Abstract
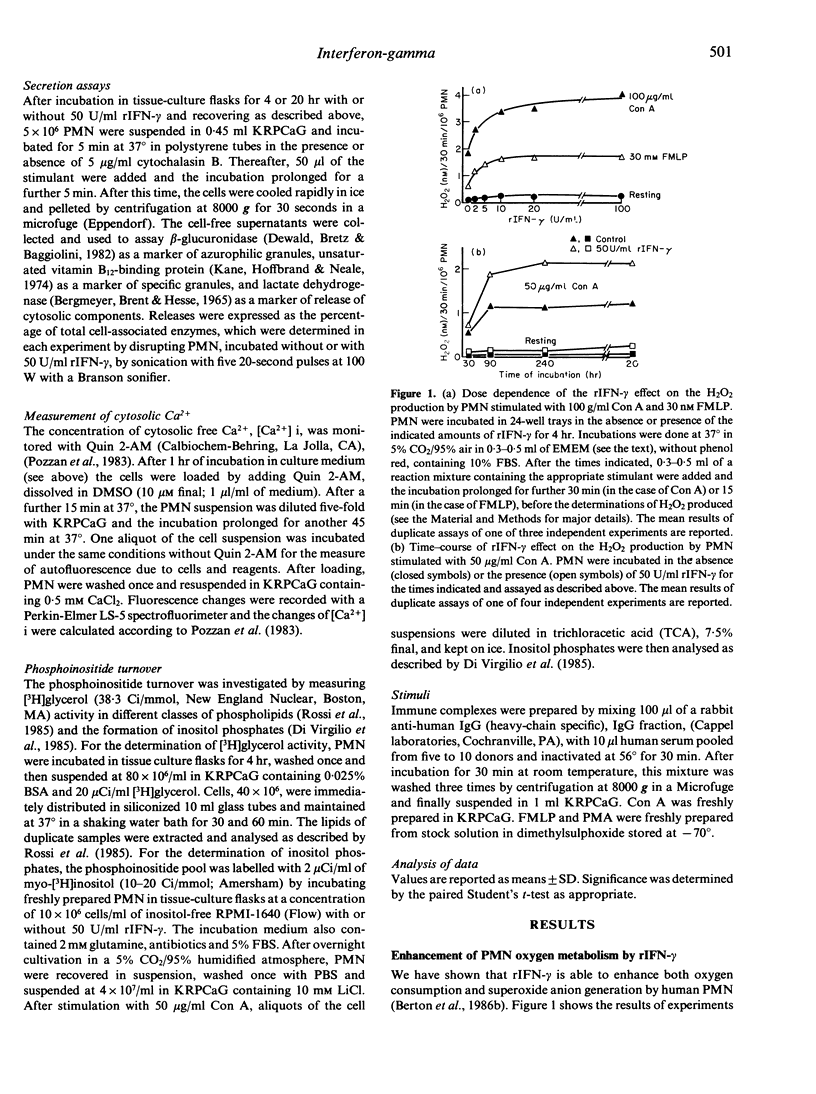
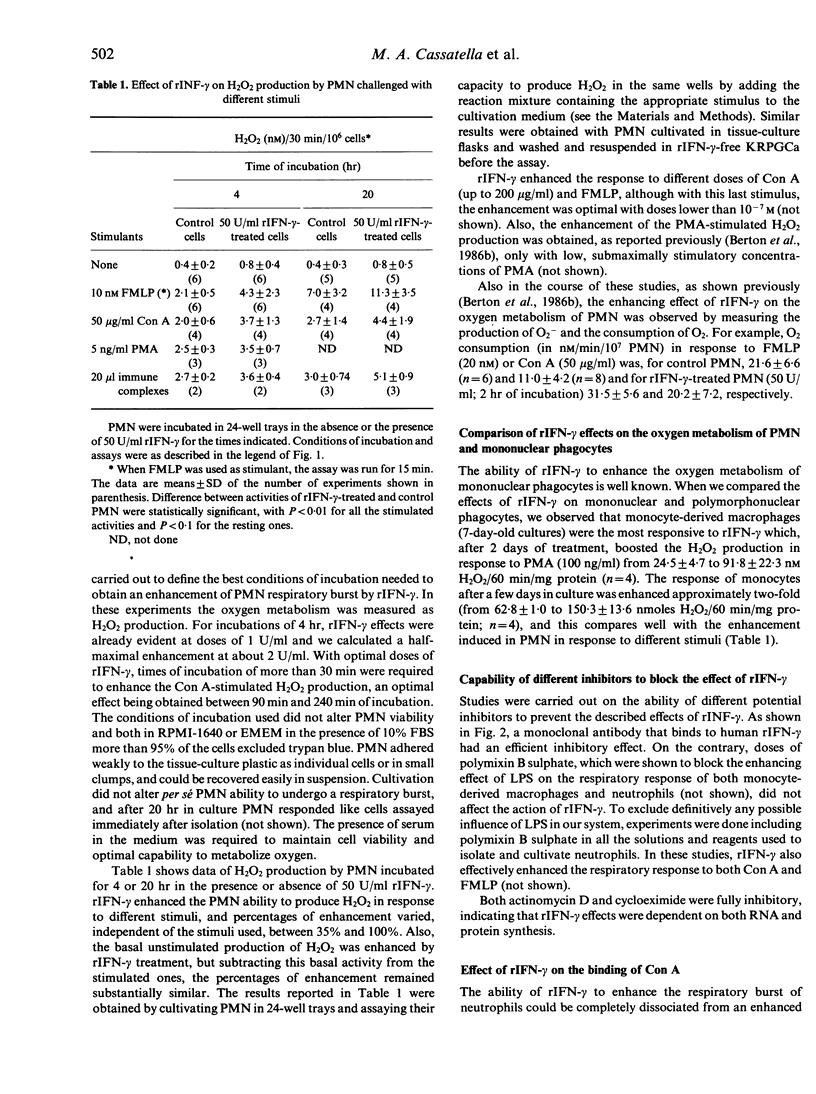
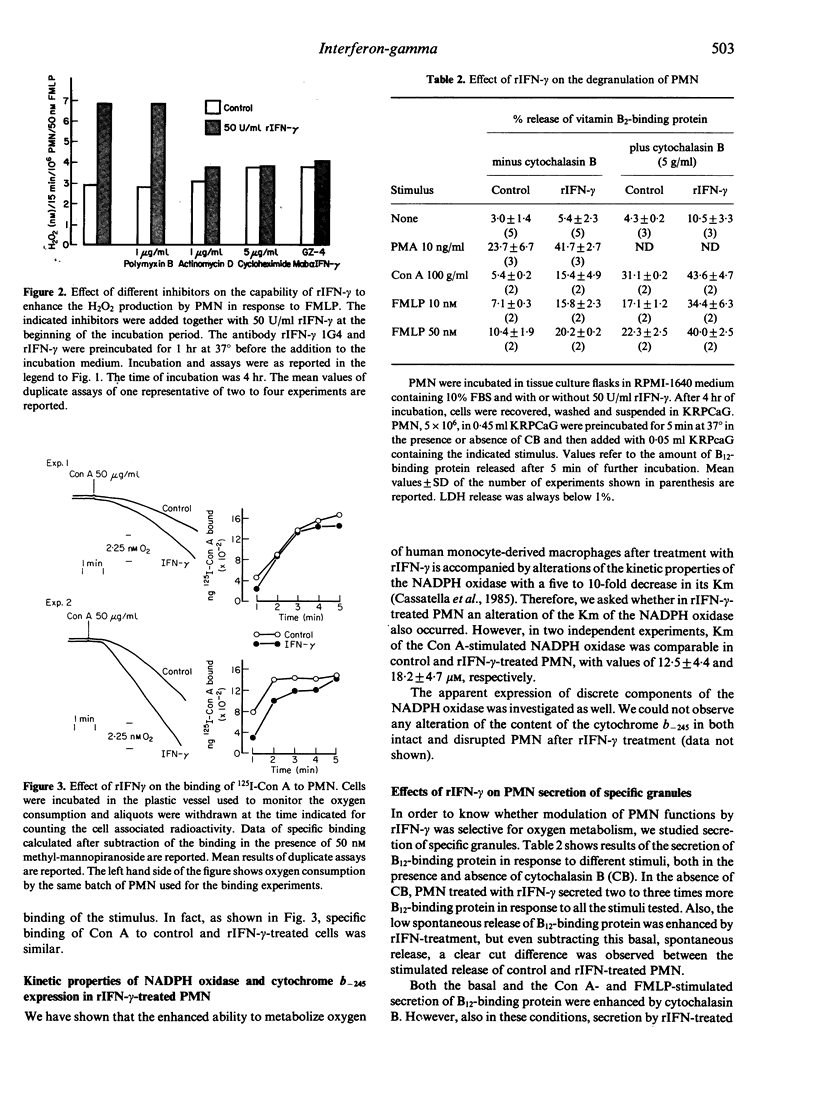
Here we have investigated the ability of recombinant interferon-gamma (rIFN-gamma) to modulate human neutrophil (PMN) functions. PMN incubated in the presence of rIFN-gamma showed an enhanced hydrogen peroxide production in response to Con A, FMLP, PMA or immune complexes. The effect of rIFN-gamma was dose dependent, being half maximal at 2 U/ml, and required between 90 min and 240 min of incubation to reach optimal response. The enhancing effect of rIFN-gamma on the respiratory response of PMN was not blocked by polymixin B sulphate, but an anti-rIFN-gamma monoclonal antibody and cycloheximide and actinomycin D were effective inhibitors. The enhancement of the response to Con A was not accompanied by an enhanced binding of the lectin. Neither the kinetic properties of the Con A-stimulated NADPH oxidase nor the expression of cytochrome b-245 were altered in rIFN-gamma-treated PMN. rIFN-gamma also enhanced granule secretion in response to Con A, FMLP and PMA. Initial studies on the possible alterations of transmembrane signalling in rIFN-gamma-treated PMN showed that neither inositol phosphates formation nor cytoplasmic calcium transients were altered.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basham T. Y., Smith W. K., Merigan T. C. Interferon enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity when suboptimal concentrations of antibody are used. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Cassatella M. A., Bellavite P., Rossi F. Molecular basis of macrophage activation. Expression of the low potential cytochrome b and its reduction upon cell stimulation in activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Cassatella M., Cabrini G., Rossi F. Activation of mouse macrophages causes no change in expression and function of phorbol diesters' receptors, but is accompanied by alterations in the activity and kinetic parameters of NADPH oxidase. Immunology. 1985 Feb;54(2):371–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Gordon S. Desensitization of macrophages to stimuli which induce secretion of superoxide anion. Down-regulation of receptors for phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):620–627. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Zeni L., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F. Gamma interferon is able to enhance the oxidative metabolism of human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borish L., O'Reilly D., Klempner M. S., Rocklin R. E. Leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) potentiates neutrophil responses to formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1897–1903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Della Bianca V., Berton G., Rossi F. Activation by gamma interferon of human macrophage capability to produce toxic oxygen molecules is accompanied by decreased Km of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):908–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91893-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Valletta E., Dusi S., Berton G. Measurement of NADPH oxidase activity in detergent lysates of human and mouse macrophage monolayers. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Sep 27;92(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. H., Mayer P., Baggiolini M. Stimulation of phagocytosis in bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: correlation with biochemical and functional parameters. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):913–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann J., Golde D. W., Weisbart R. H., Gasson J. C. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances phagocytosis of bacteria by human neutrophils. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):708–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeskowiak M., Della Bianca V., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F. Complete dissociation between the activation of phosphoinositide turnover and of NADPH oxidase by formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in human neutrophils depleted of Ca2+ and primed by subthreshold doses of phorbol 12,myristate 13,acetate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90997-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie L. A., McPhail L. C., Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Evidence for increased activity of the superoxide-producing enzyme. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1656–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. P., Hoffbrand A. V., Neale G. Indices of granulocyte activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):953–959. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Rossing T. H., Boerth L. W., Lee T. H. Isolation and partial characterization of a human alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1230–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon induces the receptor for monomeric IgG1 on human monocytic and myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1092–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Kobayashi M., Rossi M. E., Anegon I., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon enhances functional properties of human granulocytes: role of Fc receptors and effect of lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):765–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. F., Lemaire G. Macrophage activation. Introduction. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1986 Mar-Apr;137C(2):191–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Lew D. P., Wollheim C. B., Tsien R. Y. Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.6310757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Della Bianca V., Grzeskowiak M., De Togni P., Cabrini G. Relationships between phosphoinositide metabolism, Ca2+ changes and respiratory burst in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated human neutrophils. The breakdown of phosphoinositides is not involved in the rise of cytosolic free Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Grzeskowiak M., Della Bianca V. Double stimulation with FMLP and Con A restores the activation of the respiratory burst but not of the phosphoinositide turnover in Ca2+-depleted human neutrophils. A further example of dissociation between stimulation of the NADPH oxidase and phosphoinositide turnover. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbeck M. J., Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Activation of bovine neutrophils by recombinant interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1986 Mar;98(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valletta E. A., Berton G. Desensitization of macrophage oxygen metabolism on immobilized ligands: different effect of immunoglobulin G and complement. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4366–4373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. G., Mandell G. L. Anthrax toxin blocks priming of neutrophils by lipopolysaccharide and by muramyl dipeptide. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1700–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



