Abstract
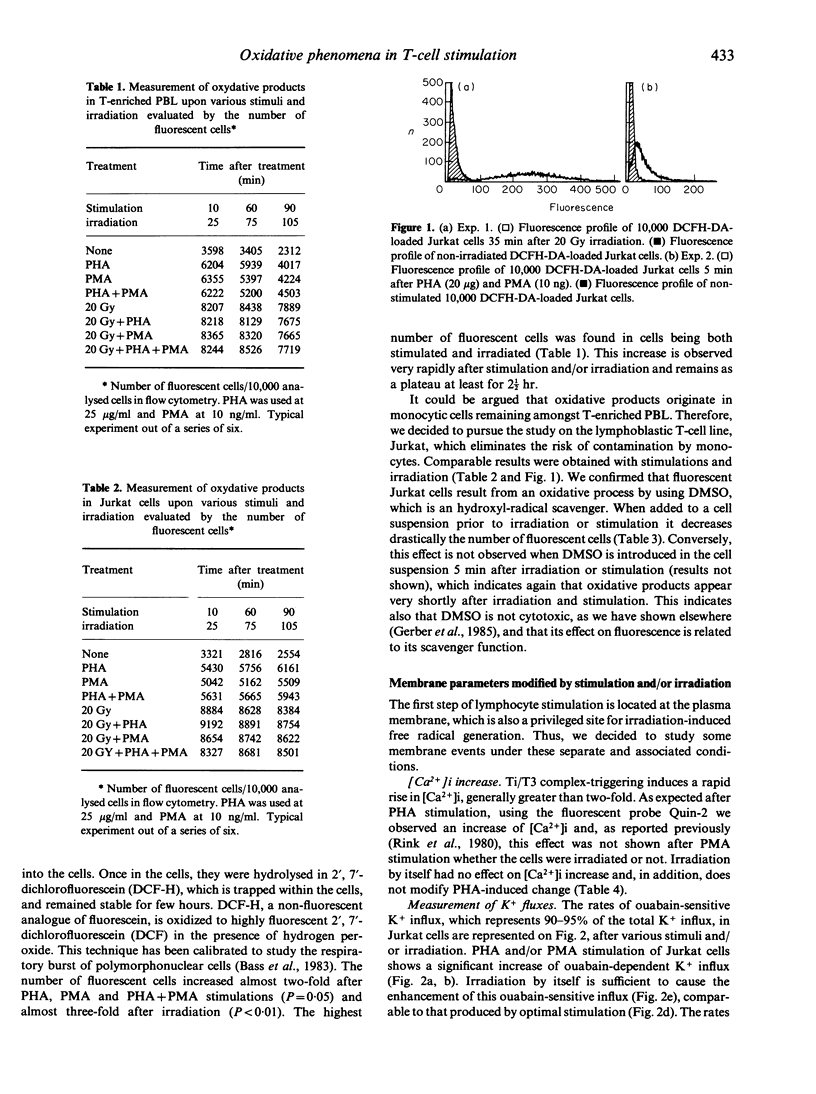
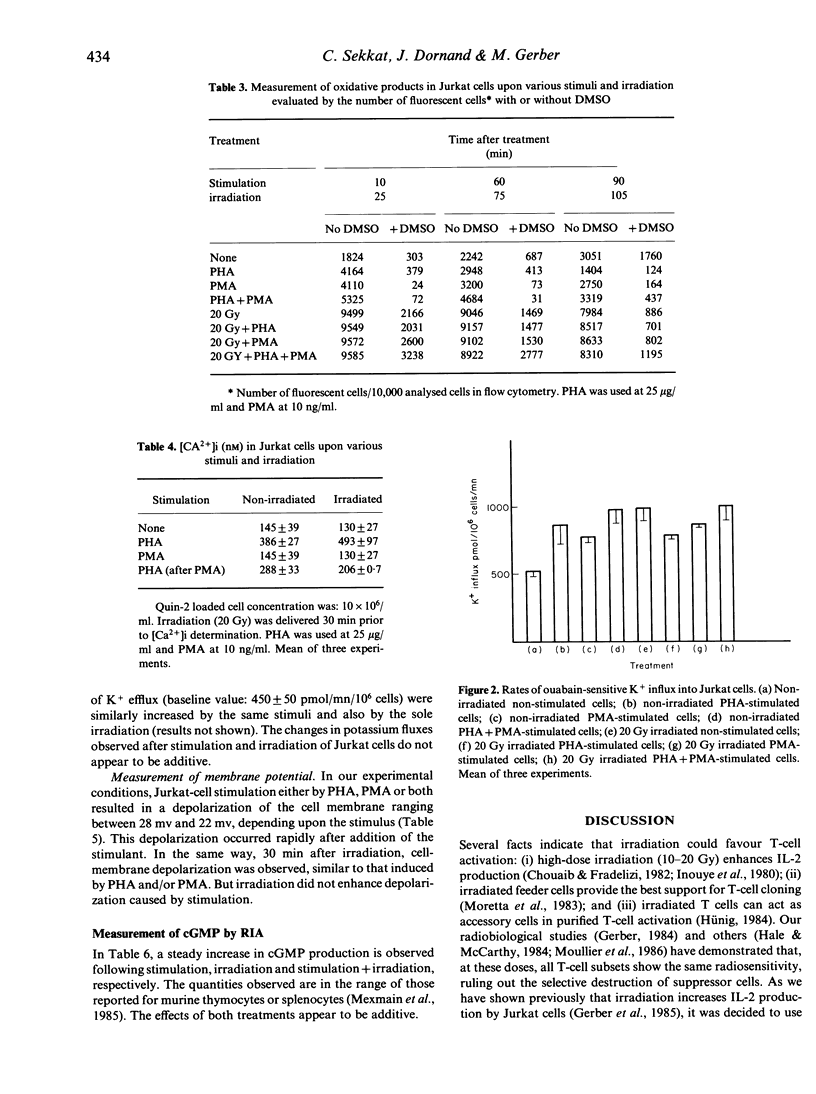
Phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and PHA + PMA stimulation of T-enriched peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) and the Jurkat malignant T-cell line leads to oxidative-product formation, as evaluated by flow cytofluorometric studies, an increase in K+ flux across the membrane, cGMP production and a depolarization of the cell membrane. Irradiation (20 Gy), which enhances IL-2 synthesis by activated T-enriched PBL and Jurkat cells, also increases oxidative product formation, K+ flux, cGMP production, and induces cell membrane depolarization. Conversely, irradiation does not produce a rise in intracellular free Ca2+, as measured in PHA-stimulated Jurkat cells. PMA is also without effect on intracellular free Ca2+, added before or after PHA stimulation. Thus, except for the rise in intracellular free Ca2+, irradiation and stimulation exert similar effects on some of the events observed in IL-2-producing Jurkat cells, but these effects are not additive. Stimulation and irradiation effects are shown to be additive or synergistic only for cGMP production. It is proposed that irradiation may increase IL-2 synthesis by participating in an additional signal related to the oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid (AA).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass D. A., Parce J. W., Dechatelet L. R., Szejda P., Seeds M. C., Thomas M. Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1910–1917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Fradelizi D. The mechanism of inhibition of human IL 2 production. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2463–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Lipsky P. E. Signals involved in T cell activation. II. Distinct roles of intact accessory cells, phorbol esters, and interleukin 1 in activation and cell cycle progression of resting T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3588–3596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornand J., Bonnafous J. C., Gavach C., Mani J. C. 5'-Nucleotidase-facilitated adenosine transport by mouse lymphocytes. Biochimie. 1979;61(8):973–977. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornand J., Sekkat C., Mani J. C., Gerber M. Lipoxygenase inhibitors suppress IL-2 synthesis: relationship with rise of [Ca++]i and the events dependent on protein kinase C activation. Immunol Lett. 1987 Nov;16(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekejindu G. O., Shifrine M., Misra H. P. Chemiluminescence of canine peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated by mitogens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Feb;11(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Humes J. L. The role of arachidonic acid metabolism in the activities of interleukin 1 and 2. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1153–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S. Mitogen-induced changes in Ca2+ permeability are not mediated by voltage-gated K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11520–11523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M., Ball D., Michel F., Crastes de Paulet A. Mechanism of enhancing effect of irradiation on production of IL-2. Immunol Lett. 1985;9(5):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. Radiosensitivity of murine T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Radiat Res. 1984 Nov;100(2):365–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstock C. L. Redox processes in radiation biology and cancer. Radiat Res. 1981 May;86(2):196–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualde N., Atluru D., Goodwin J. S. Effect of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid on proliferation of human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1125–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gukovskaya A. S., Zinchenko V. P. The effects of ionophore A23187 and concanavalin A on the membrane potential of human peripheral blood lymphocytes and rat thymocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90371-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale M. L., McCarthy K. F. Effect of sublethal ionizing radiation on rat Peyer's patch lymphocytes. Radiat Res. 1984 Jul;99(1):151–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton L. J., Kaplan J. G. Flux of 86Rb in activated human lymphocytes. Can J Biochem. 1977 Jul;55(7):774–778. doi: 10.1139/o77-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. The role of accessory cells in polyclonal T cell activation. III. No requirement for recognition of H-2-encoded antigens on accessory cells. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):483–489. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A., Stobo J. D. The antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Hank J. A., Alter B. J., Bach F. H. TCGF production for cloning and growth of functional human T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(2):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa S., Johnston R. B., Jr Relationship between membrane potential changes and superoxide-releasing capacity in resident and activated mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3417–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Weyand C., Goronzy J., Stobo J. D. T cell activation: differences in the signals required for IL 2 production by nonactivated and activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mexmain S., Cook J., Aldigier J. C., Gualde N., Rigaud M. Thymocyte cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP response to treatment with metabolites issued from the lipoxygenase pathway. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1361–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Moretta L., Cerottini J. C., Mingari M. C. Direct demonstration of the clonogenic potential of every human peripheral blood T cell. Clonal analysis of HLA-DR expression and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):743–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moullier P., Daveloose D., Dubos M., Leterrier F., Hoebeke J. Effect of in vivo gamma-irradiation on the binding of wheat germ agglutinin on lymphocyte plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 1;883(3):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S. Radiation-induced ouabain-insensitive K+ exchange of erythrocytes under the quasi-physiological conditions. J Radiat Res. 1982 Mar;23(1):119–127. doi: 10.1269/jrr.23.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrogemann K., Weidemann M. J., Peskar B. A., Staudinger H., Rietschel E. T., Fischer H. Chemiluminescence and immune cell activation. I. Early activation of rat thymocytes can be monitored by chemiluminescence measurements. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):749–752. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O. Radiation-induced crosslinks between carboxylic acids and compounds of biological interest. Radiat Res. 1986 Feb;105(2):158–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


