Abstract
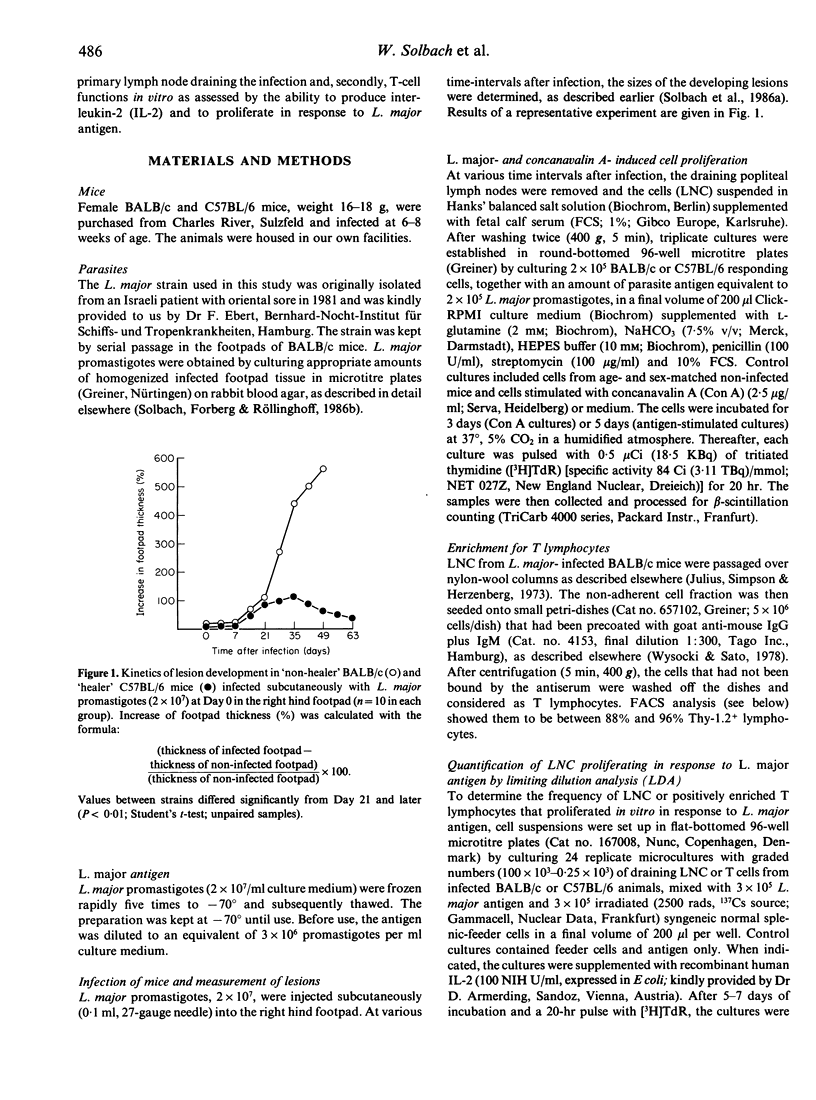
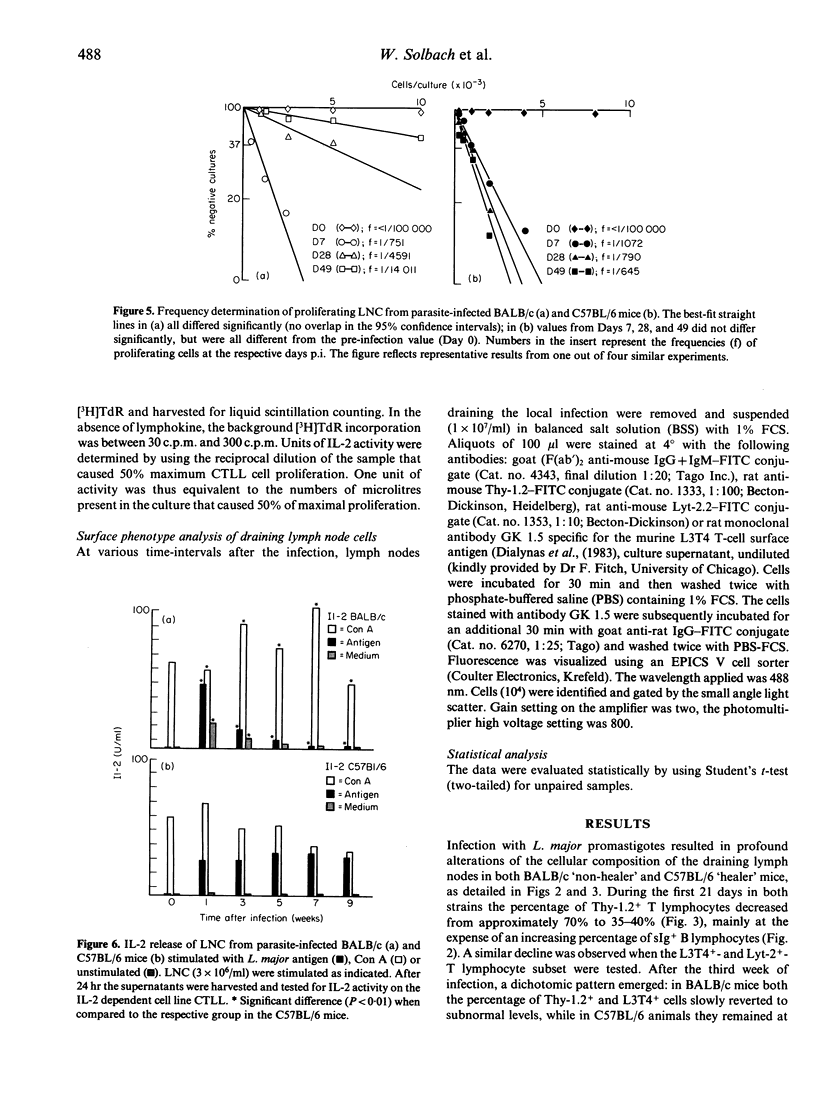
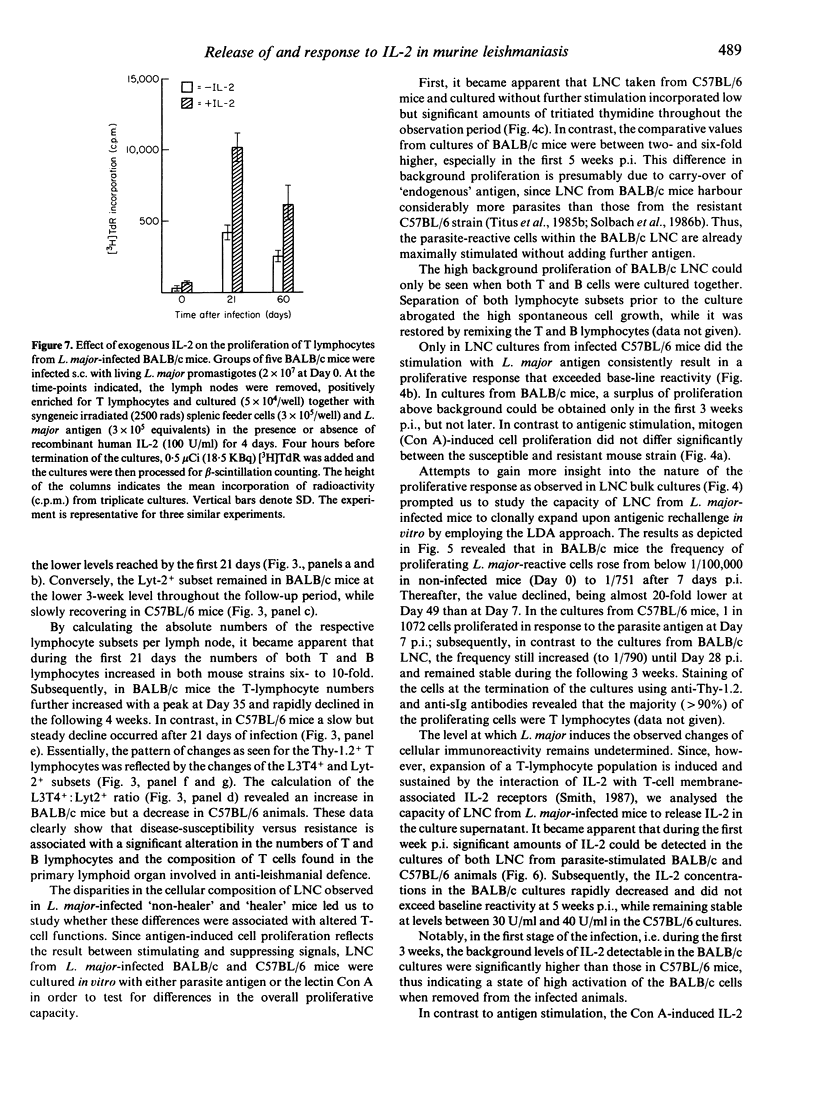
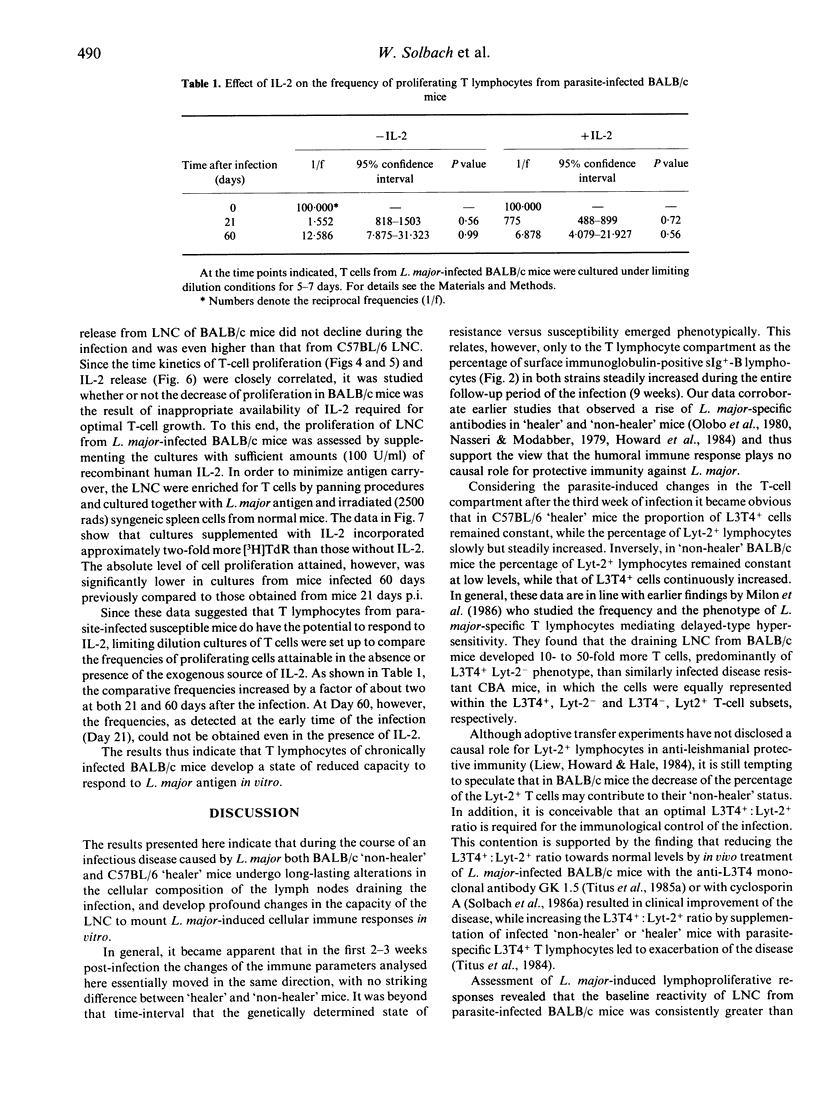
Leishmania major (L. major)-infected mice of 'non-healer' (BALB/c) and 'healer' (C57BL/6) mouse-strain origin were studied with regard to the kinetics of cell-mediated immunity developing during the course of the disease. Cells obtained from lymph nodes draining L. major-infected footpads were comparatively analysed for their representation in the respective L3T4+, Lyt-2+ and sIg+ lymphocyte subsets; they were studied for their capacity to release interleukin-2 and to proliferate in response to L. major antigen and concanavalin A, including the determination of the frequencies of T cells proliferating antigen-specifically with or without an exogenous source of IL-2. The data obtained indicate L. major infection-induced long-lasting alterations in the cellular composition of the lymph node in both 'healer' and 'non-healer' mice. Moreover, they suggest that the inability of 'non-healer' mice to recover from L. major infection is associated with a progressive impairment of their lymph node T cells to release interleukin-2 in the culture supernatant and to respond to this lymphokine in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behin R., Mauel J., Sordat B. Leishmania tropica: pathogenicity and in vitro macrophage function in strains of inbred mice. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho E. M., Badaró R., Reed S. G., Jones T. C., Johnson W. D., Jr Absence of gamma interferon and interleukin 2 production during active visceral leishmaniasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2066–2069. doi: 10.1172/JCI112209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Ceredig R., Mitchell G. F. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: disease patterns in intact and nude mice of various genotypes and examination of some differences between normal and infected macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Feb;57(1):9–29. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. IV. Prophylactic effect of sublethal irradiation as a result of abrogation of suppressor T cell generation in mice genetically susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Liew F. Y., Hale C., Nicklin S. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis. II. Further characterization of the protective immunity against fatal Leishmania tropica infection induced by irradiated promastigotes. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):450–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Hale C., Howard J. G. Immunologic regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. V. Characterization of effector and specific suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1917–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Howard J. G., Hale C. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis. III. Protection against fatal Leishmania tropica infection induced by irradiated promastigotes involves Lyt-1+2- T cells that do not mediate cutaneous DTH. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):456–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Specific suppression of responses to Leishmania tropica by a cloned T-cell line. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):630–632. doi: 10.1038/305630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milon G., Titus R. G., Cerottini J. C., Marchal G., Louis J. A. Higher frequency of Leishmania major-specific L3T4+ T cells in susceptible BALB/c as compared with resistant CBA mice. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1467–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Carriero S., Acosta A. M. Reversible defect in antigen-induced lymphokine and gamma-interferon generation in cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2250–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S., Fortier A. H. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania tropica: characterization of P/J mouse macrophage defects for lymphokine-induced antimicrobial activities against Leishmania tropica amastigotes. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3344–3350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Modabber F. Z. Generalized infection and lack of delayed hypersensitivity in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania tropica major. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):611–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.611-614.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Visceral leishmaniasis in congenic mice of susceptible and resistant phenotypes: T-lymphocyte-mediated immunosuppression. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):169–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.169-174.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olobo J. O., Handman E., Curtis J. M., Mitchell G. F. Antibodies to Leishmania tropica promastigotes during infection in mice of various genotypes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1980 Dec;58(6):595–601. doi: 10.1038/icb.1980.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaldi A., Young D. C., Herrmann F., Cannistra S. A., Griffin J. D. Interferon-gamma induces expression of the interleukin 2 receptor gene in human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):153–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Finke J. H. Interleukin 2 deficiency in murine Leishmaniasis donovani and its relationship to depressed spleen cell responses to phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1487–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Locksley R. M., Tubbs C., Raff H. V. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: resistance correlates with the capacity to generate interferon-gamma in response to Leishmania antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. A., Farrell J. P. Experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. I. Nonspecific immunodepression in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania tropica. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2395–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solbach W., Forberg K., Kammerer E., Bogdan C., Röllinghoff M. Suppressive effect of cyclosporin A on the development of Leishmania tropica-induced lesions in genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solbach W., Forberg K., Röllinghoff M. Effect of T-lymphocyte suppression on the parasite burden in Leishmania major-infected, genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):909–912. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.909-912.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpmann R. M., Näher H., Osawa H., Herrmann T., Hahn H., Diamantstein T. Production of Listeria-specific rat T-cell clones and role of interleukin-2 receptors in regulation of Listeria-dependent T-cell clone growth in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):822–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.822-826.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streck H., Bogdan C., Tingle A., Röllinghoff M. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: comparative study on the capacity of macrophages from "healer" and "non-healer" mouse strains to control L. tropica replication. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Mar;263(4):594–604. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ceredig R., Cerottini J. C., Louis J. A. Therapeutic effect of anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody GK1.5 on cutaneous leishmaniasis in genetically-susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Lima G. C., Engers H. D., Louis J. A. Exacerbation of murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by adoptive transfer of parasite-specific helper T cell populations capable of mediating Leishmania major-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1594–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Marchand M., Boon T., Louis J. A. A limiting dilution assay for quantifying Leishmania major in tissues of infected mice. Parasite Immunol. 1985 Sep;7(5):545–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



