Abstract
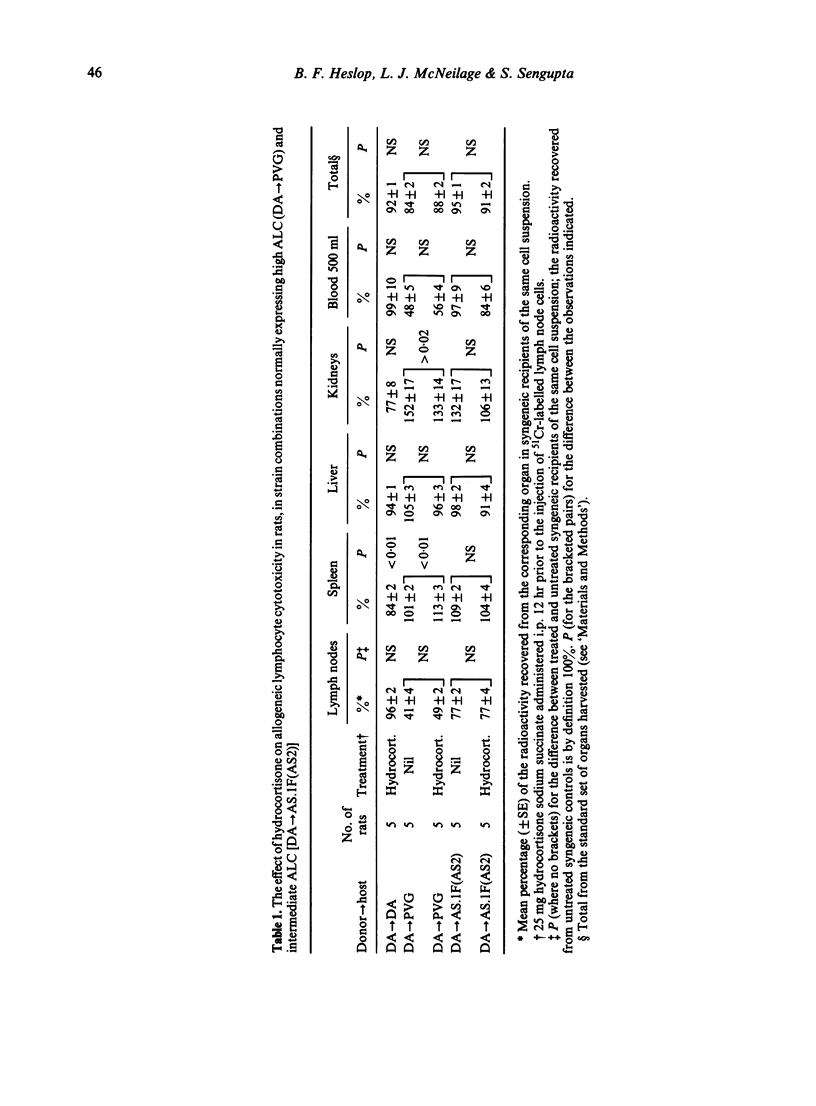
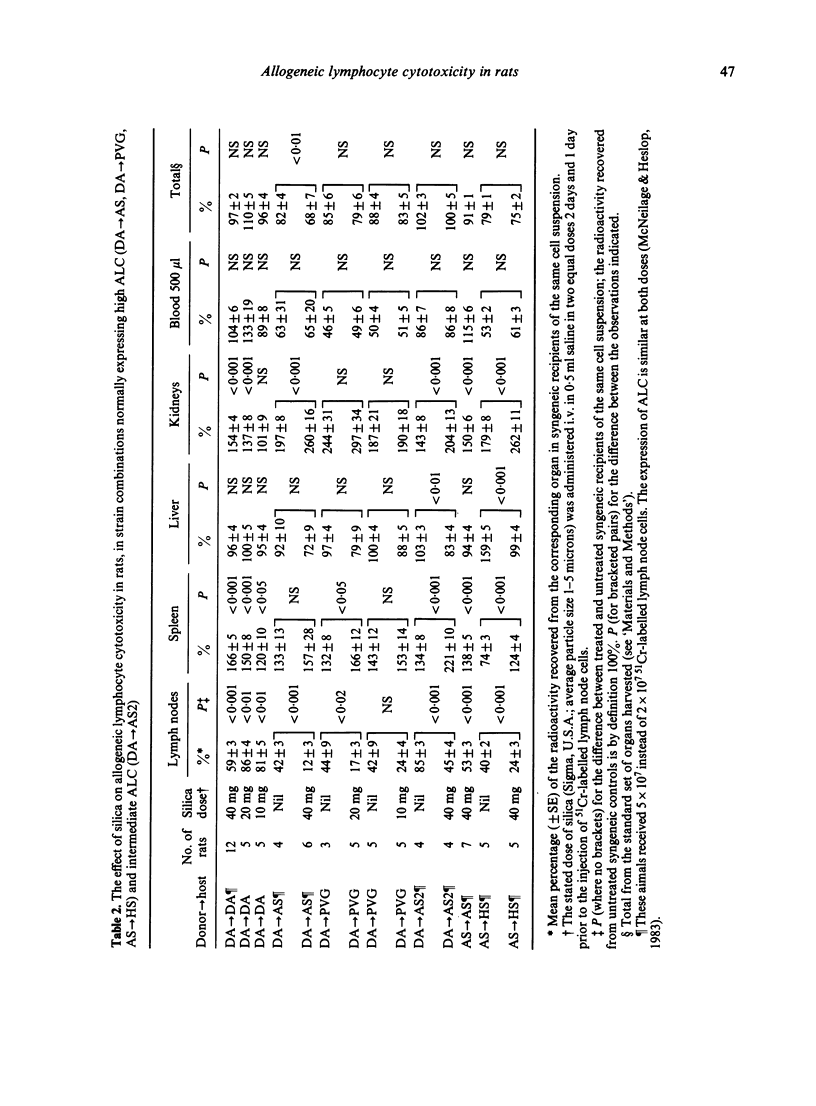
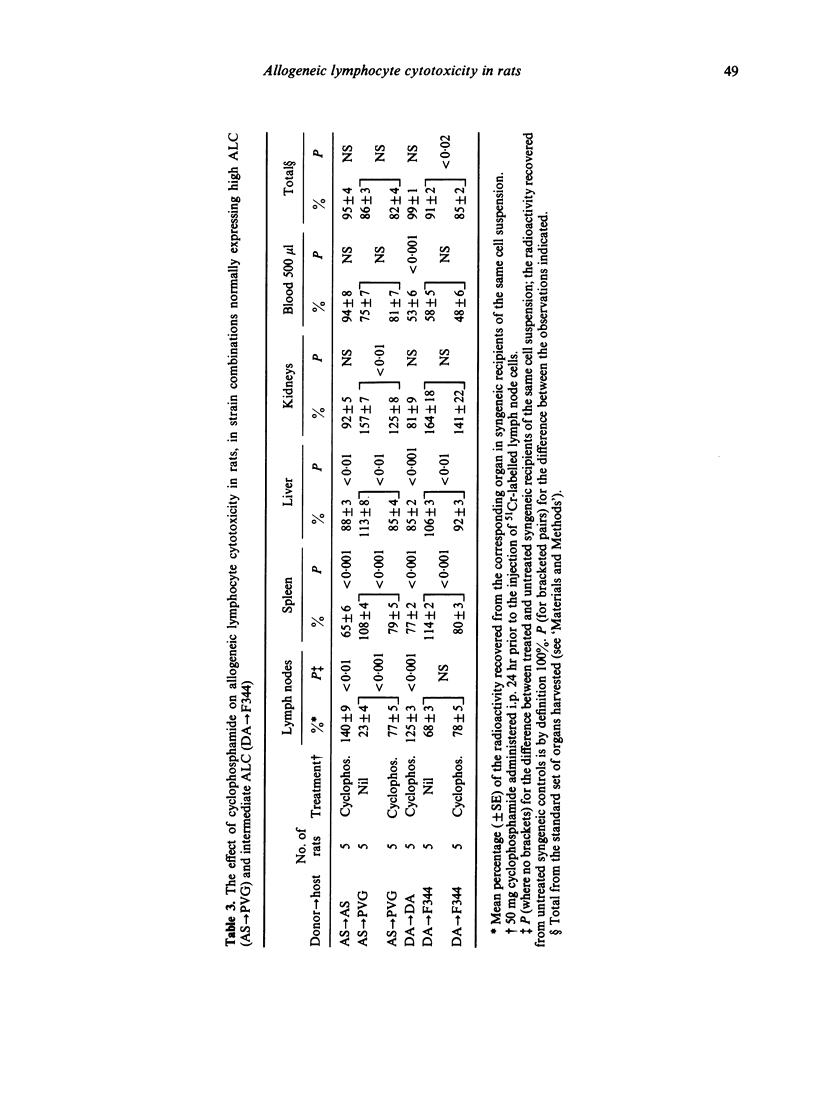
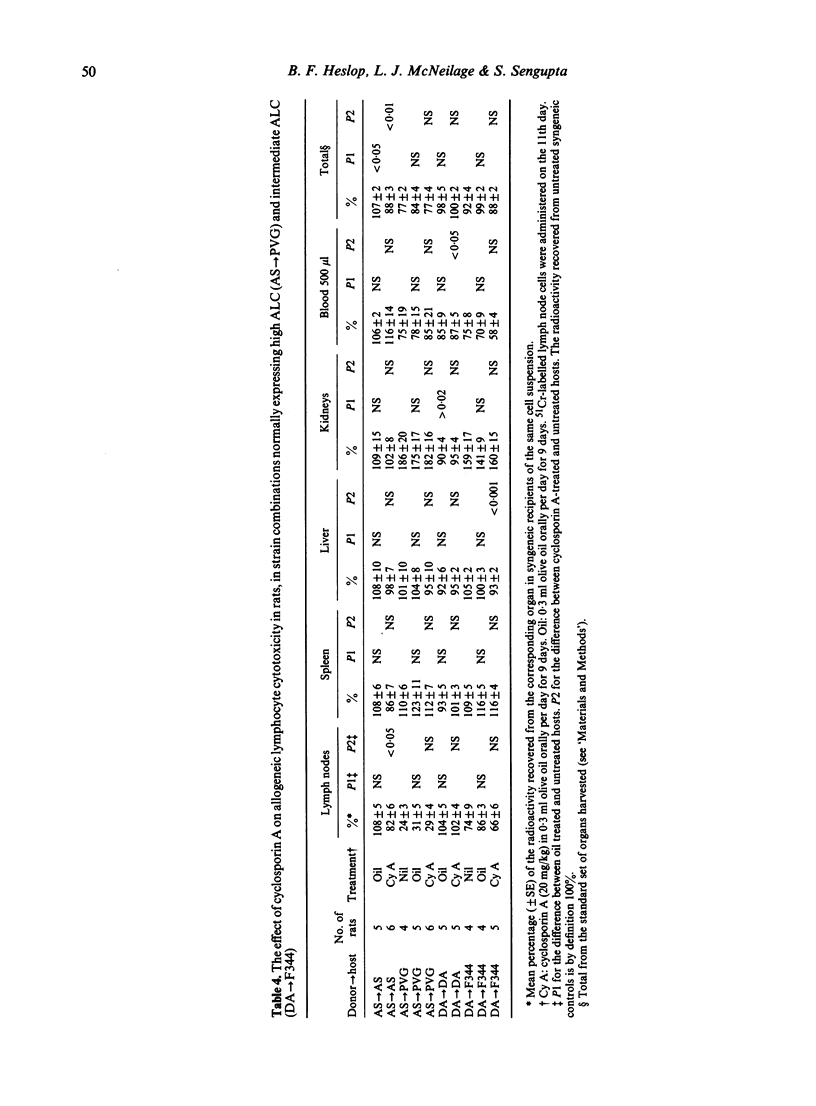
In a number of strain combinations among inbred rats, intravenously injected 51Cr-labelled lymphocytes are rapidly destroyed by unsensitized allogeneic hosts. This phenomenon has previously been referred to by a number of terms, the most explicit and least confusing of which is allogeneic lymphocyte cytotoxicity (ALC). It is characterized by reduced lymph node radioactivity, together with increased kidney and/or urine radioactivity 24 hr after injection, in allogeneic hosts as compared with syngeneic recipients of the same cell suspension. ALC has a number of features in common with other natural resistance systems. Nevertheless, the administration of hydrocortisone or silica in doses comparable to those causing diminished NK activity in rats was without effect on ALC; likewise cyclophosphamide at a dose capable of significantly impairing NK activity in rats had, at most, a minor effect on ALC. Under the conditions of administration cyclosporin A was without effect. The interferon inducer polyinosinic polycytidilic acid (poly I:C) brought about a significant augmentation of ALC.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Sprent J., Miller J. F. Radiosensitivity of T and B lymphocytes. I. Effect of irradiation on cell migration. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Mar;4(3):199–203. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S., Palacios R. Cyclosporin A--usefulness, risks and mechanism of action. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degos L., Pla M., Colombani M. H-2 restriction for lymphocyte homing into lymph nodes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Oct;9(10):808–814. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop B. F., McNeilage L. J. Natural cytotoxicity: early killing of allogeneic lymphocytes in rats. Immunol Rev. 1983;73:35–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Hochman P. S., Haller O., Shearer G. M., Wigzell H., Cudkowicz G. Evidence for a similar or common mechanism for natural killer cell activity and resistance to hemopoietic grafts. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):655–663. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Heslop B. F., Heyworth M. R., Gutman G. A. Natural cytotoxicity in rats: strain distribution and genetics. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 15;72(2):340–350. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90482-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Heslop B. F. Lymphoycte homing in syngeneic and unsensitized MHC compatible allogeneic hosts. I. Evidence for both syngeneic self-recognition and early killing of allogeneic cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):58–70. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Heslop B. F. Natural cytotoxicity in rats: radiation-induced changes in the early killing of allogeneic cells. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jun;78(2):206–216. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Herberman R. B. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rats. III. Effects of immunopharmacologic treatments on natural reactivity and on reactivity augmented by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):221–229. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler J. R., Lindsay L. R., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rats. II. In vivo augmentation of NK-cell activity. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):210–220. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Ford W. L. The rapid elimination of allogeneic lymphocytes: relationship to established mechanisms of immunity and to lymphocyte traffic. Immunol Rev. 1983;73:87–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark O., Kren V., Günther E. RtH-1 antigens in 39 rat strains and six congenic lines. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):165–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen B., Rolstad B. In vivo elimination of allogeneic lymphocytes in normal and T-cell-deficient rats. Elimination does not require T cells. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Apr;17(4):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viklický V., Micková M. Role of the H-2 complex in the homing affinity of injected lymphoid cells to the host's lymph nodes. J Immunogenet. 1979 Aug;6(4):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1979.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


