Abstract
We have confirmed that K antigens influence the sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli. Resistant strains bound more polycation and by inference therefore had a higher surface negative charge than sensitive strains.
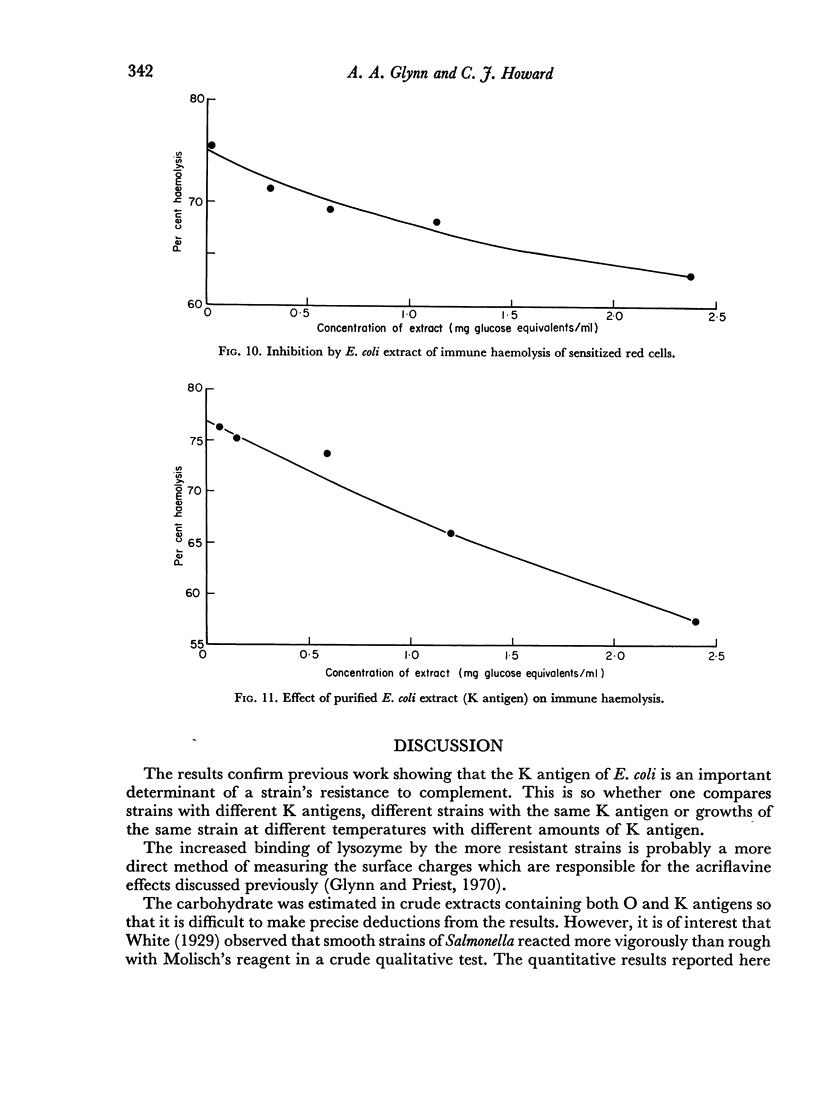
Extracts containing K antigen non-specifically inhibited red cell agglutination and this inhibitory activity was roughly proportional to complement resistance. All of five resistant strains became more sensitive to complement when grown at unusual temperatures and extracts from them then had less inhibitory activity. In four strains of serotype O6 K13 complement resistance was proportional to K antigen content measured by immunodiffusion. However, purified K antigen from a resistant strain (WF82) had much greater agglutination inhibiting activity weight for weight than purified K antigen from a sensitive strain (WF96).
In experiments with 125I-labelled haemolysin K antigens decreased the binding of both IgG and IgM antibodies and also directly reduced complement activity.
The mechanisms of action of K antigens and their relation to virulence are discussed.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi M., Glynn A. A., Lindsay M., Milne C. M. Serological properties of gamma-A antibodies to Escherichia coli present in human colostrum. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):517–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolaños R., DeWitt C. W. Isolation and characterization of the K1 (L) antigen of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):987–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.987-996.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEPPELLINI R., LANDY M. Suppression of blood group agglutinability of human erythrocytes by certain bacterial polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:321–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F. Colanic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:464–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORRILL R. H., NEEDS D. A. A simple apparatus for shaking bacterial cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jan;11(1):89–92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Priest C. M. The effect of acriflavine on complement sensitive and resistant strains of Escherichia coli and on complement resistant mutants. Immunology. 1970 Jan;18(1):19–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A. The complement lysozyme sequence in immune bacteriolysis. Immunology. 1969 Apr;16(4):463–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungerer D., Jann K., Jann B., Orskov F., Orskov I. Immunochemistry of K antigens of Escherichia coli. 4. The K antigen of E. coli O 9:K30:H12. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jul;2(1):115–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUDE A., NICOLLE P. Persistance, à l'état potentiel, de la capacité d'elaborer l'antigène Vi chez le bacille typhique cultivé en série à basse température. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1952 Apr 21;234(17):1718–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Studies on natural antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:131–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. II. Activity against Eschericha coli strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:632–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., CHAMBERLIN R. H., OSAWA E. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. I. Activity against Salmonella typhi strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):376–382. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. W., Roantree R. J. Analyses of lipopolysaccharides extracted from penicillin-resistant, serum-sensitive salmonella mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. The virulence of strains of Bacterium coli for mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Dec;35(6):528–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. T. "Complement". Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:285–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Turner K. J. Passive sensitization of Salmonella adelaide to the bactericidal action of antibody and complement. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):657–658. doi: 10.1038/217657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR C. E., WALTON K. W. The molecular characteristics determining the anticomplementary activity of dextran sulphates. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Jun;38(3):248–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




