Abstract
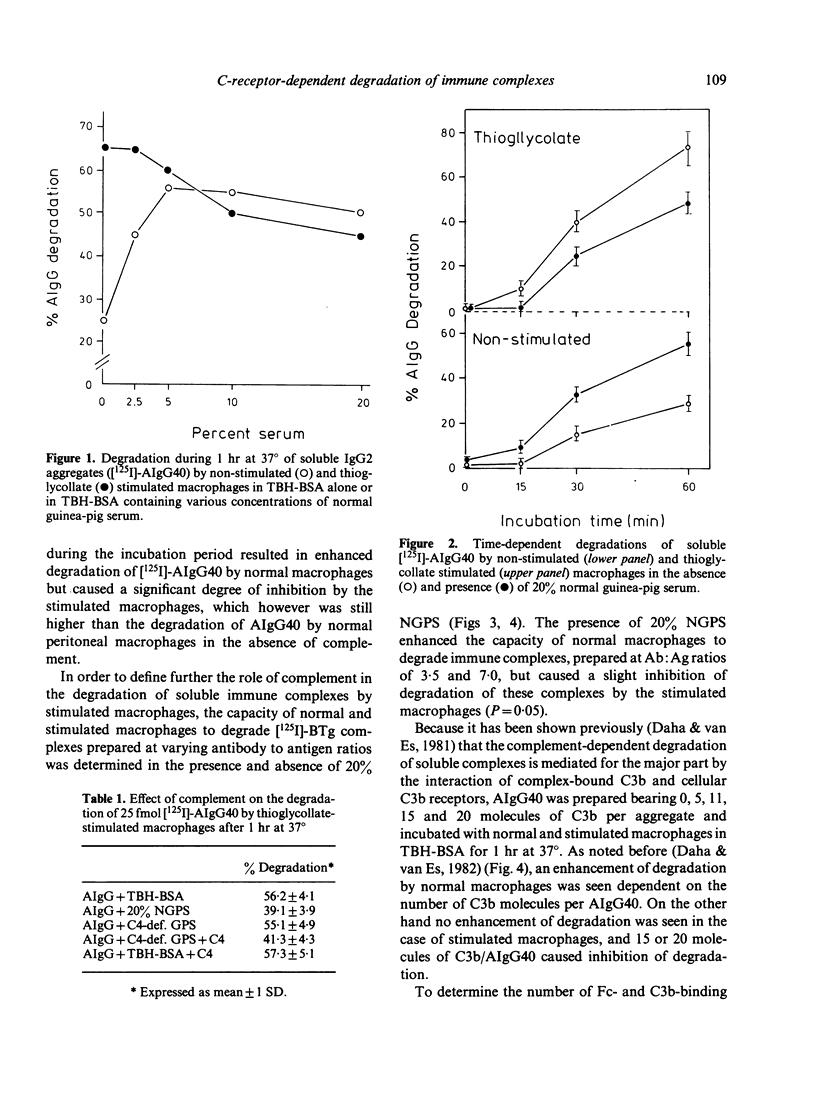
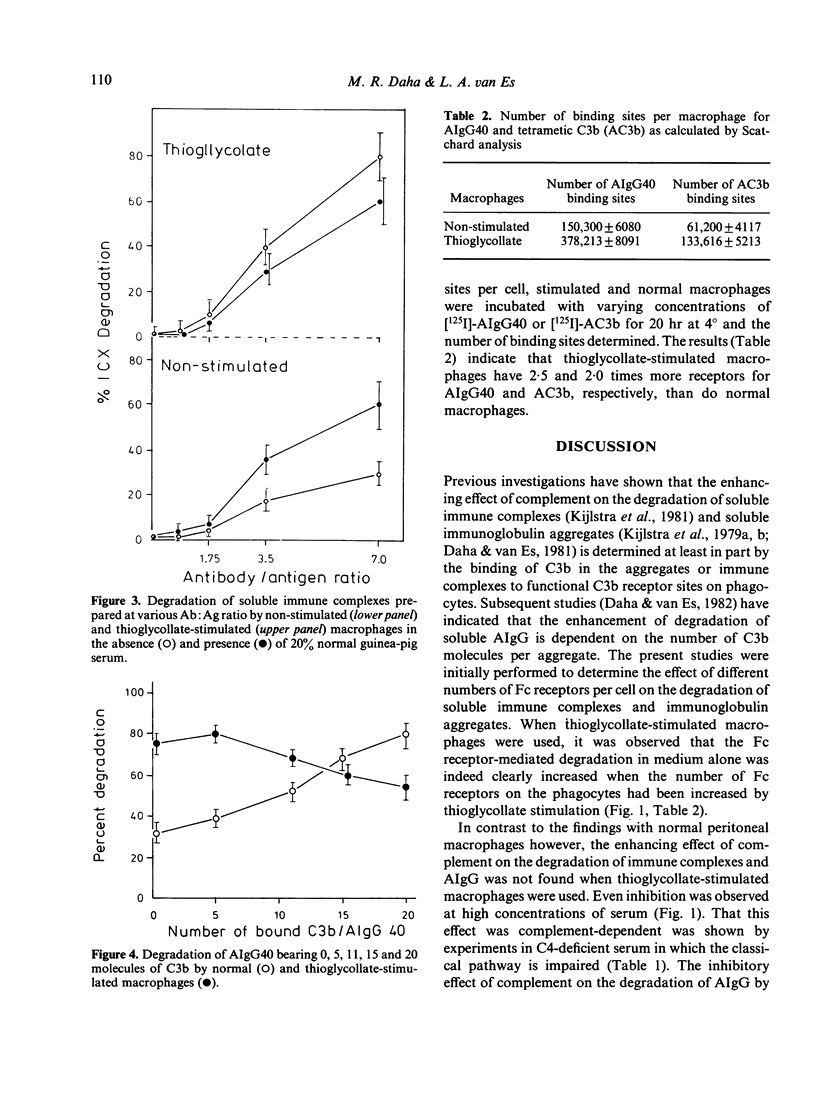
Previous studies have shown that the degradation of soluble immune complexes or aggregates (AIgG) by normal peritoneal macrophages can be enhanced by complement. The enhancement of degradation was shown to be at least in part dependent on the number of C3b molecules bound per complex. The present investigations indicate that the enhanced degradation is not found with thioglycollate-stimulated macrophages, and that at high concentrations of complement, inhibition may even occur. The Fc receptor-mediated degradation of soluble immune complexes and AIgG by stimulated macrophages was at least twice as high as that by normal macrophages. This increase was compatible with the increased number of Fc receptors on the stimulated macrophages. The inhibitory effect of high concentrations of serum, as a complement source, on the degradation of AIgG was dependent on the number of C3b molecules bound per AIgG. Although there was also a two-fold increase in the number of C3b receptor sites on the stimulated macrophages, more than 11 C3b molecules per AIgG40 caused significant inhibition of degradation. This phenomenon may be dependent on shielding of Fc-Fc receptor interaction by varying numbers of C3b molecules per complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., Frank M. M. Studies on the in vivo effects of antibody. Interaction of IgM antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):339–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI107769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Van Es L. A. Enhanced alternative complement pathway-dependent degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):513–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., van Es L. A. The role of cellular Fc and C3 receptors on the complement-dependent degradation of stable soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by normal and trypsin-treated peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1982 Sep;47(1):203–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Aggregated human immunoglobulin G stabilized by albumin: a standard for immune complex detection. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Enhanced degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages in the presence of complement. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):673–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Enhanced degradation of soluble immune complexes by guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages in the presence of complement. Immunology. 1981 Jun;43(2):345–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. The role of complement in the binding and degradation of immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2488–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., van Es L. A. The kinetics for binding and catabolism of aggregated IgG by rat peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2040–2048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Alexander M. D. Cytophilic antibodies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;88:25–104. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67331-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. C., Adles C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Cloned macrophages can be induced to kill tumor cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Aug;24(2):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Snick J. L., Masson P. L. The effect of complement on the ingestion of soluble antigen-antibody complexes and IgM aggregates by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):903–914. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


