Abstract
Despite improved diagnositc and therapeutic measures, neonatal septicemia continues to be a major clinical problem. Improvement in the management of the septic neonate should result from application of the increasing information being learned of the neonatal host defense mechanisms. The earlier concept that the neonate was “immunologically null” can now be discarded. Evidence summarized in this review has established that the neonate can marshal an immune response to most antigens and infectious agents.
A further major advance in recent years has been in understanding of the inflammatory response in the neonate, which includes such activities as chemotaxis, phagocytosis and bactericidal killing of ingested bacteria by phagocytes.
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTEMEIER W. A., SMITH R. T. IMMUNOLOGIC ASPECTS OF RESISTANCE IN EARLY LIFE. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1965 Aug;12:663–686. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31739-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMER J., OTT E., IBBOTT F. A., O'BRIEN D., KEMPE C. H. The effect of monthly gamma-globulin administration on morbidity and mortality from infection in premature infants during the first year of life. Pediatrics. 1963 Jul;32:4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDREWS B. F., THOMPSON J. W. Materno-fetal transfusion: a common phenomenon? Pediatrics. 1962 Mar;29:500–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman B. D., Taylor W. F., O'Loughlin B. J. Serum immunoglobulin levels in postmature infants. Pediatrics. 1969 Jun;43(6):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adinolfi M. Anti-I antibody in normal human newborn infants. Immunology. 1965 Jul;9(1):43–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adinolfi M., Gardner B. Synthesis of beta-1E and beta-1C components of complement in human foetuses. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Sep;56(5):450–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford C. A., Jr Studies on antibody in congenital rubella infections. I. Physicochemical and immunologic investigations of rubella neutralizing antibody. Am J Dis Child. 1965 Oct;110(4):455–463. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1965.02090030475019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford C. A., Schaefer J., Blankenship W. J., Straumfjord J. V., Cassady G. A correlative immunologic, microbiologic and clinical approach to the diagnosis of acute and chronic infections in newborn infants. N Engl J Med. 1967 Aug 31;277(9):437–449. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196708312770901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allansmith M., McClellan B. H., Butterworth M., Maloney J. R. The development of immunoglobulin levels in man. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):276–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGES R. A., CONDIE R. M., ZAK S. J., GOOD R. A. The morphologic basis of antibody formation development during the neonatal period. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Mar;53(3):331–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER N. R., BARR M., GLENNY A. T. Immunization of young babies against diphtheria. Br Med J. 1954 Feb 27;1(4860):476–481. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4860.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P. C., Vaughan J. H., Greendyke R. M. Immunoglobulin levels in sudden unexpected deaths of infants. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):689–692. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Orgel H. A., Hamburger R. N. IgE levels in normal infants and mothers and an inheritance hypothesis. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):794–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T. Immunoglobulin levels in infants with low birth weights. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1968 Sep;57(5):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1968.tb07307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T. The immunoglobulin development during the first year of life. A longitudinal study. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1969 May;58(3):229–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1969.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman A. B., Ray C. G., Pomeroy M. A., Wahl P. W., Beckwith J. B. Studies of the sudden infant death syndrome in King County, Washington. 3. Epidemiology. Pediatrics. 1972 Jun;49(6):860–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship W. J., Cassady G., Schaefer J., Straumfjord J. V., Alford C. A., Jr Serum gamma-M globulin responses in acute neonatal infections and their diagnostic significance. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1271–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
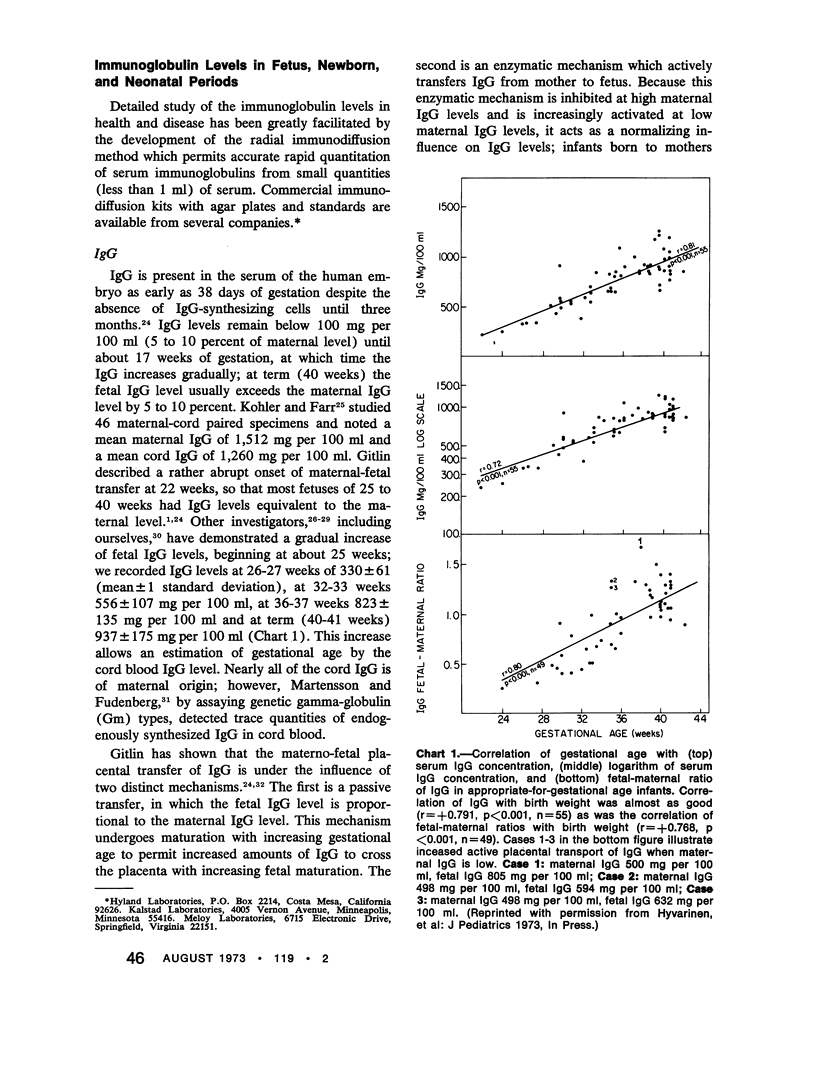
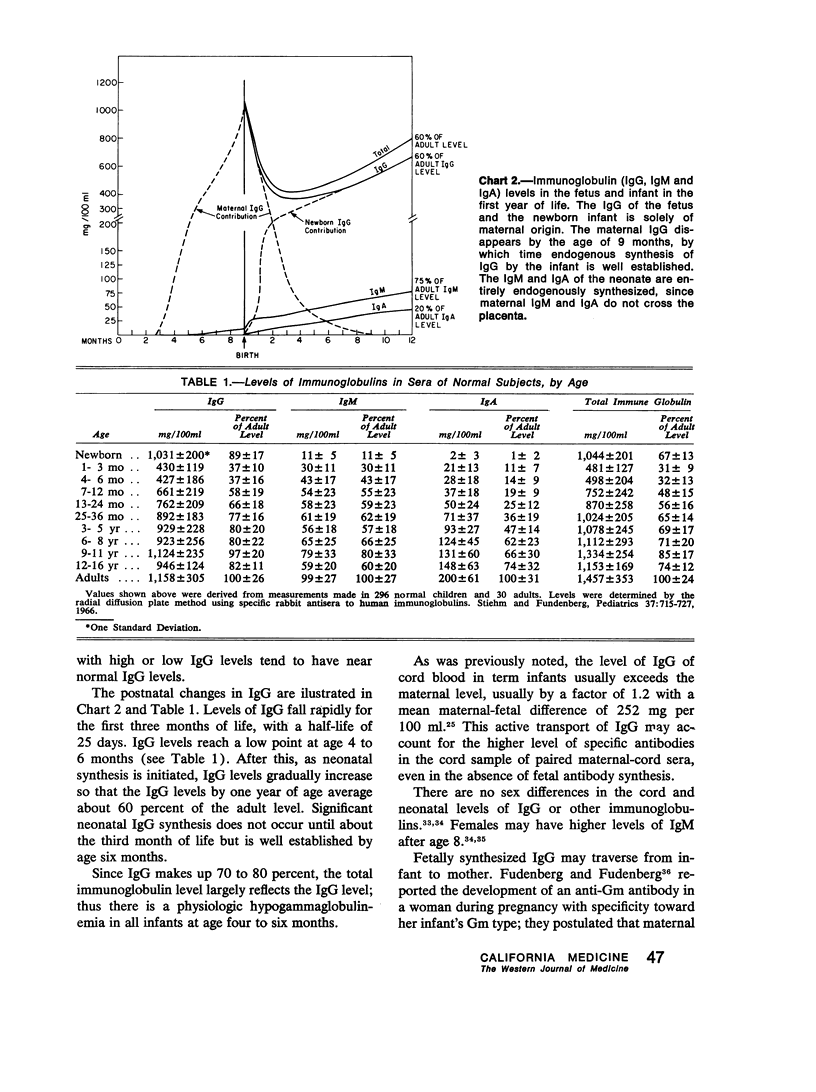
- Blankenship W. J., Cassady G., Schaefer J., Straumfjord J. V., Alford C. A., Jr Serum gamma-M globulin responses in acute neonatal infections and their diagnostic significance. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1271–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasher G. W., Hartley T. F. Quantitation of IgA and IgM in umbilical cord serum of normal newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1969 May;74(5):784–788. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Younger J. B., Brumley G. W. Evaluation of serum immunoglobulin concentrations in the perinatal period by use of a standardized method of measurement. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1143–1148. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock J. D., Robertson A. F., Bodenbender J. G., Kontras S. B., Miller C. E. Inflammatory response in the neonate re-examined. Pediatrics. 1969 Jul;44(1):58–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush S. T., Swedlund H. A., Gleich G. J. Low molecular weight IgM in human sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Feb;73(2):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth M., McClellan B., Allansmith M. Influence of sex in immunoglobulin levels. Nature. 1967 Jun 17;214(5094):1224–1225. doi: 10.1038/2141224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COFFIN G. S., HOOK W. A., MUSCHEL L. H. Antibacterial substances in placentas and serums of mothers and newborn infants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jun;104:239–243. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi P., Marianelli L. Phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in premature infants. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1967 Apr;22(1):110–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen R., Grush O., Kauder E. Studies of bactericidal activity and metabolism of the leukocyte in full-term neonates. J Pediatr. 1969 Sep;75(3):400–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Norins L. C. Antibiodies of the IgG, IgM, and IgA classes in newborn and adult sera reactive with gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1053–1062. doi: 10.1172/JCI105795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell J. T., Connell E. B., Lidd D. Studies on the placental transfer of skin-sensitizing antibody, specific binding of a ragweed fraction, and immunoglobulins. J Allergy. 1967 Jan;39(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(67)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANCIS J., OSBORN J. J., KUNZ H. W. Studies of the immunology of the newborn infant. IV. Antibody formation in the premature infant. Pediatrics. 1953 Aug;12(2):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P. B., Finkel A., Iturzaeta N., Gent M., Bienenstock J. Intrauterine infection and cord immunoglobulin M. I. Analysis of methods of assay and levels of immunoglobulin M in normal newborns. Can Med Assoc J. 1972 Apr 22;106(8):889–893. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnell G. N., Ng W. G., Hodgman J. E., Bergren W. R. Galactose metabolism in the newborn infant. Pediatrics. 1967 Jun;39(6):829–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dossett J. H., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Studies on interaction of bacteria, serum factors and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in mothers and newborns. Pediatrics. 1969 Jul;44(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EITZMAN D. V., SMITH R. T. The nonspecific inflammatory cycle in the neonatal infant. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 Mar;97(3):326–334. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010328011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. G., SMITH J. W. RESPONSE OF THE YOUNG INFANT TO ACTIVE IMMUNIZATION. Br Med Bull. 1963 Sep;19:225–229. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EWALD R. A., WILLIAMS J. H., BOWDEN D. H. Serum complement in the newborn. An investigation of complement activity in normal infants and in Rh and AB hemolytic disease. Vox Sang. 1961 May;6:312–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1961.tb03168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V., Fong S. W., Tan M. Naturally-occurring macroglobulin antibody of foetal origin in the normal human newborn. Immunology. 1966 Mar;10(3):259–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. E., Akpata S. O., Glass L. Serum immunoglobulin levels in premature and full-term infants. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;56(3):416–418. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHEL C. W., PEARLMAN D. S. Complement components of paired mother-cord sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:695–699. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H., FUDENBERG B. R. ANTIBODY TO HEREDITARY HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULIN (GM) FACTOR RESULTING FROM MATERNAL-FETAL INCOMPATIBILITY. Science. 1964 Jul 10;145(3628):170–171. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3628.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H. GM GENES AND GAMMA-G-GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN FETUS. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fireman P., Zuchowski D. A., Taylor P. M. Development of human complement system. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman M. L., Stiehm E. R. Impaired opsonic activity but normal phagocytosis in low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 23;281(17):926–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910232811704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg H. H., Gold E. R., Vyas G. N., Mackenzie M. R. Human antibodies to human IgA globulins. Immunochemistry. 1968 Mar;5(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V. A., Sieber O. F., Jr, Claman H. N., Merrill D. Serum immunoglobulin measurement during the first year of life and in immunoglobulin-deficiency states. J Pediatr. 1966 May;68(5):723–730. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., KUMATE J., URRUSTI J., MORALES C. THE SELECTIVITY OF THE HUMAN PLACENTA IN THE TRANSFER OF PLASMA PROTEINS FROM MOTHER TO FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1938–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI105068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., ROSEN F. S., MICHAEL J. G. Transient 19S gammaglobulin deficiency in the newborn infant, and its significance. Pediatrics. 1963 Feb;31:197–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLUCK L., SILVERMAN W. A. Phagocytosis in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1957 Dec;20(6):951–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Biasucci A. Development of gamma G, gamma A, gamma M, beta IC-beta IA, C 1 esterase inhibitor, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, hemopexin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, alpha 1-antitrypsin, orosomucoid, beta-lipoprotein, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and prealbumin in the human conceptus. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1433–1446. doi: 10.1172/JCI106109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoff S. P., Gadzala C., Ying R. L., Wendell P. W. Relationship of neonatal IgM values to congenital abnormalities and mental retardation. J Pediatr. 1971 Jun;78(6):1020–1025. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusdon J. P., Jr, Pritchard D. Immunoglobulin D in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Mar 15;112(6):867–867. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODES H. L. Should the premature infant receive gamma-globulin? Pediatrics. 1963 Jul;32:1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: laboratory methods of detection. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1179–1185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Mellits E. D., Gilkeson M. R., Sever J. L. Serum immunoglobulin levels in newborn infants. 3. Some preliminary observations from a survey of cord blood levels in 2,600 infants. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1211–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Mellits E. D., Gilkeson M. R., Sever J. L. Serum immunoglobulin levels in newborn infants. 3. Some preliminary observations from a survey of cord blood levels in 2,600 infants. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1211–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth J. C., Dilling L. Concentration of gamma-A-globulin in serum, saliva, and nasopharyngeal secretions of infants and children. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jun;67(6):922–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Davis J. A. Serum gamma-G-globulin levels and gestational age in premature babies. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):757–759. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Hughes M. I., Walker W. Immunoglobulin levels in infants after intrauterine transfusion. Lancet. 1968 Jun 29;1(7557):1400–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91977-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland N. H., Holland P. Immunological maturation in an infant of an agammaglobulinaemic mother. Lancet. 1966 Nov 26;2(7474):1152–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Fatal granulomatous disease of childhood. An inborn abnormality of phagocytic function. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1225–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakata S., Rhodes A. J., Labzoffsky N. A. The significance of specific IgM antibody in the diagnosis of rubella employing the immunofluorescence technique. Can Med Assoc J. 1972 Feb 19;106(4):327–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G. Serum IgND levels in healthy children and adults. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(1):1–8. doi: 10.1159/000230089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH F., SCHULTZE H. E., SCHWICK G. Komplementfaktoren und Properdin beim gesunden Saugling im ersten Lebensjahr. Klin Wochenschr. 1958 Jan 1;36(1):17–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01491122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W. N., Ali R. V., Werthmann M., Ross S. Immunoglobulin M determinations in neonates and infants as an adjunct to the diagnosis of infection. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1282–1286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Mendenhall H. W. Immunoglobulin D concentration in pregnant women. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):912–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW M. L., WARREN R. J., GRAY N., INGRAM V. G., ROBBINS F. C. Effect of Sabin Type 1 poliomyelitis vaccine administered by mouth to newborn infants. N Engl J Med. 1961 May 25;264:1071–1078. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196105252642102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechtig A., Mata L. J. Cord IgM levels in Latin American neonates. J Pediatr. 1971 May;78(5):909–910. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATOTH Y. Phagocytic and ameboid activities of the leukocytes in the newborn infant. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):748–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., ROSEN F. S. ASSOCIATION OF "NATURAL" ANTIBODIES TO GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA WITH THE GAMMA-1-MACROGLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:619–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Eichenwald H. F. Leukocyte function and the development of opsonic and complement activity in the neonate. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Feb;121(2):120–126. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02100130074008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Hardy J. B., Chen T. C., Hoffman L. S., Gilkeson M. R., Sever J. L. Serum immunoglobulin levels in newborn infants. II. Survey of cord and follow-up sera from 123 infants with congenital rubella. J Pediatr. 1969 Mar;74(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay E., Thom H., Gray D. Immunoglobulins in umbilical cord plasma. II. Congenital deformities, other abnormalities, and multiple pregnancies. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Jun;42(223):264–274. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.223.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay E., Thom H. Observations on neonatal tears. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1245–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J. Reversible agglutination of trypsinised red cells by a gamma-M-globulin synthesized by the human foetus. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(4):310–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits E. D. Relationships between cord serum immunoglobulin levels and later abnormalities. Is neonatal screening for IgM a worth-while procedure? Johns Hopkins Med J. 1971 Jun;128(6):306–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Mellman, Cohen M. M., Kohn G., Dietz W. H., Jr Depressed mmunoglobulin G in newborn infants witDown's syndrome. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):996–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Nilsson U. R. A familial deficiency of the phagocytosis-enhancing activity of serum related to a dysfunction of the fifth component of complement (C5). N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 12;282(7):354–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002122820702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E. Phagocytosis in the newborn infant: humoral and cellular factors. J Pediatr. 1969 Feb;74(2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Sunshine P. J., Remington J. S. Quantitation of cord serum IgM and IgA as a screening procedure to detect congenital infection: results in 5,006 infants. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1287–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K. Phagocytic activity of leucocytes in premature infants. I. Comparison of the phagocytic activity of leucocytes between premature infants and full-term infants. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1965 Mar;14(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Hitzig W. H., Barandun S. IgG subclasses: development of the serum concentrations in "normal" infants and children. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):960–964. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E., Kleemola M. Human IgG subclasses in maternal and fetal serum. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN J. J., DANCIS J., JULIA J. F. Studies of the immunology of the newborn infant. I. Age and antibody production. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS F. T., YETTS R., GAISFORD W. Response of infants to a third dose of poliomyelitis vaccine given 10 to 12 months after primary immunization. Br Med J. 1959 Mar 14;1(5123):680–682. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5123.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS F. T., YETTS R., GAISFORD W. Serological response of infants to poliomyelitis vaccine. Br Med J. 1958 Jul 12;2(5088):68–71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5088.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou P., Papadatos C., Papaevangelou G., Alexiou D., Skardoutsou A., Kourea E. Immunoglobulin A and M levels in premature infants with gastroenteritis. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Oct;46(249):671–675. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.249.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadatos C., Papaevangelou G. J., Alexiou D., Mendris J. Serum immunoglobulin G levels in small-for-dates newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):570–572. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Holmes B., Good R. A. Metabolic activities in leukocytes of newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1970 Feb;76(2):237–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchalski J. E., Clem L. W., Small P. A., Jr 7S gamma-M immunoglobulins in normal human cord serum. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Aug;256(2):107–111. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196808000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propp R. P., Alper C. A. C'3 synthesis in the human fetus and lack of transplacental passage. Science. 1968 Nov 8;162(3854):672–673. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3854.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provenzano R. W., Wetterlow L. H., Sullivan C. L. Immunization and antibody response in the newborn infant. I. Pertussis inoculation within twenty-four hours of birth. N Engl J Med. 1965 Oct 28;273(18):959–965. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196510282731804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBUCK J. W., CROWLEY J. H. A method of studying leukocytic functions in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):757–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Schafer I. A. Transport piece in the urines of premature infants. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):364–365. doi: 10.1038/217364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S. The present status of the IgM fluorescent antibody technique in the diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1116–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M. Immunoglobulin and specific antibody synthesis during the first weeks of life of premature infants. J Pediatr. 1969 Sep;75(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Gigli I., Austen K. F. The complement system of man. 4. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 28;287(13):642–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209282871306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON W. H., CALDWELL J. B. The mononuclear cell phase of inflammation in the newborn. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1963 May;112:258–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T., EITZMAN D. V. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE RESPONSE OF THE HUMAN INFANT AND ADULT TO IMMUNIZATION WITH SALMONELLA VACCINES. Pediatrics. 1964 Feb;33:163–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever J. L., Hardy J. B., Korones S. B., Gilkeson M. R., Corridon L., Ley A. C., Tzan N., Yarnick D. Cord immunoglobulins in a middle class Caucasian population. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1224–1230. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Hayes K., Dudgeon J. A. The immunoglobulins in congenital rubella. Lancet. 1966 Jun 25;1(7452):1385–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- South M. A., Copper M. D., Wollheim F. A., Good R. A. The IgA system. II. The clinical significance of IgA deficiency: studies in patients with agammaglobulinemia and ataxia-telangiectasia. Am J Med. 1968 Feb;44(2):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D. D., Orgel H. A., Hamburger R. N., Reid R. T. Development of IgE in newborn human infants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Aug;48(2):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Ammann A. J., Cherry J. D. Elevated cord macroglobulins in the diagnosis of intrauterine infections. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 3;275(18):971–977. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611032751801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Gold E. Immune globulin levels in the sudden death syndrome. Pediatrics. 1968 Jul;42(1):61–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom H., McKay E., Gray D. W. Protein concentrations in the umbilical cord plasma of premature and mature infants. Clin Sci. 1967 Dec;33(3):433–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomaidis T., Agathopoulos A., Matsaniotis N. Natural isohemagglutinin production by the fetus. J Pediatr. 1969 Jan;74(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasi T. B., Jr Secretory immunoglobulins. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 7;287(10):500–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209072871008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes-Dapena M. A., Arey J. B. The causes of neonatal mortality: an analysis of 501 autopsies on newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1970 Sep;77(3):366–375. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A., Pettay O., Kunnas M. Congenital rubella: immune response of the neonate and diagnosis by demonstration of specific IgM antibodies. J Pediatr. 1969 Oct;75(4):658–664. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80463-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Levin A. S., Fudenberg H. H. Intrauterine isoimmunization caused by maternal IgA crossing the placenta. Nature. 1970 Jan 17;225(5229):275–276. doi: 10.1038/225275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Faulk W. P., Stuckey M. A., Fudenberg H. H. Chemical differences of adult, fetal and hypogammaglobulinemic IgG immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):703–708. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Insubstantial leukotaxis. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jun;79(6):873–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil W. B., Jr A unified guide to parenteral fluid therapy. I. Maintenance requirements and repair of dehydration. J Pediatr. 1969 Jul;75(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg J., Wessner G. Does breast milk protect against septicaemia in the newborn? Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1091–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91836-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Hobbs J. R. Serum-gamma-G-globulin levels in normal premature, post-mature, and "small-for-dates" newborn babies. Lancet. 1968 Jun 1;1(7553):1167–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91865-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The immunological development of the human fetus. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1173–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


