Abstract
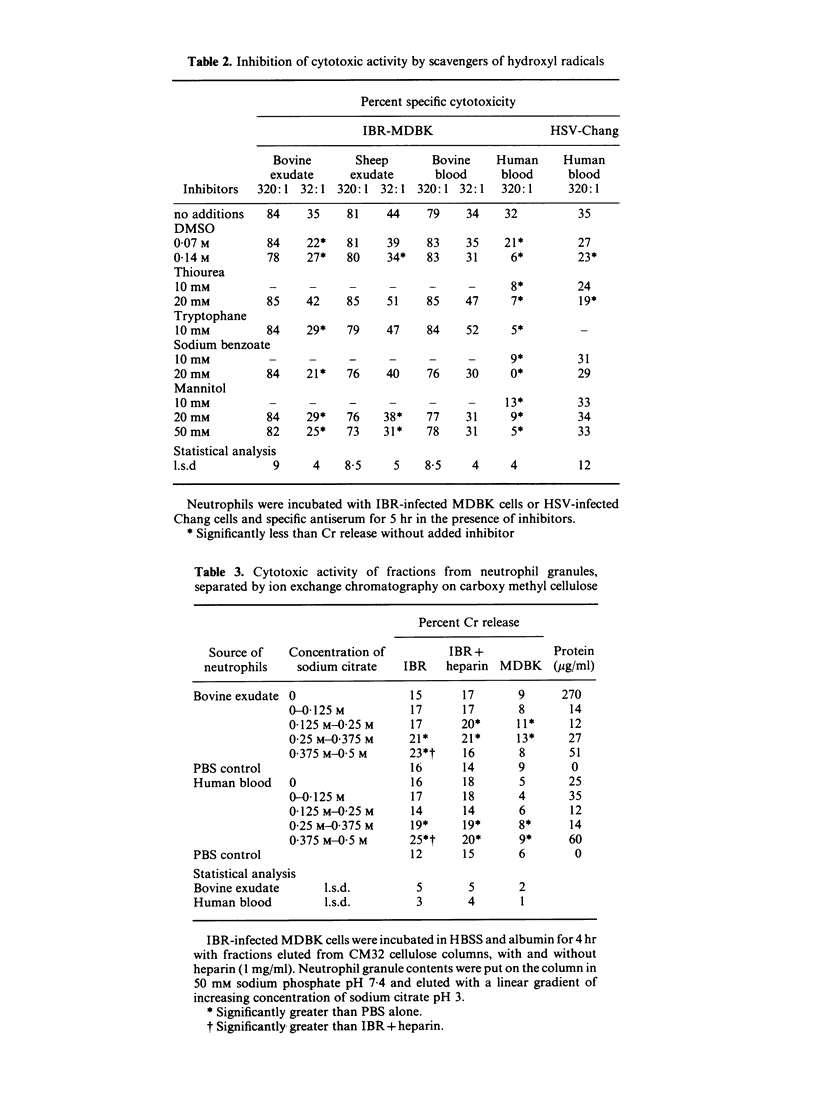
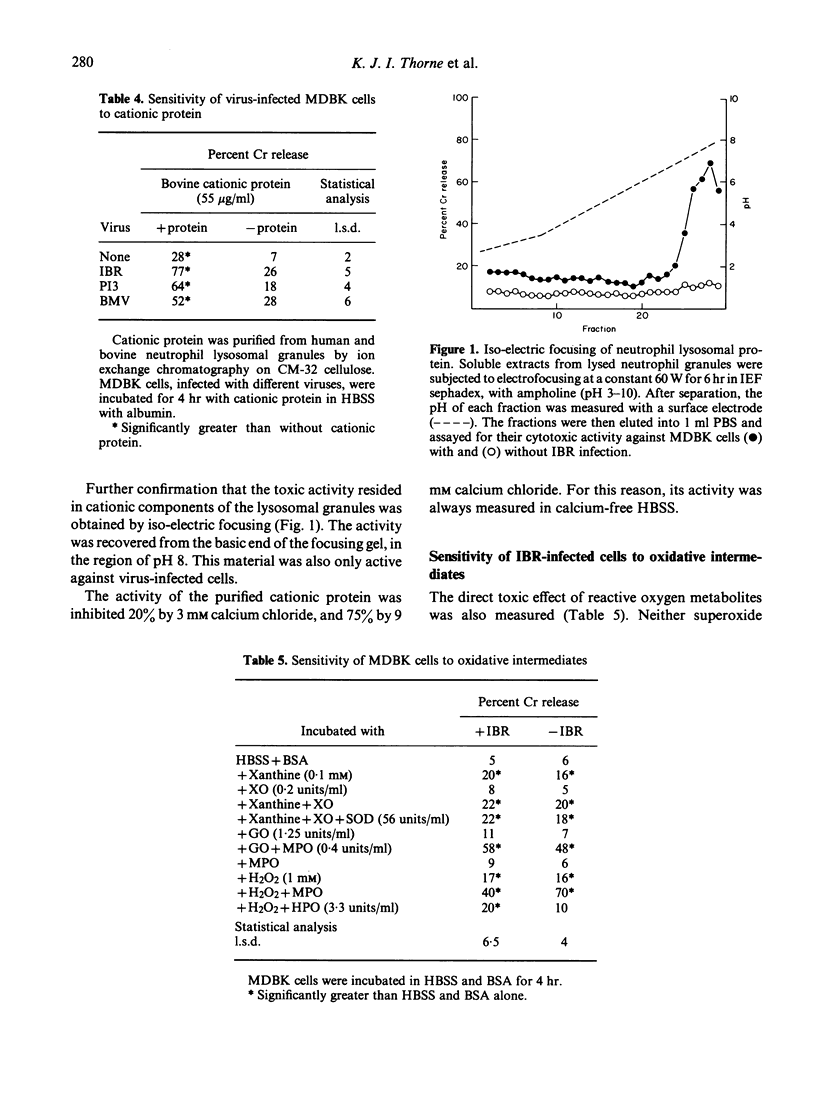
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR)-infected bovine kidney cells (MDBK) by neutrophils was demonstrated. Neutrophils from bovine and sheep mammary exudate and peripheral blood, and also from human peripheral blood, were all active in the presence of anti-IBR antibody. The component of the ruminant neutrophil granules which was responsible for cytotoxicity appeared to be cationic protein since purified cationic protein lysed the virus-infected cells and heparin inhibited cytotoxicity. Human neutrophil cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus (HSV)-infected human Chang liver cells was also inhibited by heparin. Human neutrophil cytotoxicity to IBR-infected bovine kidney cells did not appear to be mediated by cationic protein since it was inhibited by the chelators of oxidative intermediates DMSO, thiourea, tryptophane, benzoate and mannitol, and not by heparin.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L., Leung K. N., Ertl H. An analysis of effector T cell generation and function in mice exposed to influenza A or Sendai viruses. Immunol Rev. 1981;58:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Olsson I., Klebanoff S. J. Cytotoxicity for tumor cells of cationic proteins from human neutrophil granules. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):719–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R. E., Lehrer R. I. Fungicidal properties of a chymotrypsin-like cationic protein from human neutrophils: adsorption to Candida parapsilosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):382–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.382-388.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R., Benacerraf B. Induction, control and consequences of virus specific cytotoxic T cells. Immunol Rev. 1981;58:157–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimiya Y., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Human neutrophil--mediated destruction of antibody sensitized herpes simplex virus type I infected cells. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):182–186. doi: 10.1139/m78-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A. A., Steinberg S. P. Inactivation of varicella zoster virus in vitro: effect of leukocytes and specific antibody. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.507-511.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya H., Starr S. E., Arbeter A. M., Plotkin S. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against varicella-zoster virus-infected targets. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):554–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.554-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Drath D. B., Loo L. S. Murine cellular cytotoxicity to syngeneic and xenogeneic herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1231–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1231-1241.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., McKean J. R., Olsson I., Venges P., Kay A. B. Morphological studies on the killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by human eosinophil and neutrophil cationic proteins in vitro. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):359–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Shore S. L., Ades E. W., Phillips D. J. The mononuclear cell in human blood which mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to virus-infected target cells. II. Identification as a K cell. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):567–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I., Venge P. Cationic proteins of human granulocytes. IV. Esterase activity. Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;32(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Singh M., Sweeley C. C., Sung S. J., Srere P. A. The configuration and location of the ribosidic linkage in the prosthetic group of citrate lyase (Klebsiella aerogenes). J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1000–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in cows: comparison of effector cell activity against heterologous erthrocyte and herpesvirus-infected bovine target cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1433–1441. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1433-1441.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. The role of antibody dependent cytotoxicity in recovery from herpesvirus infections. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 1;22(1):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of activation of human natural killer cells against tumor and virus-infected cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:125–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-mediated destruction of virus-infected cells. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:209–260. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60045-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Free J., Franks D. Role of sulphydryl groups in T lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Dec;50(3):644–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Oliver R. C., Barrett A. J. Lysis and killing of bacteria by lysosomal proteinases. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):555–563. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.555-563.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson C., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Reversible envelope effects during and after killing of Escherichia coli w by a highly-purified rabbit polymorpho-nuclear leukocyte fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 4;436(1):154–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Arginine-rich proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. Antimicrobial specificity and biochemical heterogeneity. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):927–941. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


