Abstract
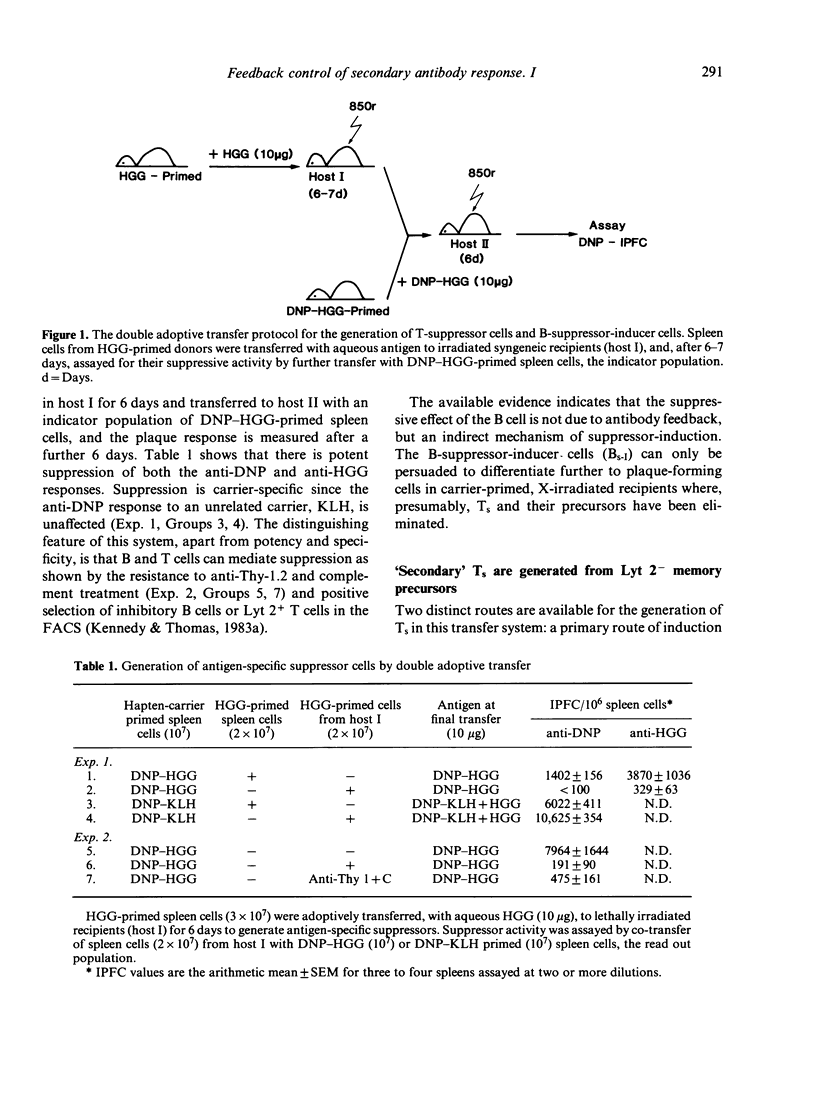
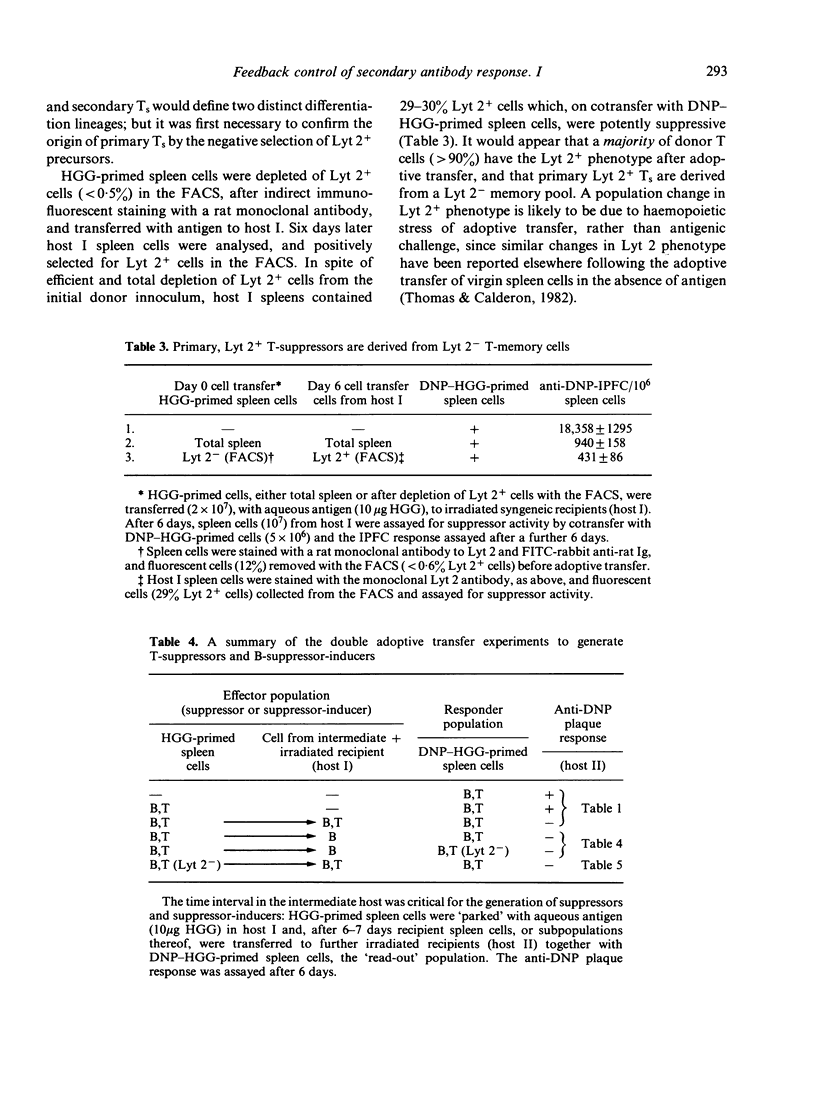
The cellular elements of an antigen-specific suppressor system for secondary antibody responses have been identified, using positive cell-selection techniques in the fluorescence-activated cell sorter. In a double-adoptive transfer of memory cells for a thymus-dependent antigen, from one irradiated recipient to another, antigen-specific suppressor T cells are recruited after a critical time in the primary recipient. It is also a source of B cells that are able to induce further suppressors in carrier-primed, but otherwise naive donors. There are two distinct routes, therefore, for the generation of suppressor T cells: primary induction by adoptive transfer with antigen, or secondary induction by B cells recruited in the primary irradiated host. We have shown that both primary and secondary suppressors are recruited from a Lyt 2- memory population, although the Lyt 2 alloantigen is expressed at the effector stage.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basten A., Miller J. F., Johnson P. T cell-dependent suppression of an anti-hapten antibody response. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:130–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., Kapp J. A., Debré P., Pierce C. W., de la Croix F. The stimulation of specific suppressor T cells in genetic non-responder mice by linear random copolymers of L-amino acids. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:21–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S., Möller G. Regulation of antibody synthesis against Escherichia coli endotoxin. I. Suppressive effect of endogenously produced and passively transferred antibodies. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Gershon R. K. Immunological circuits: cellular composition. Fed Proc. 1979 Jun;38(7):2058–2064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. II. Activation by antigen: after immunization, antigen-specific suppressor and helper activities are mediated by distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1391–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Gershon R. K. Induction of specific suppressor T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):313–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Hugenberger J., McVay-Boudreau L., Shen F. W., Gershon R. K., Cantor H. Immunoregulatory circuits among T-cell sets. I. T-helper cells induce other T-cell sets to exert feedback inhibition. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1106–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K. Expression and function of idiotypes of lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:195–254. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Thomas D. B. A regulatory role for the memory B cell as suppressor-inducer of feedback control. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):547–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Thomas D. B. Feedback control of the secondary antibody response. II. Differences in the rate of induction of T-helper and T-suppressor memory. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):297–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Rouse R. V., Micklem H. S., Herzenberg L. A. T cell subsets defined by expression of Lyt-1,2,3 and Thy-1 antigens. Two-parameter immunofluorescence and cytotoxicity analysis with monoclonal antibodies modifies current views. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):280–295. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Hale C., Howard J. G. Immunologic regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. V. Characterization of effector and specific suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1917–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T., Levy J. G., Kilburn D. G. The Lyt phenotype of cells involved in the cytotoxic response to syngeneic tumor and of tumor-specific suppressor cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Dec;56(2):392–399. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. Association of Ly phenotypes, T cell function and MHC recognition. Fed Proc. 1980 Nov;39(13):3110–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Wormsley S., Dutton R. W. The Lyt phenotype of a long-term allospecific T cell line. Both helper and killer activities to IA are mediated by Ly-1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Calderon R. A. T helper cells change their Lyt-1,2 phenotype during an immune response. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):16–23. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic D., Juretic A., Nagy Z. A., Klein J. Lyt phenotypes of primary cytotoxic T cells generated across the A and E region of the H-2 complex. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):499–504. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


