Abstract
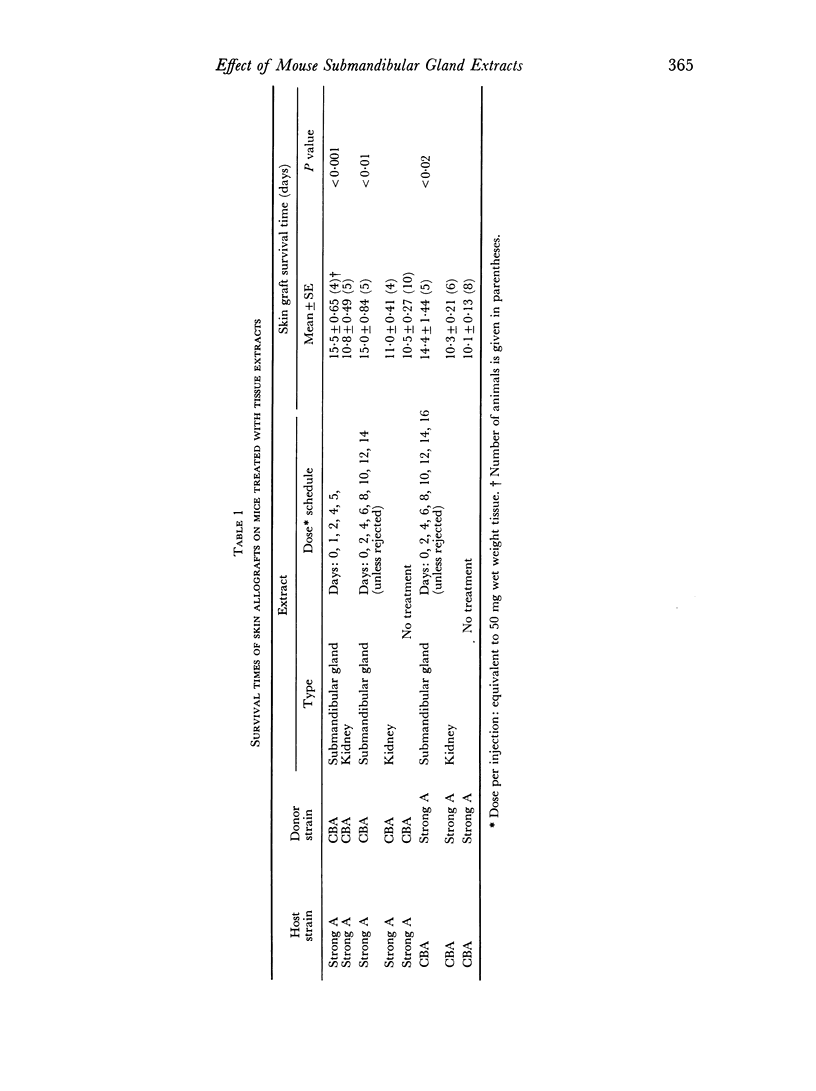
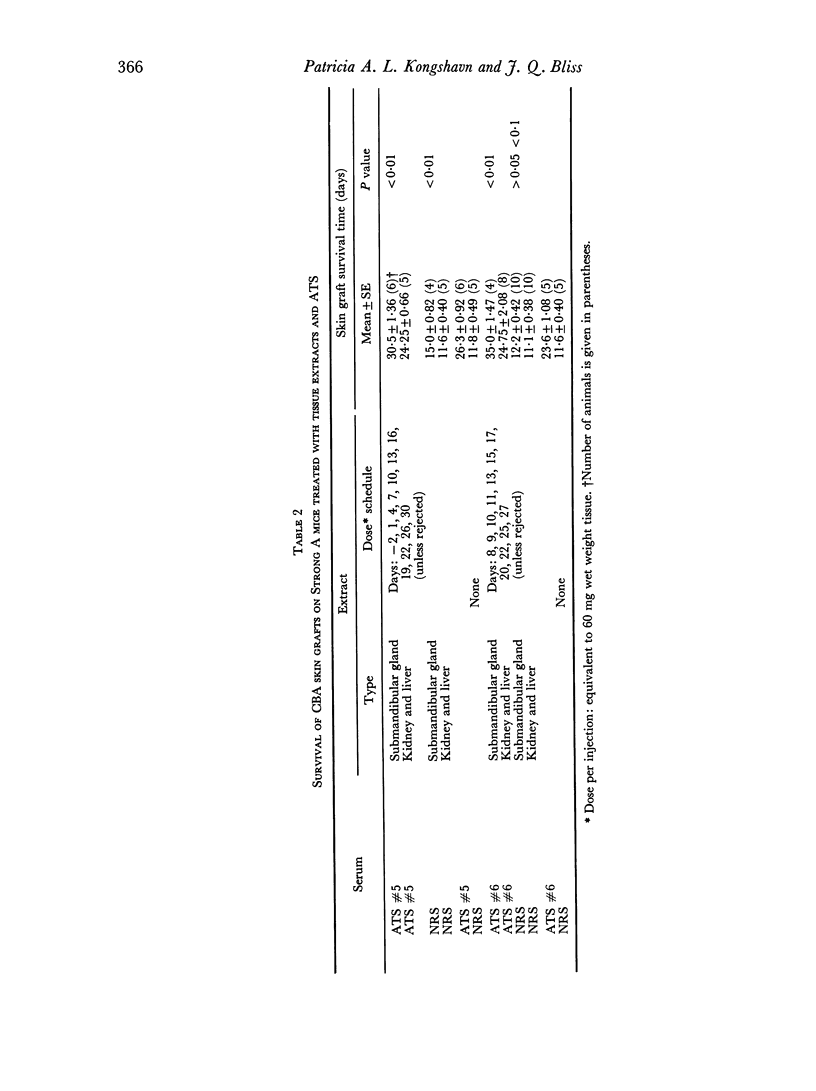
Crude saline extracts of male mouse submandibular glands prolonged graft survival time in CBA and Strong A strains of mice, both when used alone and when used in conjunction with antithymocytic serum. It is suggested that this effect is produced by a lymphoid tissue inhibitory substance found in male mouse submandibular glands.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lapp W. S., Bliss J. Q. The effects of allelic dosage and graft size on skin graft survival across a weak histocompatibility barrier. Immunology. 1967 Jan;12(1):103–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H., Medawar P. B. Nature and mode of action of antilymphocytic antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1130–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Grollman A. Inhibitory action of submaxillary gland on thymus and lymphoid tissues of the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1337–1342. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Yamasaki Y., Yamabe H., Suzuki Y., Haebara H., Irino T., Grollman A. Atrophy of the lymphoid tissues of mice induced by extracts of the submaxillary gland. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):212–216. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


