Abstract
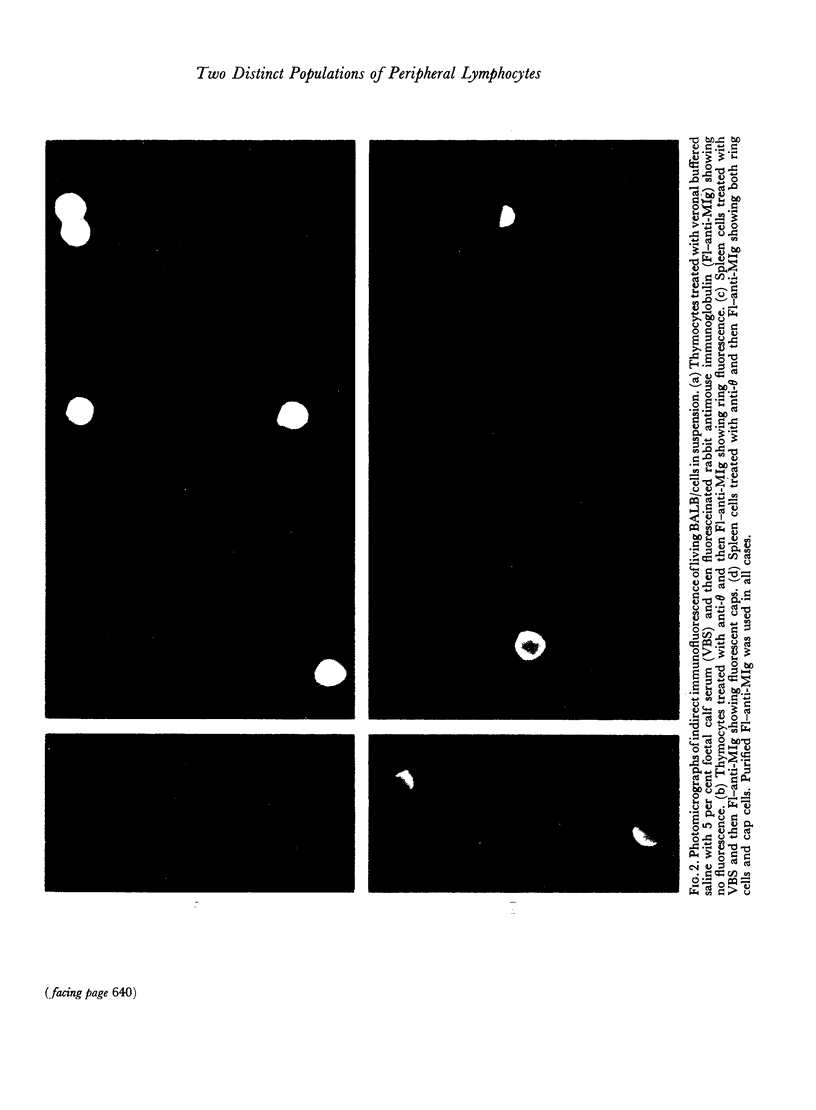
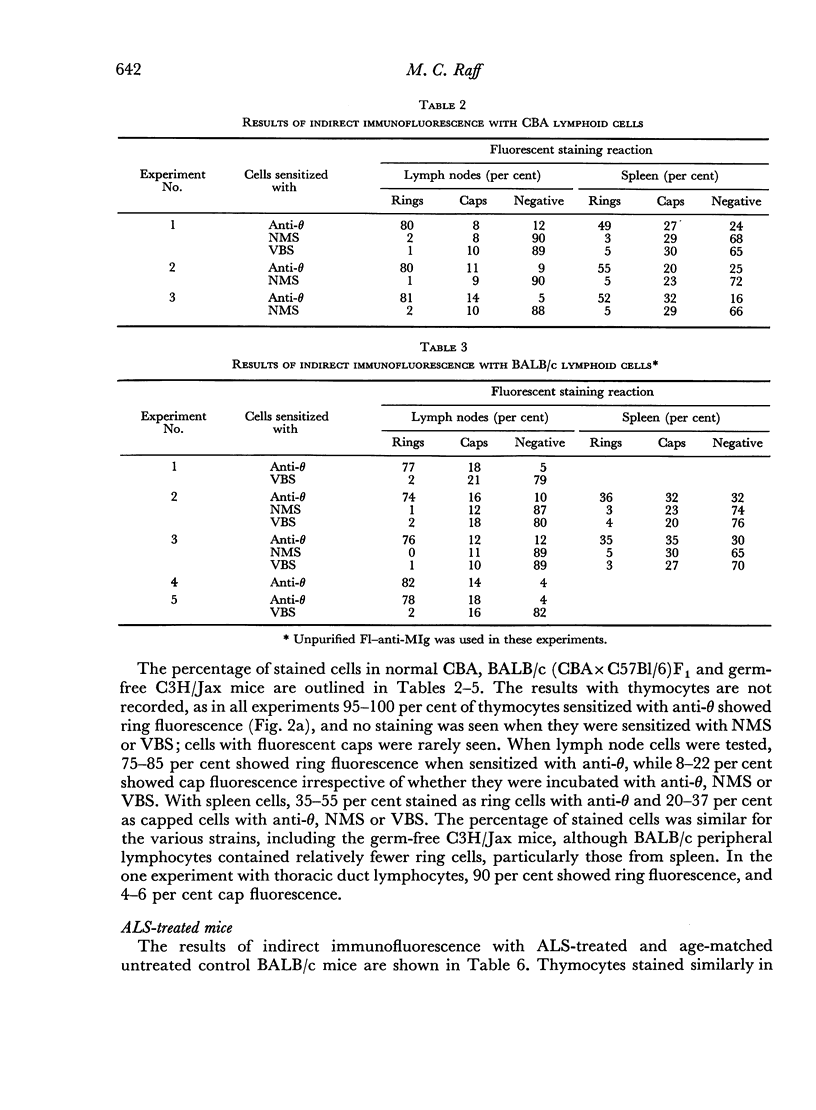
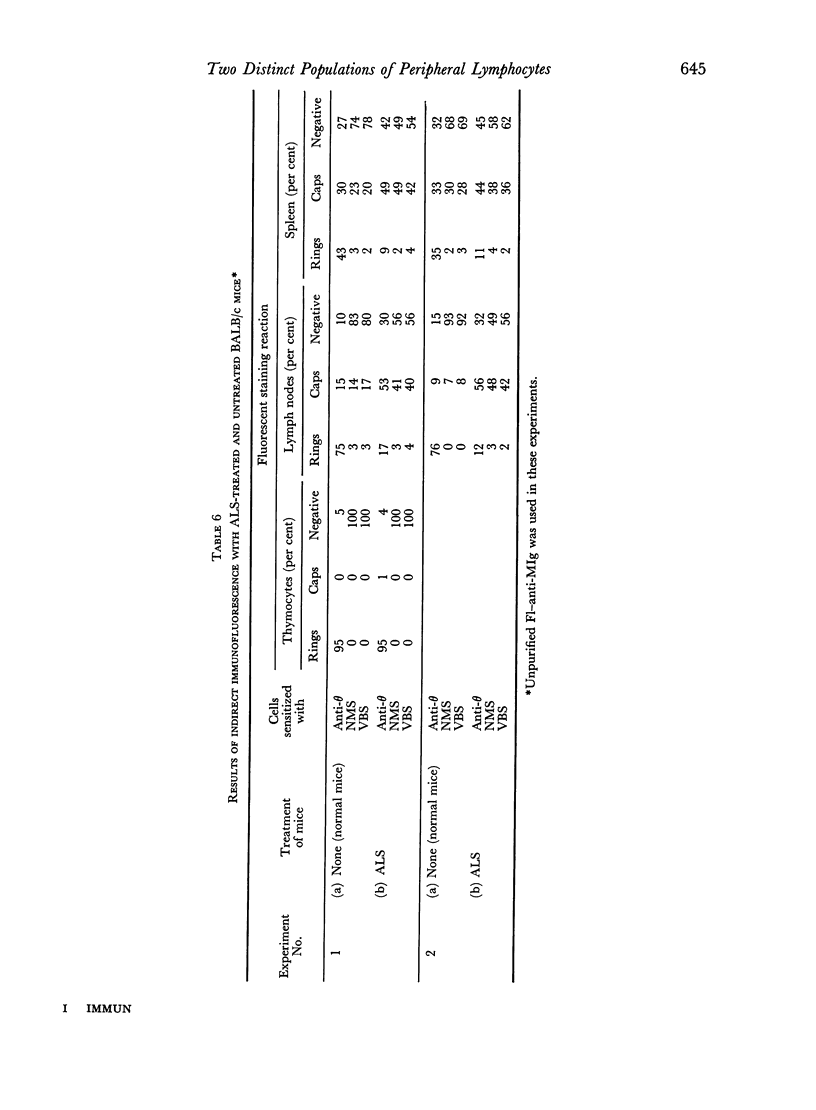
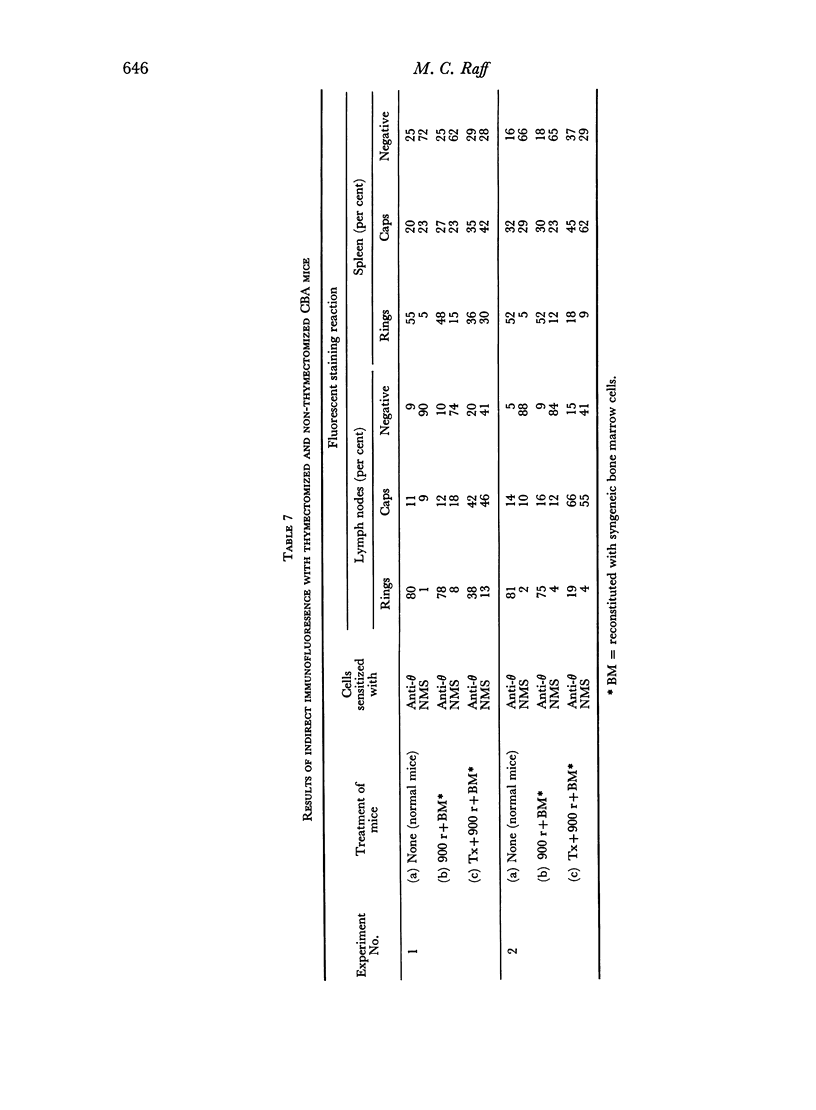
Immunofluorescent staining has been used to detect antigenic determinants on the surface of living lymphoid cells of mice. It has been possible to distinguish two distinct populations of peripheral lymphocytes: one population carries the theta isoantigen and is thymus-dependent; the other has naturally-occurring immunoglobulin determinants on the cell surface and appears to be thymus-independent. The relative proportions of these two populations of cells is characteristic for each type of lymphoid tissue and these proportions have been determined for thymus, lymph node, spleen, and thoracic duct cells.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A. A study on globulin formation by plasma-cell neoplasm (5563) transplantable in mice. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:33–43. doi: 10.1042/bj0790033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm G. V., Peterson R. D. Antibody and immunoglobulin production at the cellular level in bursectomized-irradiated chickens. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1247–1259. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOAK J. L., WOODRUFF M. F. A MODIFIED TECHNIQUE FOR COLLECTING MOUSE THORACIC DUCT LYMPH. Nature. 1965 Jan 23;205:396–397. doi: 10.1038/205396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Miyazawa M., Aoki T., Old L. J. Ly-A and Ly-B: two systems of lymphocyte isoantigens in the mouse. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):175–193. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F., SHEPARD C. C. A DIALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR PREPARING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:642–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J. The thymus and the cellular basis of immunity. Transplant Rev. 1969;1:43–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1969.tb00136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doré C. F., Balfour B. M. A device for preparing cell spreads. Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):403–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. Blocking of the lymphocyte receptor site for cell mediated hypersensitivity and transplantation reactions by anti-light chain sera. Nature. 1969 May 31;222(5196):885–886. doi: 10.1038/222885a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N., MANN S. O. The isolation of glycerol-fermenting and lipolytic bacteria from the rumen of the sheep. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:227–240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi J., Marvanova H., Skamene E. Immunoglobulin synthesis and lymphocyte transformation by anti-immunoglobulin sera in bursectomized chickens. Immunology. 1969 Sep;17(3):325–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. F. Immunological function of the thymus. Lancet. 1961 Sep 30;2(7205):748–749. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland W., Heilman D. H., Moorhead J. F. Functional anatomy of the lymphocyte in immunological reactions in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):851–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Miller J. F. Cell to cell interaction in the immune response. II. The source of hemolysin-forming cells in irradiated mice given bone marrow and thymus or thoracic duct lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):821–837. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIF A. E., ALLEN J. M. THE AKR THYMIC ANTIGEN AND ITS DISTRIBUTION IN LEUKEMIAS AND NERVOUS TISSUES. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:413–433. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. Theta isoantigen as a marker of thymus-derived lymphocytes in mice. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):378–379. doi: 10.1038/224378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif A. E., Allen J. M. Mouse thymic iso-antigens. Nature. 1966 Jan 29;209(5022):521–523. doi: 10.1038/209521b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBER H. A., PETERSON E. A. Protein chromatography on ion exchange cellulose. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1116–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M., Yron I. Antigenic changes in lymph-node cells after administration of antiserum to thymus cells. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1412–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy L., Burr B. The use of affinity chromatography for the specific purification of antibodies and antigens. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):380–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




