Abstract
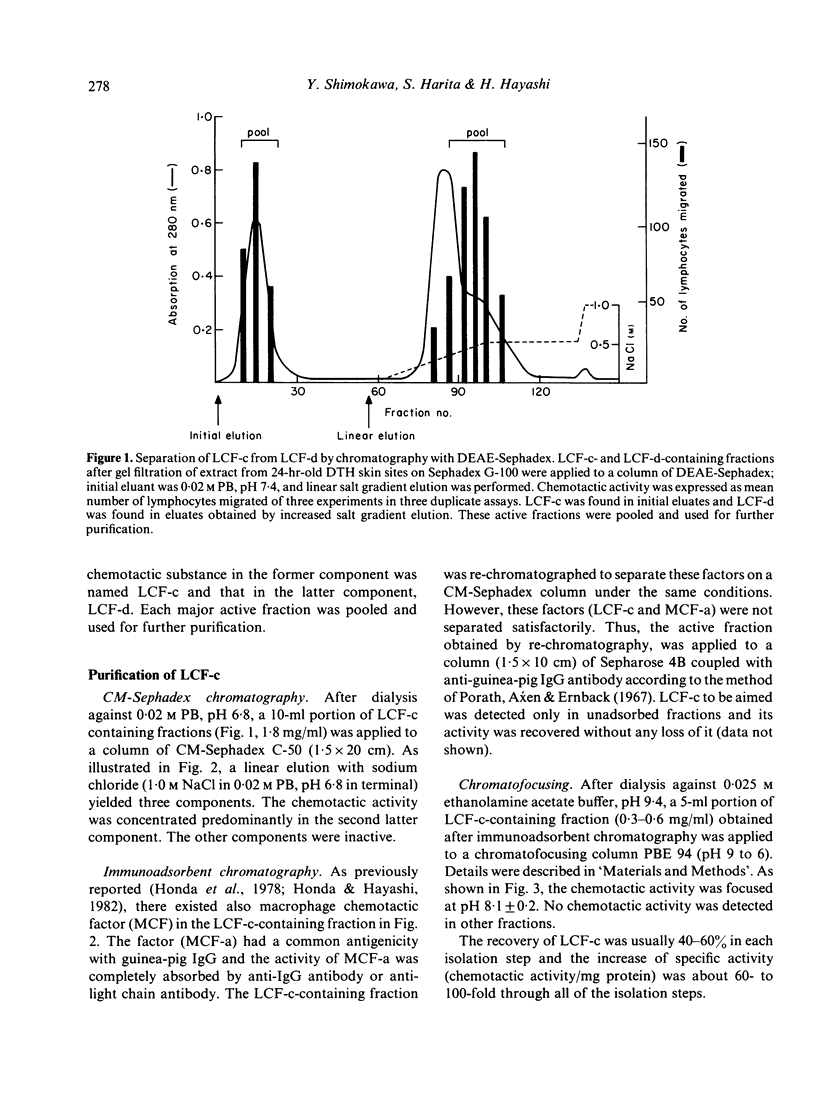
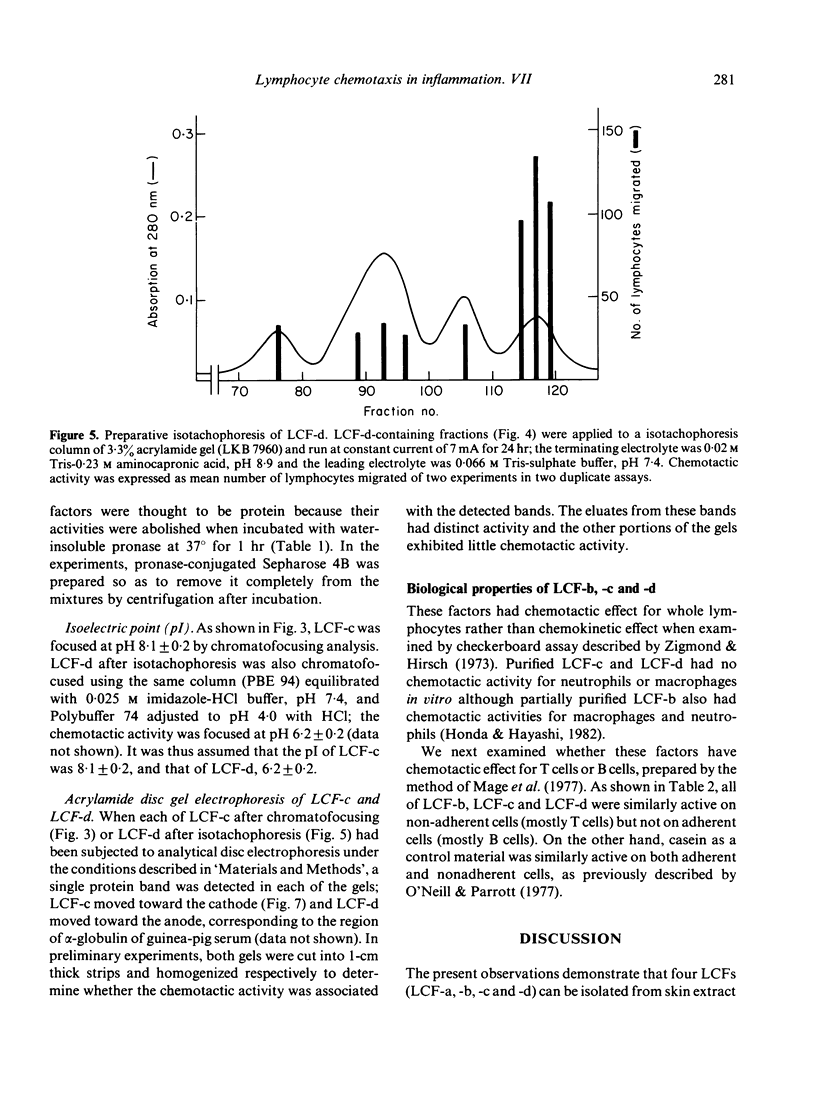
Four types of lymphocyte chemotactic factor (LCF-a, -b, -c and -d) could be isolated from extract of 24-hr-old delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin reaction sites induced with purified protein derivative (PPD) in guinea-pigs by gel filtration on Sephadex G-100 followed by chromatography with DEAE-Sephadex. Partially purified LCF-b was thought to be a heat-stable protein with a molecular weight (mol. wt.) of about 14,000. LCF-c separated from LCF-d by chromatography with DEAE-Sephadex was highly purified by chromatography with CM-Sephadex, immunoadsorbent chromatography coupled with anti-IgG antibody, and chromatofocusing in that order. It was considered to be a heat-labile protein with a mol. wt. of about 160,000 and with pI of 8.1 +/- 0.2. LCF-d first separated from LCF-c was also highly purified by chromatography with CM-Sephadex followed by preparative isotachophoresis. The factor was considered to be a heat-labile protein with a mol. wt. of approximately 300,000 and with pI of 6.2 +/- 0.2. These factors were similarly active for non-adherent cells (mostly T cells) but not for cells (mostly B cells) adherent to anti-IgG antibody-coated petri-dishes. Since LCF-a was active for B cells as described earlier, it is thus suggested that LCF-b, LCF-c and LCF-d may be important for T cell migration in the DTH site to PPD.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braathen L. R., Førre O., Natvig J. B. An anti-human T-lymphocyte antiserum: in situ identification of T cells in the skin of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, chronic photosensitivity dermatitis, and mycosis fungoides. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Jun;13(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Center D. M., Cruikshank W. Modulation of lymphocyte migration by human lymphokines. I. Identification and characterization of chemoattractant activity for lymphocytes from mitogen-stimulated mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2563–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudy A. L., Schmitt D., Viac J., Alario A., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Morphological, immunological and immunocytochemical identification of lymphocytes extracted from cutaneous infiltrates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):61–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ward P. A., Yoshida T., Burek C. L. Biologic activity of extracts of delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction sites. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar A. K., Van Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Human-B and T-lymphocyte locomotion in response to casein, C5a, and f-met-leu-phe. Cell Immunol. 1980 Dec;56(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harita S., Shimokawa Y., Hayashi H. Production of two lymphocyte chemotactic factors by antigen-stimulated guinea pig lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;70(2):118–123. doi: 10.1159/000233308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harita S., Shimokawa Y., Mibu Y., Ishida M., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. IX. Further characterization of lymphocyte chemotactic lymphokines produced by purified protein derivative-stimulation in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):295–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H. The intracellular neutral SH-dependent protease associated with inflammatory reactions. Int Rev Cytol. 1975;40:101–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Honda M., Hayashi H. Production of chemotactic factor for lymphocytes by neutral SH-dependent protease of rabbit PMN leukocytes from immunoglobulins, especially IgM. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jan;15(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Ishida M., Hayashi H. A lymphocyte chemotactic peptide released from immunoglobulin G by neutrophil neutral thiol protease. Cell Immunol. 1979 Sep 1;46(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Hayashi H. Characterization of three macrophage chemotactic factors from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity reaction sites in guinea pigs, with special reference to a chemotactic lymphokine. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):171–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Hirashima M., Nishiura M., Hayashi H. A macrophage chemotactic factor sharing common antigenicity with immunoglobulin G from DNP-ascaris extract-induced skin lesion in guinea-pig. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1978 Jun 19;27(4):317–333. doi: 10.1007/BF02889004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYASHI H., MIYOSHI H., NITTA R., UDAKA K. Proteolytic mechanism in recurrence of Arthus-type inflammation by thiol compounds. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Oct;43:564–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Parrott D. M. Locomotion of human lymphoid cells. I. Effect of culture and con A on T and non-T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Oct;33(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Higuchi Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. III. Demonstration of lymphocyte chemotactic activity in extract from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Aug;63(4):355–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Higuchi Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. IV. Isolation of lymphocyte chemotactic factors from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig, with special reference to a factor chemotactic for B cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Aug;63(4):362–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Mibu Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. VIII. Demonstration of lymphocyte chemotactic lymphokines in PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Offen C. D., Montgomery J. R. Chemoattractants of leukocytes, with special reference to lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1721–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Unanue E. R., Goralnick S. J., Schreiner G. F. Chemotaxis of rat lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):416–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Roberts J. A., Russell R. J., McLoughlin M. Chemotaxis of mitogen-activated human lymphocytes and the effects of membrane-active enzymes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):280–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



