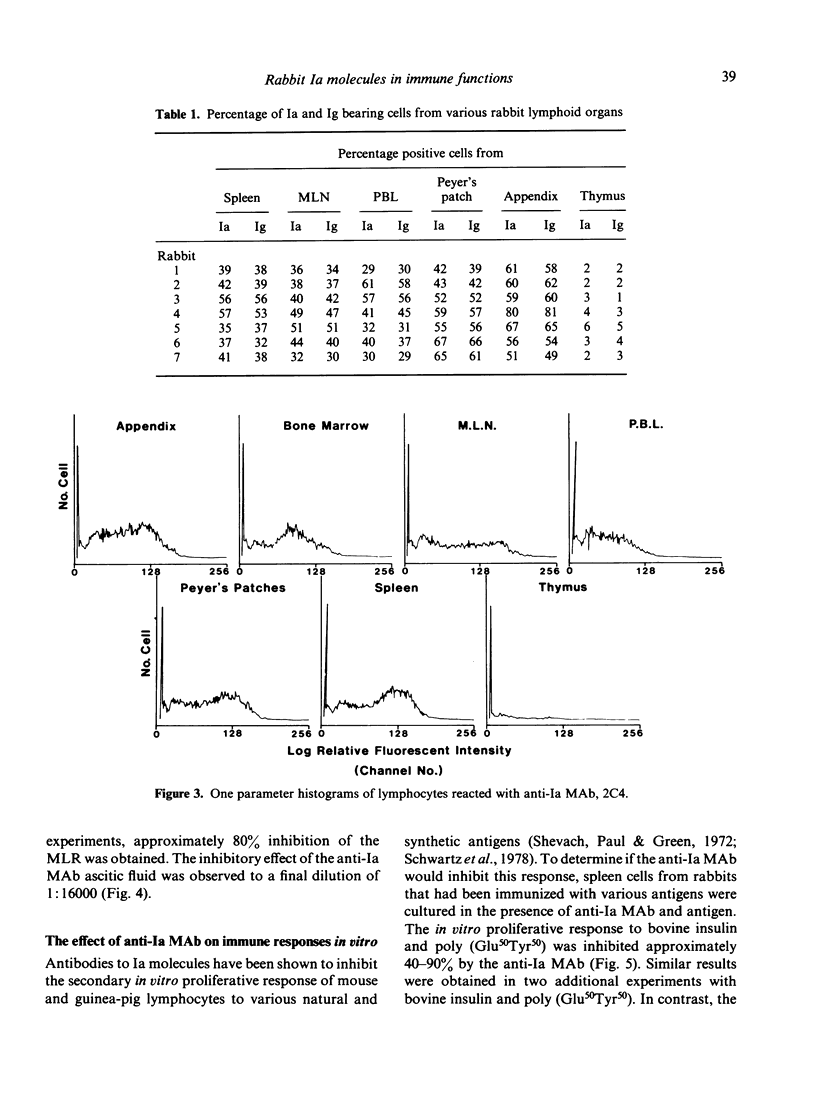
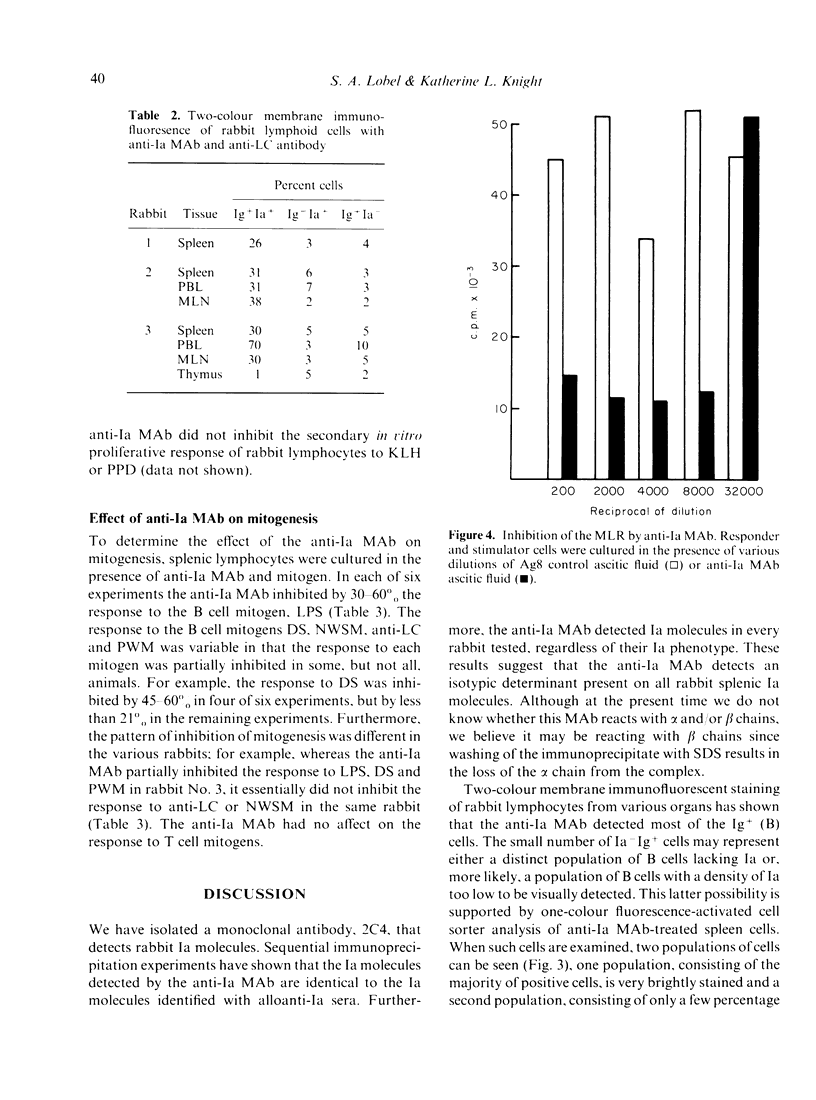
Abstract
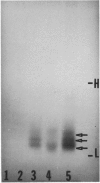
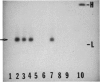
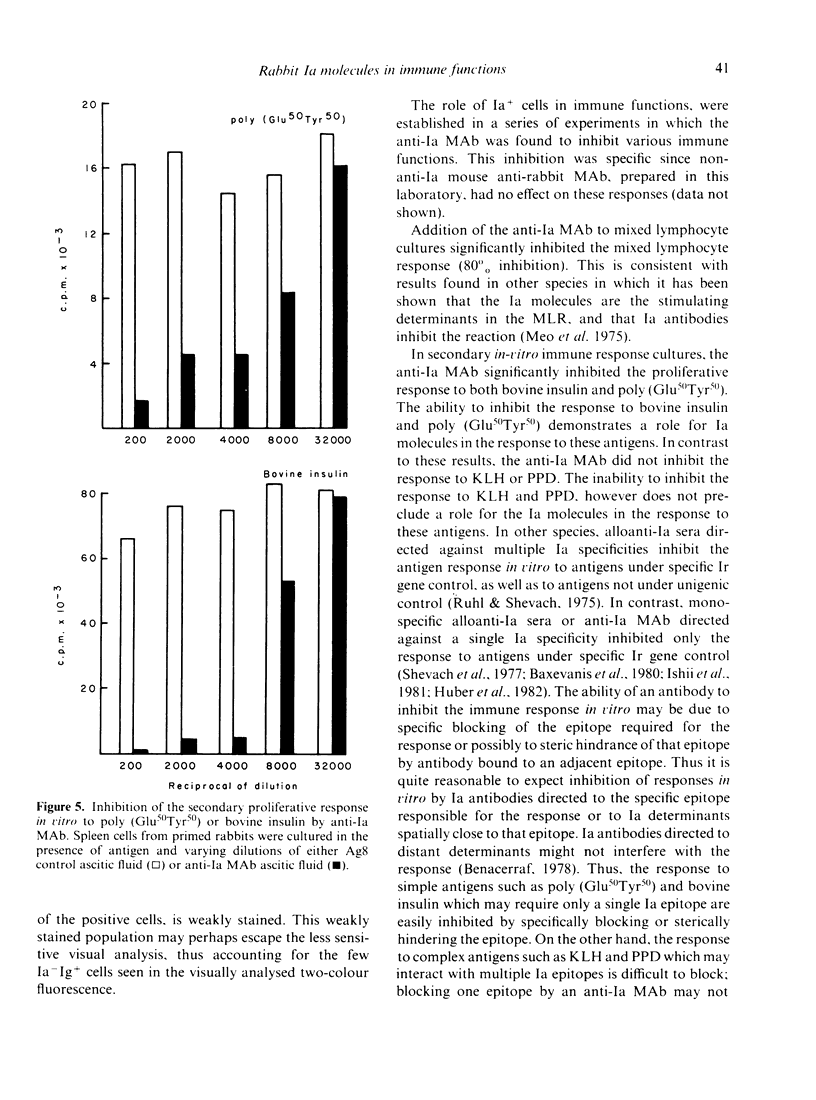
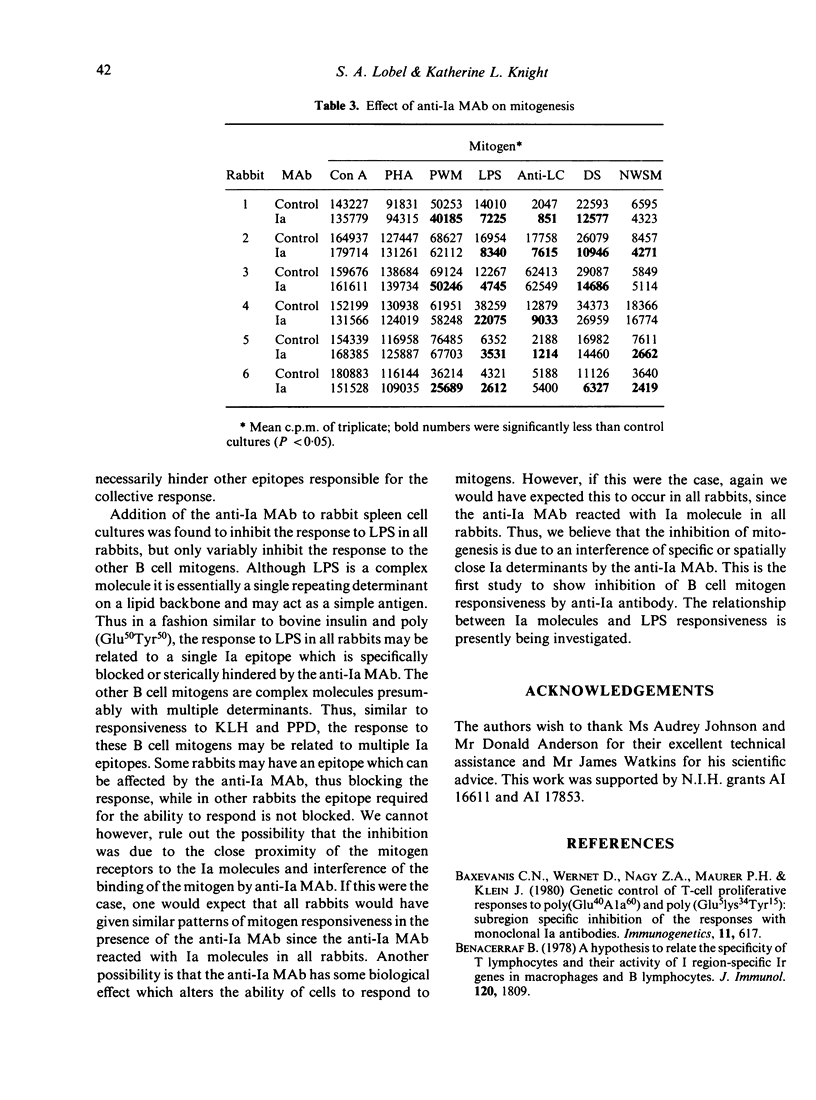
We have produced a mouse anti-rabbit Ia monoclonal antibody (MAb) that detects an isotypic determinant on all rabbit Ia molecules. This MAb precipitates three polypeptide chains with molecular weights of 28,000, 31,000 and 35,000, corresponding to the Ia beta, Ii and alpha chains, respectively. The anti-Ia MAb inhibits the mixed lymphocyte culture by 80%. In secondary in vitro immune response cultures, the anti-Ia MAb inhibits the proliferative response to bovine insulin and poly (Glu50Tyr50). In studies on mitogenesis it was found that the anti-Ia MAb inhibited the response to LPS but not to concanavalin A or phytohaemagglutinin. The effect of the anti-Ia MAb on other mitogens was found to vary from rabbit to rabbit.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxevanis C. N., Wernet D., Nagy Z. A., Maurer P. H., Klein J. Genetic control of T-cell proliferative responses to poly(glu40ala60) and poly(glu51lys34tyr15): subregion-specific inhibition of the responses with monoclonal Ia antibodies. Immunogenetics. 1980;11(6):617–628. doi: 10.1007/BF01567830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. A hypothesis to relate the specificity of T lymphocytes and the activity of I region-specific Ir genes in macrophages and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1809–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Damais C., Chedid L. Blastic transformtion of mouse spleen lymphocytes by a water-soluble mitogen extracted from Nocardia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1602–1606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathings W. E., Mage R. G., Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R., Young-Cooper G. O. Immunofluorescence studies on the expression of VH a allotypes by pre-B and B cells of homozygous and heterozygous rabbits. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):200–206. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber B. T., Hansen T. H., Skelly R. R., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Ia.W39 expression correlates with a specific Ir function. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2349–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Baxevanis C. N., Nagy Z. A., Klein J. Selection of H-2 molecules for the context of antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(3-4):283–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00342197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancki D. W., Tissot R. G., Cohen C. Histocompatibility in the rabbit: genetic control of rabbit mixed leukocyte culture reactivity. Transplantation. 1979 Feb;27(2):79–86. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197902000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J. M., Raffeld M., Loken M. R., Reiter H., Knight K. L. Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit lymphoid cells: preparation and characterization of a T-cell-specific antibody. Mol Immunol. 1981 Sep;18(9):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhl H., Shevach E. M. The effect of alloantisera on antigen-induced T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1493–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., David C. S., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Paul W. E. Inhibition of dual Ir gene-controlled T-lymphocyte proliferative response to poly (Glu56Lys35Phe9)n with anti-Ia antisera directed against products of either I-A or I-C subregion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2387–2391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Lundquist M. L., Geczy A. F., Schwartz B. D. The guinea pig I region. II. Functional analysis. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):561–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Paul W. E., Green I. Histocompatibility-linked immune response gene function in guinea pigs. Specific inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by alloantisera. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1207–1221. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot R. G., Cohen C. Histocompatibility in the rabbit. Identification of the major locus. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(3):267–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]