Abstract
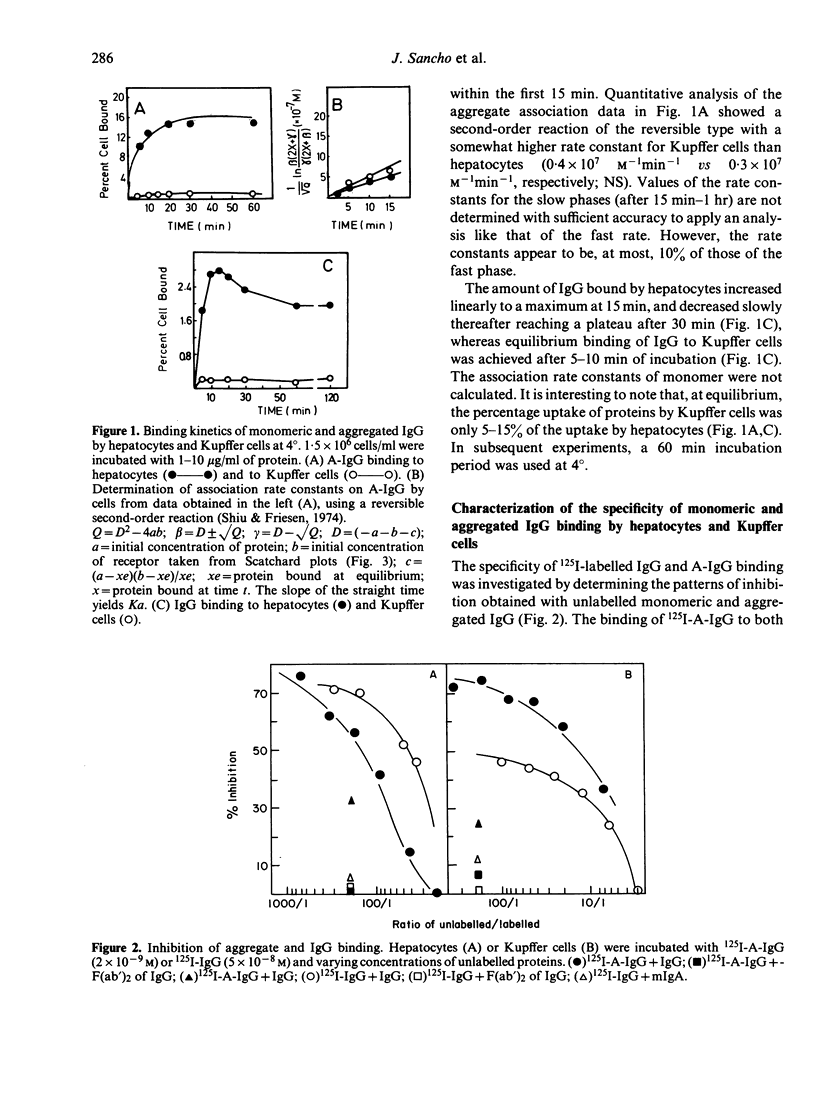
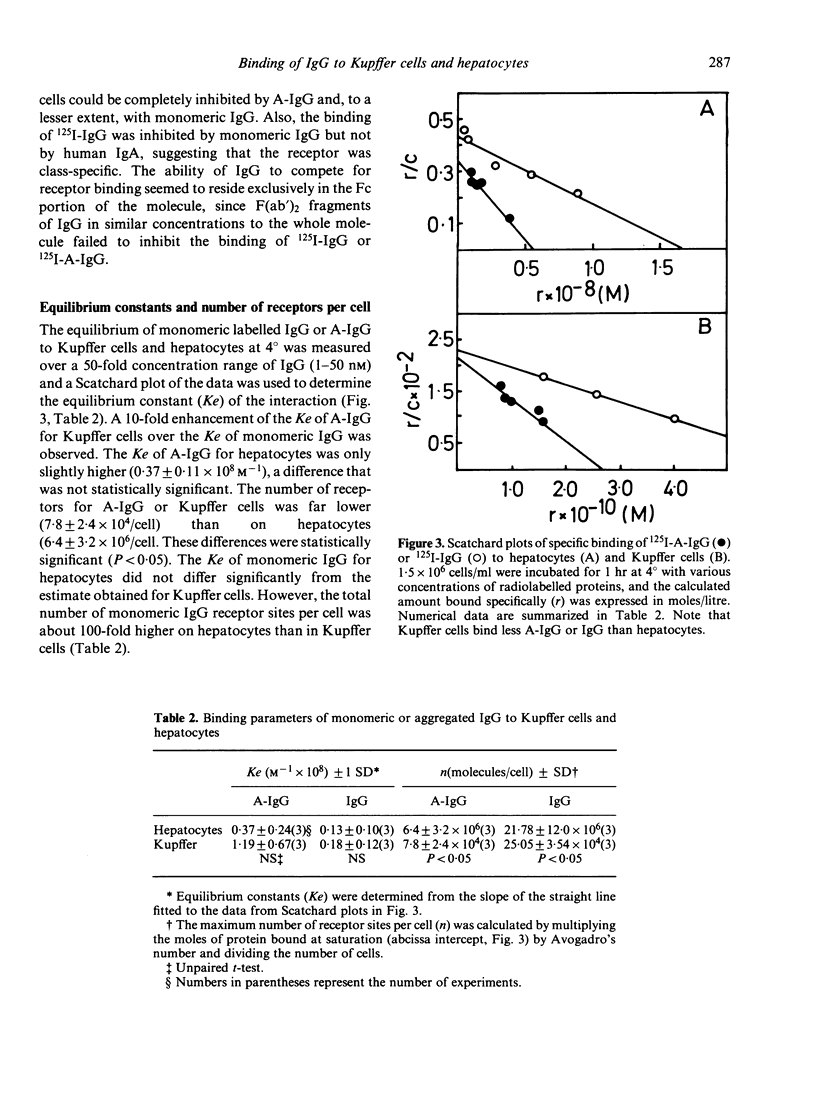
The binding kinetics of human monomeric IgG and stable heat-aggregated IgG (A-IgG) to Fc receptors of hepatocytes and Kupffer cells isolated from mice was studied. After injection of radiolabelled proteins the 60-70% of hepatic uptake was recovered in parenchymal cells (hepatocytes). In experiments in vitro the A-IgG bound in larger amounts to hepatocytes and Kupffer cells than monomeric IgG. The association rate constants of aggregates were somewhat higher for Kupffer cells than for hepatocytes whereas the percentage uptake of aggregates by Kupffer cells was only 5-15% of that of hepatocytes. The equilibrium constants of aggregates binding to both cells amounted to 0.4-1 X 10(8) M-1 for A-IgG compared with an equilibrium constant for monomeric IgG of 1-2 X 10(7)M-1. The maximum number of IgG and A-IgG molecules bound per cell was higher on hepatocytes (mean 14 X 10(6)) than on Kupffer cells (mean 2 X 10(5)) which is in agreement with the higher binding capacity of hepatocytes for these proteins observed in vivo and in vitro experiments. The ability to compete for receptor binding seemed to reside exclusively in the Fc portion of IgG since F(ab')2 fragments of IgG failed to inhibit labelled monomeric IgG or A-IgG. The receptor seems to be specific for IgG since unlabelled monomeric IgA demonstrated no binding inhibition of labelled IgG or A-IgG on hepatocytes and Kupffer cells. The overall results further suggest that hepatocytes might through Fc receptors play a collaborative role with the mononuclear phagocytic system in the clearance of circulating immune complexes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. II. Quantification of tissue uptake of soluble complexes in normal and complement-depleted rabbits. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):63–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. The macrophage receptor for IgG: number and affinity of binding sites. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamness G. C., McGuire W. L. Scatchard plots: common errors in correction and interpretation. Steroids. 1975 Oct;26(4):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofton R. W., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. M., van Furth R. The origin, kinetics, and characteristics of the Kupffer cells in the normal steady state. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):1–17. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. F., Thornburg R. W., Thorpe S. R., Baynes J. W. Carbohydrate-mediated clearance of antibody . antigen complexes from the circulation. The role of high mannose oligosaccharides in the hepatic uptake of IgM . antigen complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2360–2365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Magilavy D. B., Harford J. B., Rifai A., Plotz P. H. Influence of antigen on immune complex behavior in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):214–224. doi: 10.1172/JCI110238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Dierich M. P. Demonstration of binding sites for IgG Fc and the third complement component (C3) on isolated hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):639–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Schaefer H. E., Hess G., Meyer Zum Büschenfelde K. H. In vivo uptake of immune complexes by parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells in mice. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):250–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Lentz H., van Es L. A. Isolation of stable aggregates of IgG by zonal ultracentrifugation in sucrose gradients containing albumin. Immunol Commun. 1979;8(3):337–345. doi: 10.3109/08820137909050047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. C., Bricker M. D., Cooper S. M. Fc receptors of mouse cell lines. II. IgG binding specificity and identification of the Fc receptor on a lymphoid leukemia. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1825–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G. The binding of soluble immune complexes of guinea pig IgG2 to homologous peritoneal macrophages. Determination of the avidity constants at 4 degrees C. Eur J Immunol. 1980 May;10(5):317–322. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magilavy D. B., Rifai A., Plotz P. H. An abnormality of immune complex kinetics in murine lupus. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):770–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Bhan A. K., Collins A. B., McCluskey R. T. Effect of circulating immune complexes on Fc and C3 receptors of Kupffer cells in vivo. Lab Invest. 1981 May;44(5):442–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., González E., Rivera F., Escanero J. F., Egido J. Hepatic and kidney uptake of soluble monomeric and polymeric IgA aggregates. Immunology. 1984 May;52(1):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Rivera F., Sánchez-Crespo M., Egido J. The effect of the injection of a synthetic platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) on the fate of IgG aggregates in mice. Immunology. 1982 Dec;47(4):643–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Properties of a prolactin receptor from the rabbit mammary gland. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):301–311. doi: 10.1042/bj1400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Clarenburg R. Unique distribution of glycoprotein receptors on parenchymal and sinusoidal cells of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4457–4461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Day J. F., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. Carbohydrate-mediated clearance of immune complexes from the circulation. A role for galactose residues in the hepatic uptake of IgG-antigen complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6820–6825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Eisen H. N. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulins to Fc receptors of mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1520–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagawa K., Onoue K., Aida Y. Structural studies of Fc receptors. I. Binding properties, solubilization, and partial characterization of fc receptors of macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):366–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


