Abstract
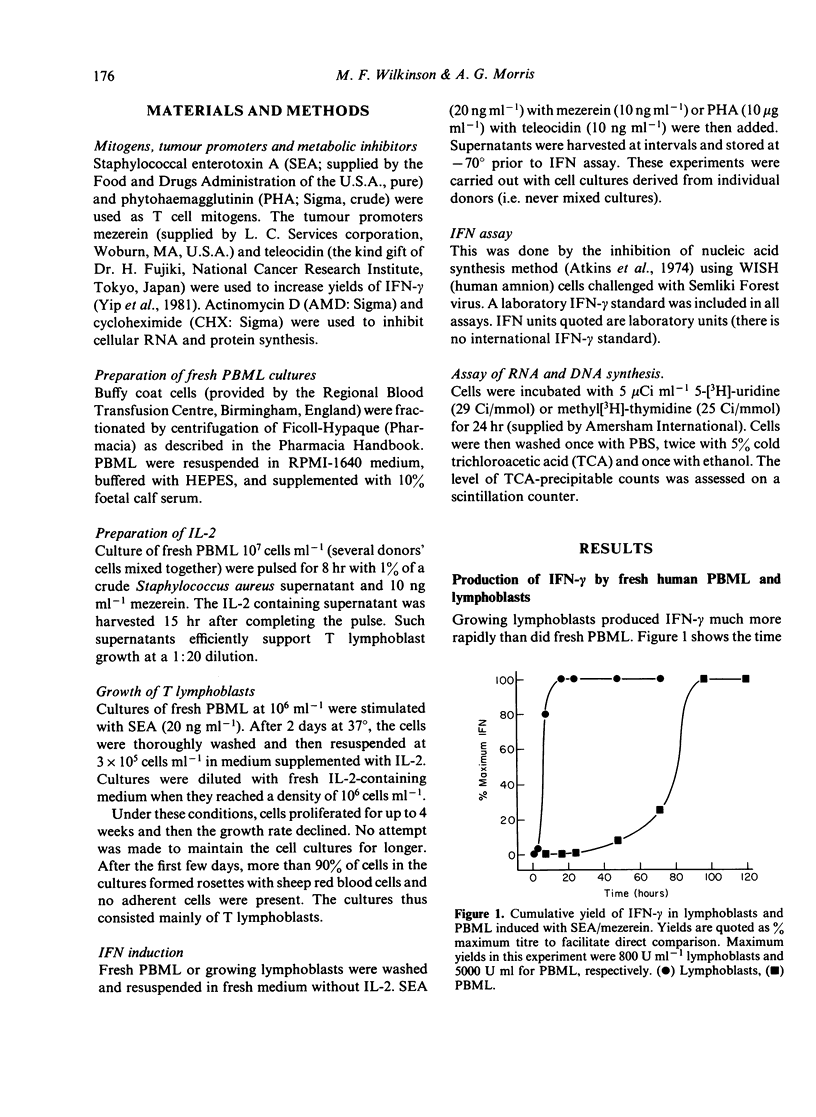
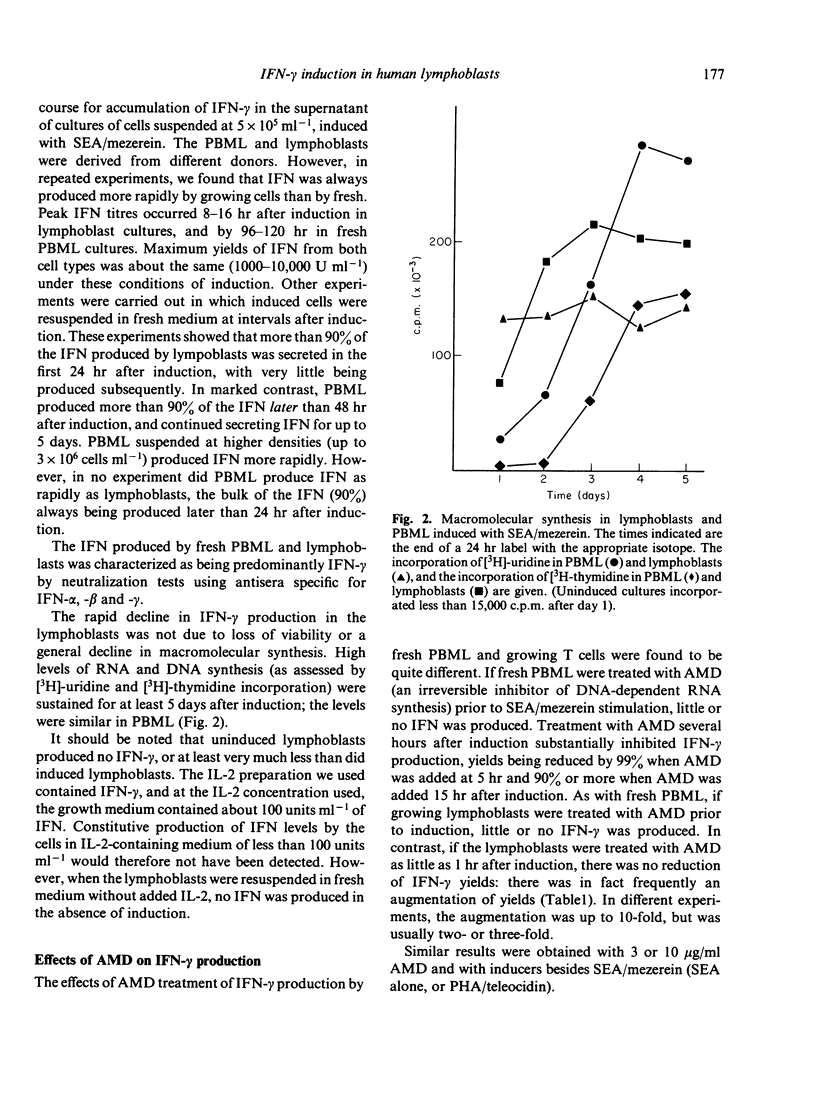
The mechanisms of gamma-interferon (IFN-gamma) induction in fresh human peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes (PBML) and proliferating lymphoblasts were compared. Cotreatment with mitogen (Staphylococcal enterotoxin A) and tumour promoter (mezerein) was used to induce maximum IFN-gamma production and thus to study the induction process under optimum conditions. Total IFN yields were about the same from both cell types. Proliferating lymphocytes produced IFN much earlier and more transiently than fresh PBML. Experiments with actinomycin D indicated that de novo synthesis of RNA was required for IFN-gamma production in both PBML and lymphoblasts, but that for maximal IFN-gamma production, lymphoblasts required RNA synthesis for a shorter period (1 hr) after induction than did fresh PBML (greater than 15 hr). Appropriate schedules of treatment with metabolic inhibitors actually increased IFN production in lymphoblasts. This 'superinduction' could not be demonstrated for fresh PBML, implying differences in the turn-off of IFN-gamma production in these two cell types. Taken together, these results indicate that IFN-gamma expression is regulated differently in quiescent and activated lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Johnston M. D., Westmacott L. M., Burke D. C. Department of Biological Sciences, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV47AL, England. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):381–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Gershon R. K. Interleukin 1 can replace the requirement for I-A-positive cells in the proliferation of antigen-primed T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4747–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. The interaction of human macrophages and lymphocytes in the phytohemagglutinin-stimulated production of interferon. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):744–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. Methylation and gene control. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):602–603. doi: 10.1038/296602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., Andersson L. C. Generation of T memory cells in one-way mixed lymphocyte culture. II. Anamnestic responses of "secondary" lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):823–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Weigent D. A., Georgiades J. A., Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J. Antibody to staphylococcal enterotoxin A-induced human immune interferon (IFN gamma). J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1620–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama M., Sugamura K., Kawade Y., Hinuma Y. Production of immune interferon by human cytotoxic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):450–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gilbride K. J., Favata M. F. Lymphocyte activating factor promotes T-cell growth factor production by cloned murine lymphoma cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):853–855. doi: 10.1038/287853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres B. A., Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M. Interleukin 2 regulates immune interferon (IFN gamma) production by normal and suppressor cell cultures. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2217–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F. Interferon-like virus-inhibitor induced in human leukocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Science. 1965 Jul 16;149(3681):310–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip Y. K., Pang R. H., Oppenheim J. D., Nachbar M. S., Henriksen D., Zerebeckyj-Eckhardt I., Vilcek J. Stimulation of human gamma interferon production by diterpene esters. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):131–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.131-139.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


