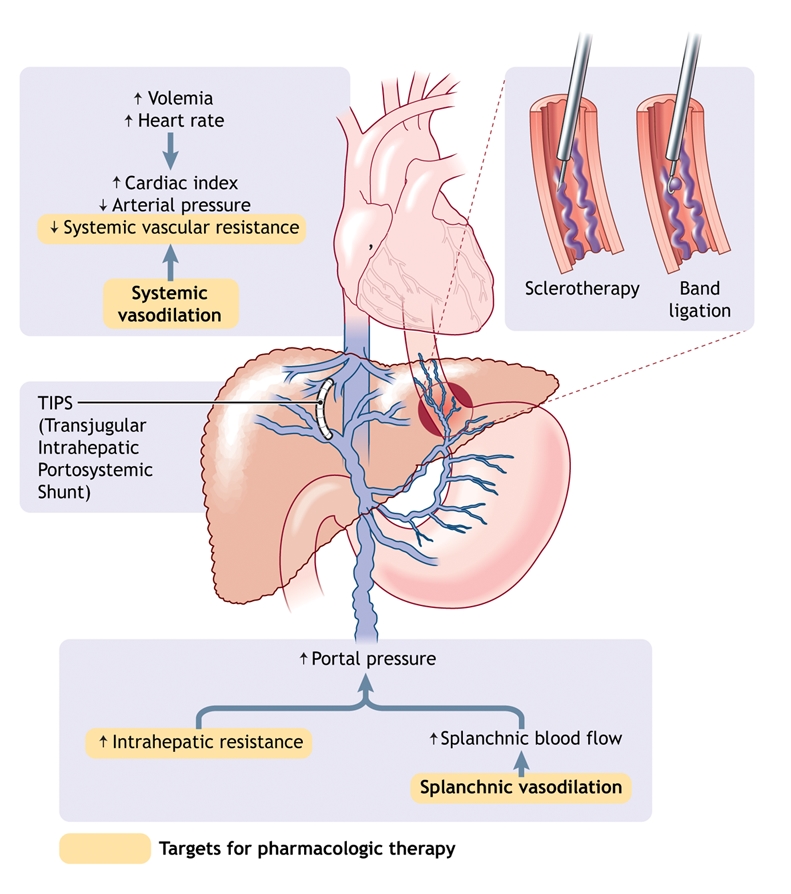
Fig. 1: Pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Portal hypertension results from increased intrahepatic vascular resistance and portal–splanchnic blood flow. In addition, cirrhosis is characterized by splanchnic and systemic arterial vasodilation. Splanchnic arterial vasodilation leads to increased portal blood flow and thus elevated portal hypertension. An increased hepatic venous pressure gradient leads to the formation of portosystemic venous collaterals. Esophagogastric varices represent the most clinically important collaterals given their associated high risk of bleeding. Treatment consists of pharmacologic therapy to decrease portal pressure, endoscopic treatment of varices (band ligation or sclerotherapy) to treat variceal bleeding, and creation of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) to reduce portal pressure if drug therapy and endoscopic treatment fail.
