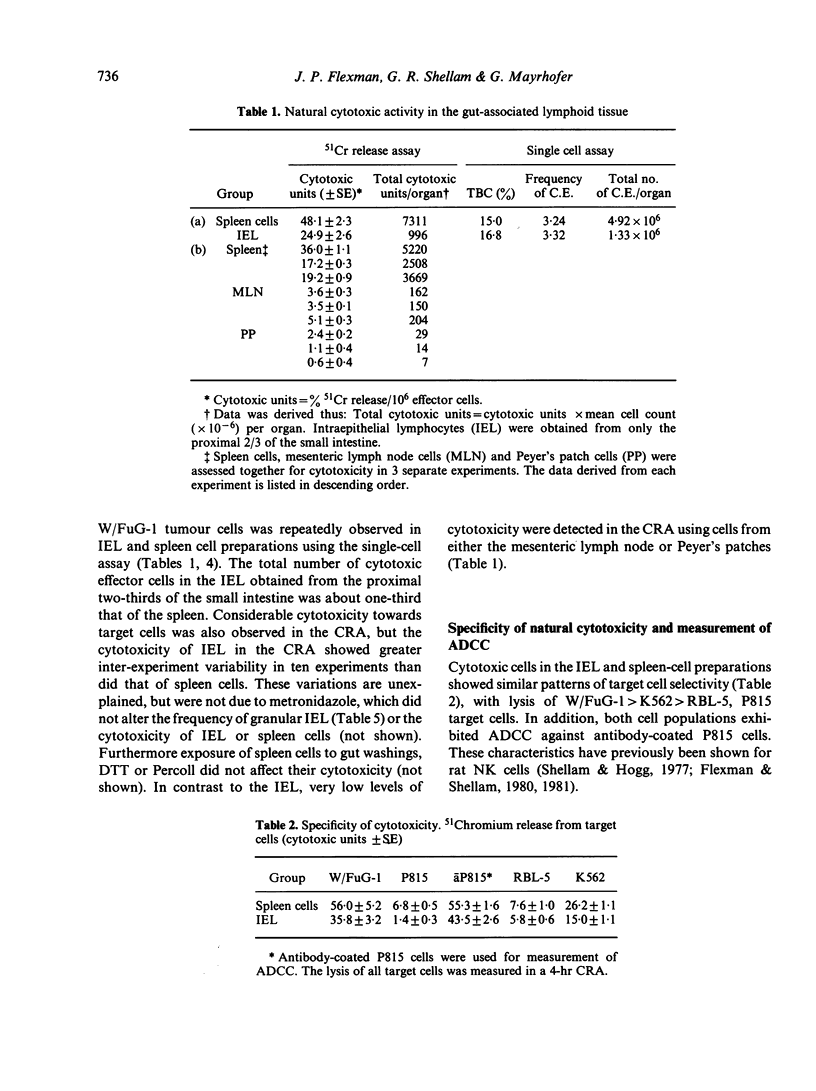
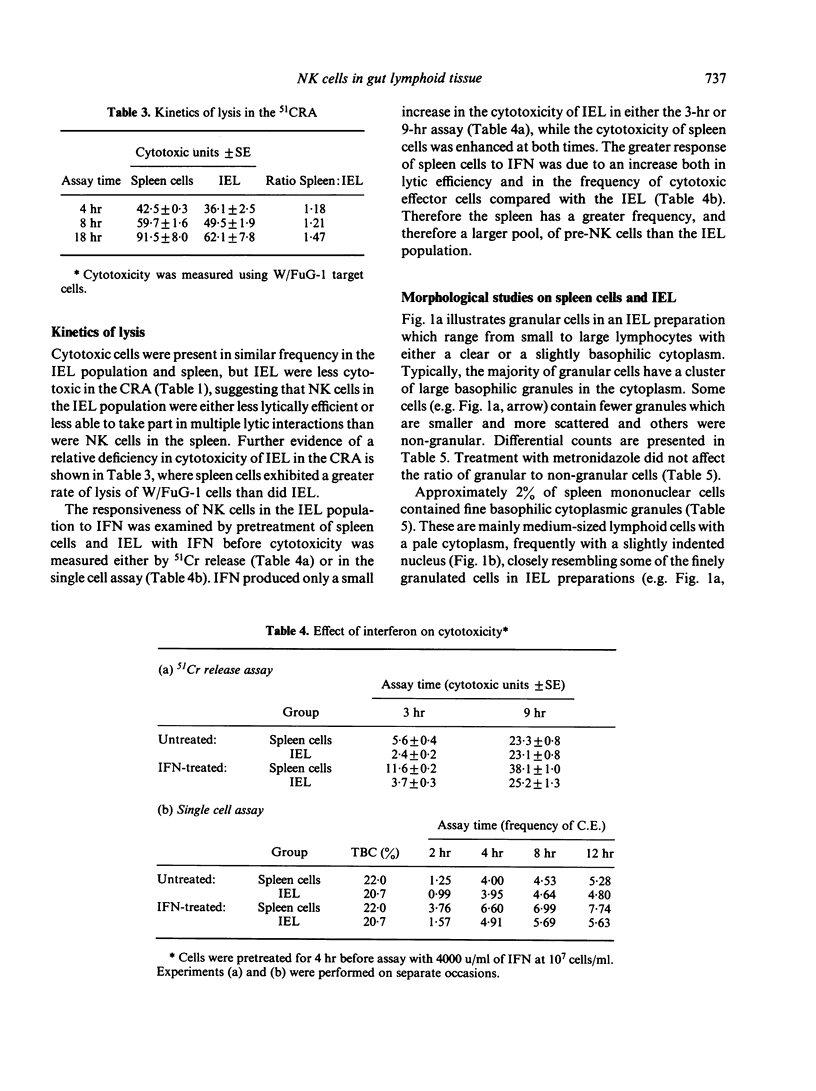
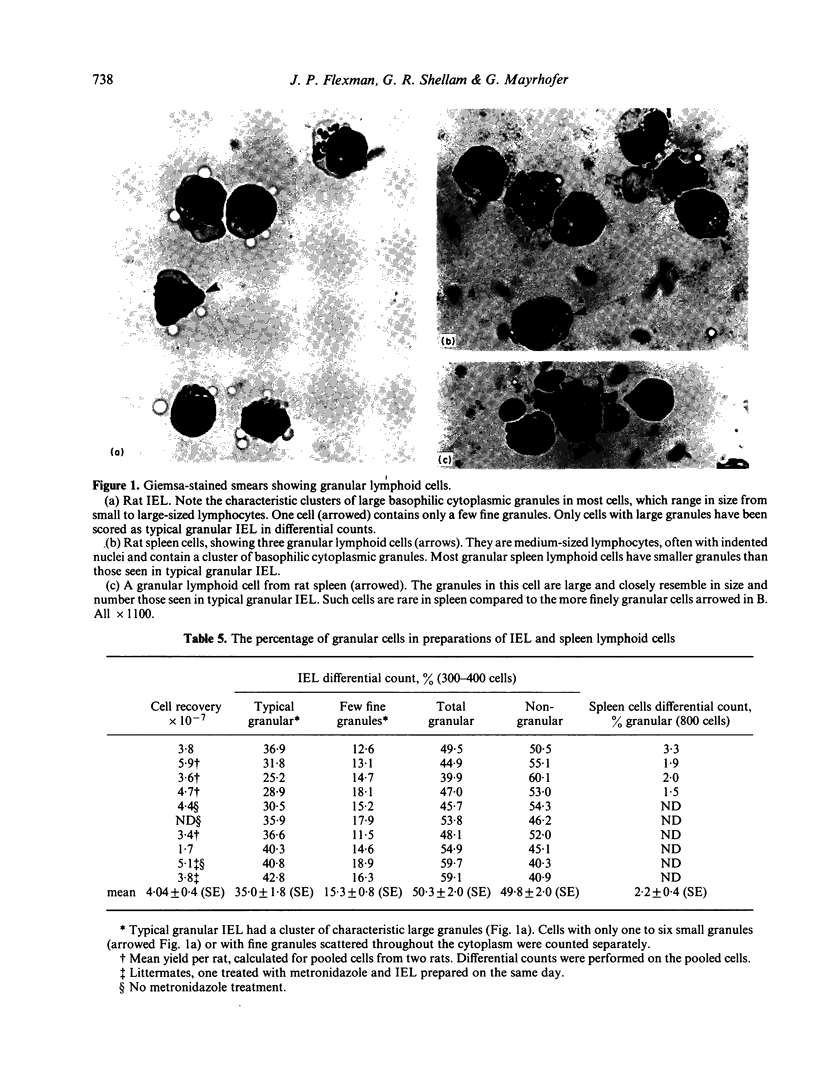
The expression of natural cytotoxicity in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue of the rat was investigated. Intra-epithelial lymphocytes (IEL) isolated from the small intestine had a similar frequency of cytotoxic and tumour target binding cells as the spleen. However, cytotoxic activity was low in Peyer's patches and mesenteric lymph node. Cytotoxic IEL exhibited similar target-cell specificity to splenic natural killer (NK) cells, and substantial antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. However, their cytotoxicity and lytic efficiency was not rapidly increased following exposure to interferon and IEL probably contain only a relatively small pool of pre-NK cells. IEL contained approximately 50% of cells with basophilic cytoplasmic granules, compared to approximately 2% of granule-containing mononuclear cells in the spleen. Direct observation using the uptake of acridine orange to detect cytoplasmic granules established that some cytotoxic IEL were granular. However, substantial cytotoxicity was also mediated by non-granular IEL and not all granular IEL which bound to target cells were cytotoxic. Counts of granulated cells in Giemsa-stained preparations of spleen cells and results from single-cell assays using unfractionated splenocytes suggest that the majority of target-binding cells and at least half of the naturally cytotoxic cells must also be non-granular.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan W., Mayrhofer G. The distribution and traffic of specific homocytotropic antibody-synthesizing cells in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis-infested rats. Comparison of synthesis with the kinetics of antibody and IgE levels in serum and lymph. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1981 Dec;59(Pt 6):723–737. doi: 10.1038/icb.1981.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Bundy B. M., O'Neill M., Bienenstock J., Nelson D. L. Cytotoxic activities of gut mucosal lymphoid cells in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins H. J., Shellam G. R. Augmentation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity to a rat lymphoma. I. Stimulation of non-T-cell cytotoxicity in vivo by tumour cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Aug;24(2):235–243. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Huang K. Y., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer activity and induction of interferon by tumor cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):781–789. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS DE ST GROTH S., WHITE D. O. An improved assay for the infectivity of in influenza viruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Mar;56(1):151–162. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. Gut. 1977 Nov;18(11):921–937. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.11.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flexman J. P., Shellam G. R. Mechanism of stimulation of natural killer-cell cytotoxicity by interferon and an interferon-inducer in the rat. Immunology. 1981 Oct;44(2):311–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flexman J. P., Shellam G. R. Target-effector interactions in the rat natural killer cell system. I. The measurement of cytotoxicity at the single cell level. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jun;12(6):457–463. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The gut-associated lymphoid system: nature and properties of the large dividing cells. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jun;4(6):435–443. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Tidman N., Selby W. S., Thomas J. A., Granger S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Human T lymphocytes of inducer and suppressor type occupy different microenvironments. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):81–84. doi: 10.1038/288081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery P. K., Reid L. New observations of rat airway epithelium: a quantitative and electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1975 Nov;120(Pt 2):295–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luini W., Boraschi D., Alberti S., Aleotti A., Tagliabue A. Morphological characterization of a cell population responsible for natural killer activity. Immunology. 1981 Aug;43(4):663–668. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Bazin H. Nature of the thymus dependency of mucosal mast cells. III. Mucosal mast cells in nude mice and nude rats, in B rats and in a child with the Di George syndrome. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;64(3):320–331. doi: 10.1159/000232710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G. Fixation and staining of granules in mucosal mast cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes in the rat jejunum, with special reference to the relationship between the acid glycosaminoglycans in the two cell types. Histochem J. 1980 Sep;12(5):513–526. doi: 10.1007/BF01011925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G. Thymus-dependent and thymus-independent subpopulations of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes: a granular subpopulation of probable bone marrow origin and relationship to mucosal mast cells. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):532–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., McDaniel D. O. In vitro reactivity of natural killer (NK) cells against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Wigzell H. Natural killer cells may be the only cells in normal mouse lymphoid cell populations endowed with cytolytic ability for antibody-coated tumour target cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Apr;7(4):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puccetti P., Santoni A., Riccardi C., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic effector cells with the characteristics of natural killer cells in the lungs of mice. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jan 15;25(1):153–158. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Timonen T., Ranki A., Häyry P. Morphological and functional characterization of isolated effector cells responsible for human natural killer activity to fetal fibroblasts and to cultured cell line targets. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:71–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of activation of human natural killer cells against tumor and virus-infected cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:125–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Hogg N. Gross-virus-induced lymphoma in the rat. IV. Cytotoxic cells in normal rats. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):212–224. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Winterbourn V., Dawkins H. J. Augmentation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity to a rat lymphoma. III. In vitro stimulation of natural killer cells by a soluble factor. Int J Cancer. 1980 Mar 15;25(3):331–339. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Anders R. F., Mitchell G. F. Giardiasis in mice: studies on the characteristics of chronic infection in C3h/He mice. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):669–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




