Abstract
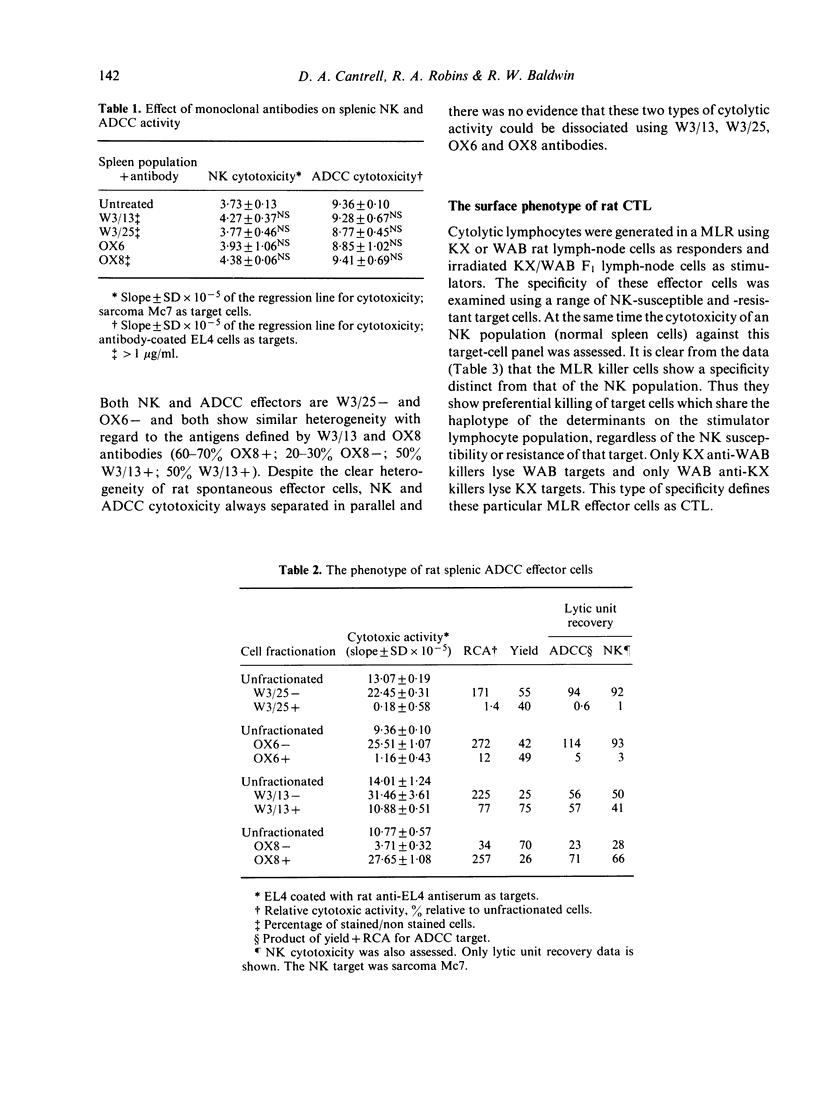
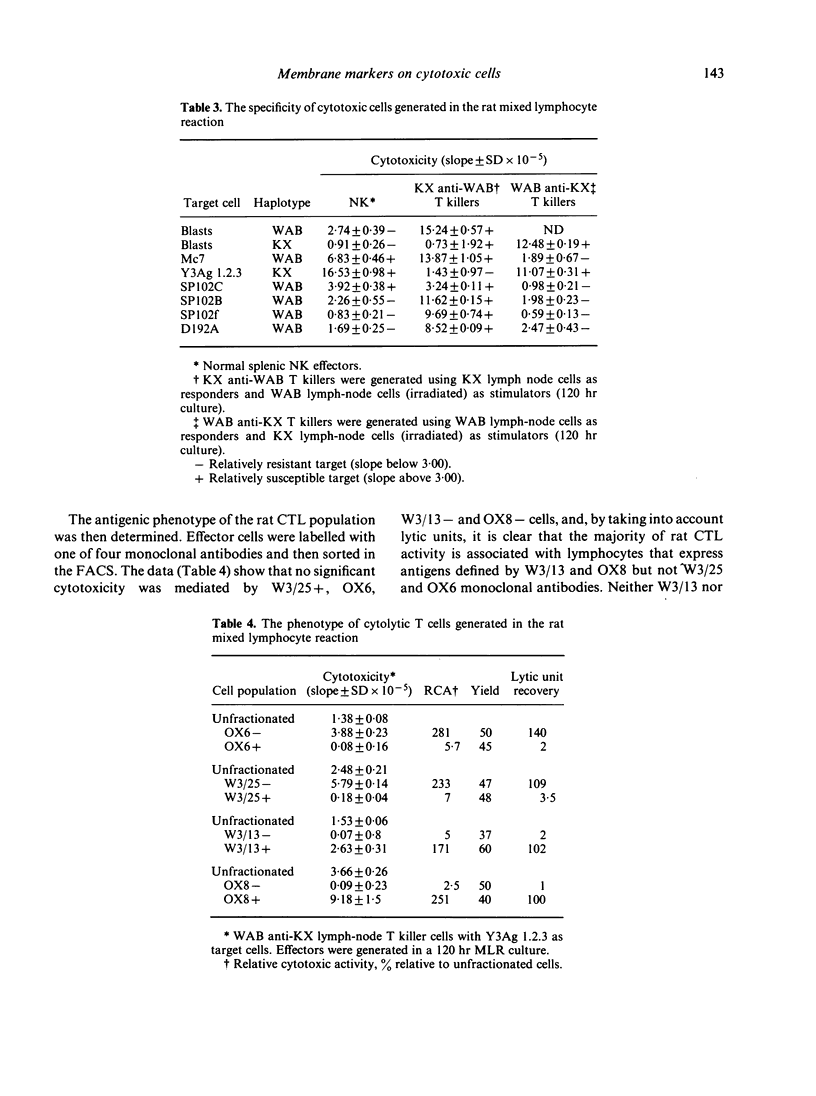
The antigenic characteristics of cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and cells mediating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) were defined using monoclonal antibodies W3/13, W3/25 and MRC OX8, and compared with the phenotype of natural killer (NK) cells previously defined by these antibodies. CTL, ADCC effector cells and NK cells were also tested for expression of Ia antigen using MRC OX6 monoclonal antibody. The fluorescence-activated cell sorter was used to separate effector populations into antigen-positive and antigen-negative subsets, and the cytotoxicity of the resultant lymphocyte fractions was then assessed using 6 hr 51Cr release assay and a quantitative method of analysis based on consideration of target cell lysis as an enzyme substrate reaction. CTL, ADCC effector cells and NK cells were W3/25 negative and OX6 negative. CTL were positive for W3/13 and OX8 antibody with no cytotoxicity in the W3/13 negative and OX8 negative fractions. In contrast, ADCC effector cells showed heterogeneity of staining with W3/13 and OX8 antibodies, with 50% cytotoxic activity in the W3/13 negative fraction, and 20-30% cytotoxic activity in the OX8 negative fraction. In parallel experiments, NK cells and ADCC effector cells showed identical marker heterogeneity when tested with W3/13 and OX8 antibodies.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Flannery G. R. Quantitative studies of natural immunity to solid tumours in rats. Persistence of natural immunity throughout reproductive life, and absence of suppressor cells in infant rats. Immunology. 1980 Feb;39(2):187–194. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Rees R. C., Leach R. H. High nonspecific reactivity of normal lymphocytes against mycoplasma-infected target cells in cytotoxicity assays. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Feb;9(2):159–165. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Wayner E. A., Webb P. J., Gray J. D., Kenwrick S., Baldwin R. W. The specificity of rat natural killer cells and cytotoxic macrophages on solid tumor-derived target cells and selected variants. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2477–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte A. J., Carpenter C. B., Strom T. B. Expression of T cell differentiation antigens and Ia on rat cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Hansen J. A., Newman W. Evidence for T cell nature and heterogeneity within natural killer (NK) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) effectors: a comparison with cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL). J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):448–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Cruz E., Woda B. A., Feldman J. D. Elimination of syngeneic sarcomas in rats by a subset of T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):823–841. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. D., Brooks C. G., Baldwin R. W. Detection of either rapidly cytolytic macrophages or NK cells in "activated" peritoneal exudates depends on the method of analysis and the target cell type. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):561–568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Blocking effect of lyt-2 antibodies on T cell functions. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):674–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo G. C., Jacobson J. B., Hammerling G. J., Hammerling U. Antigenic profile of murine natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1003–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Amos D. B., Buckley R. H. Natural killing in immunodeficient patients. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):796–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loop S. M., Bernstein I. D., Wright P. W. T cell synergy in the rat: serologic characterization of T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1237–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Bucalo L. R., Allard J., Wigzell H., Cantor H. Multiple activities of a cloned cell line mediating natural killer cell function. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1582–1591. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. E. Human killer cells and natural killer cells: distinct subpopulations of Fc receptor-bearing lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2604–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Wigzell H. Natural killer cells may be the only cells in normal mouse lymphoid cell populations endowed with cytolytic ability for antibody-coated tumour target cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Apr;7(4):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K., Snow P., Terhorst C., Schlossman S. F. Antibody directed at a surface structure inhibits cytolytic but not suppressor function of human T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):168–170. doi: 10.1038/294168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Sharrow S. O., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Natural killer activity in the rat. II. Analysis of surface antigens on LGL by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2204–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J., Duwe A. The beige mutation in the mouse selectively impairs natural killer cell function. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):451–453. doi: 10.1038/278451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Mason D. W., Williams A. F., Galfre G., Milstein C. T-lymphocyte heterogeneity in the rat: separation of functional subpopulations using a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):664–673. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woan M. C., McGregor D. D., Goldschneider I. T cell-mediated cytotoxicity induced by Listeria monocytogenes. III. Phenotypic characteristics of mediator T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2330–2334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Kung P. C. Monoclonal antibodies which distinguish between human NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):394–396. doi: 10.1038/288394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



