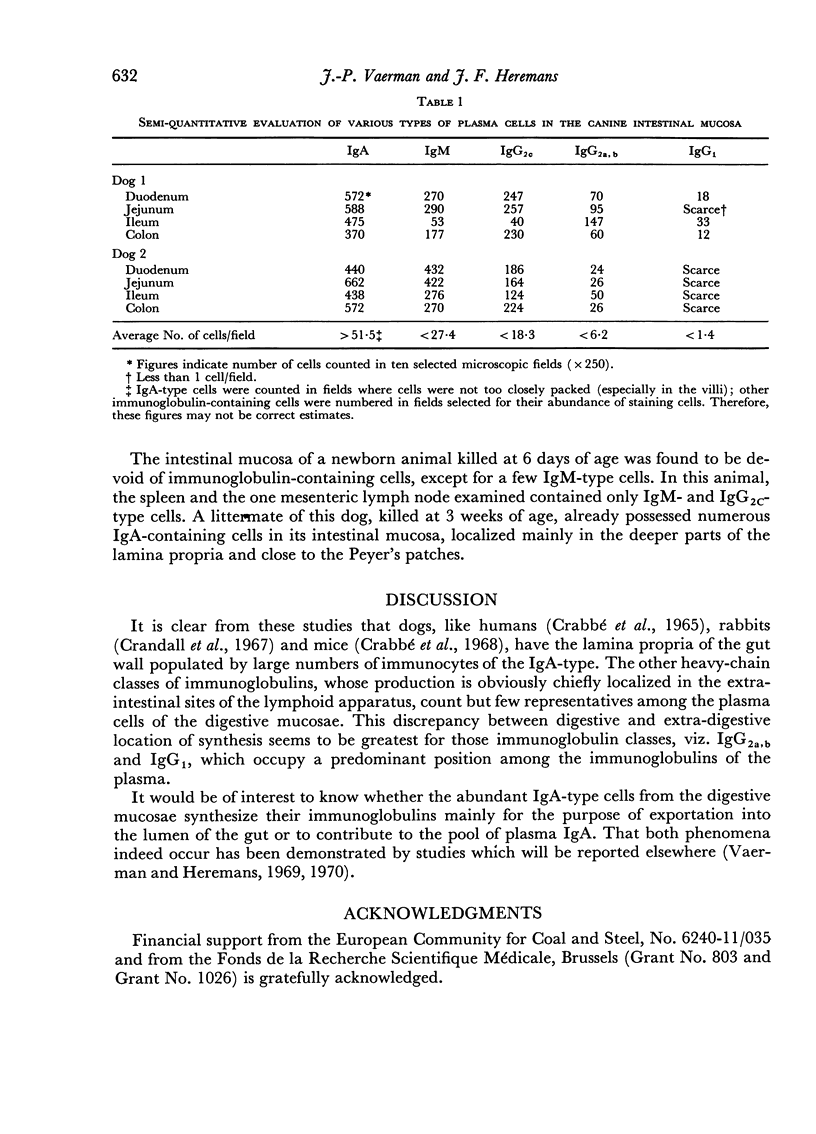
Abstract
The spleen, lymph nodes and gastro-intestinal mucosae of the dog were investigated with respect to the size and nature of their plasma cell populations. As in all other mammals so far studied, the gastro-intestinal mucosae of the dog were conspicuous by their wealth of IgA-containing plasma cells.
Full text
PDF
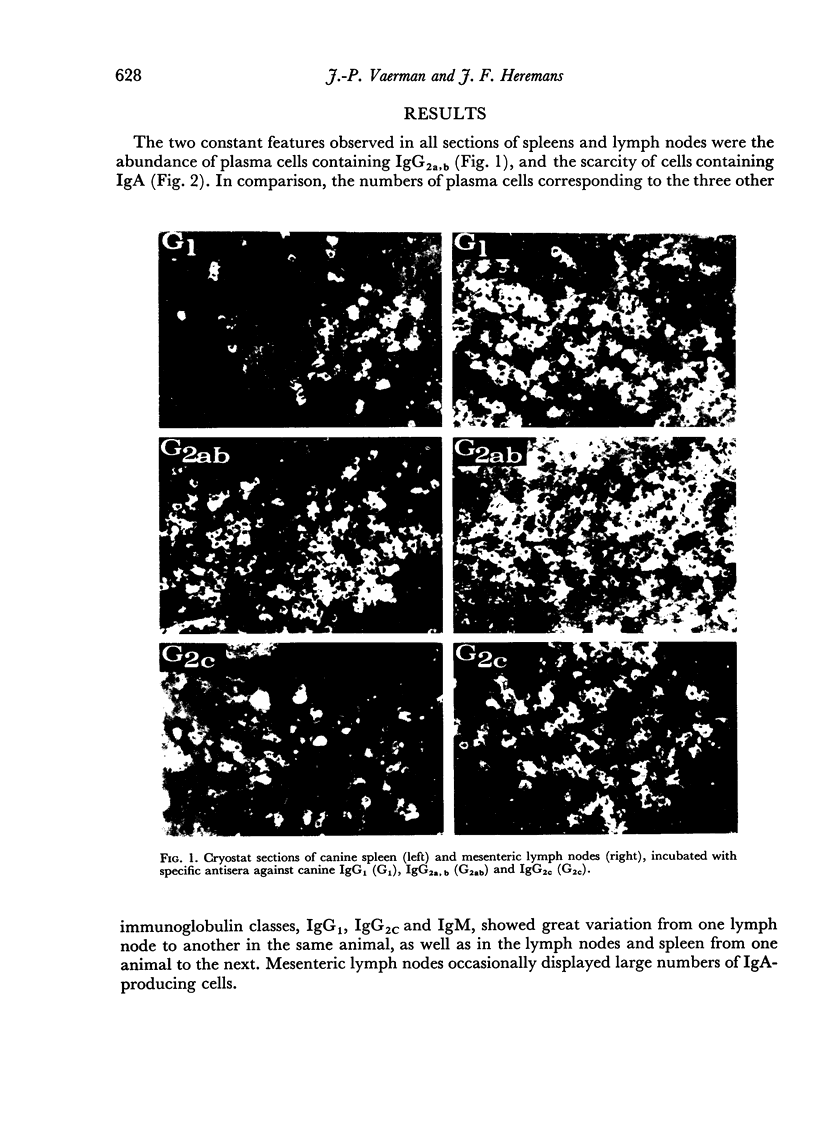
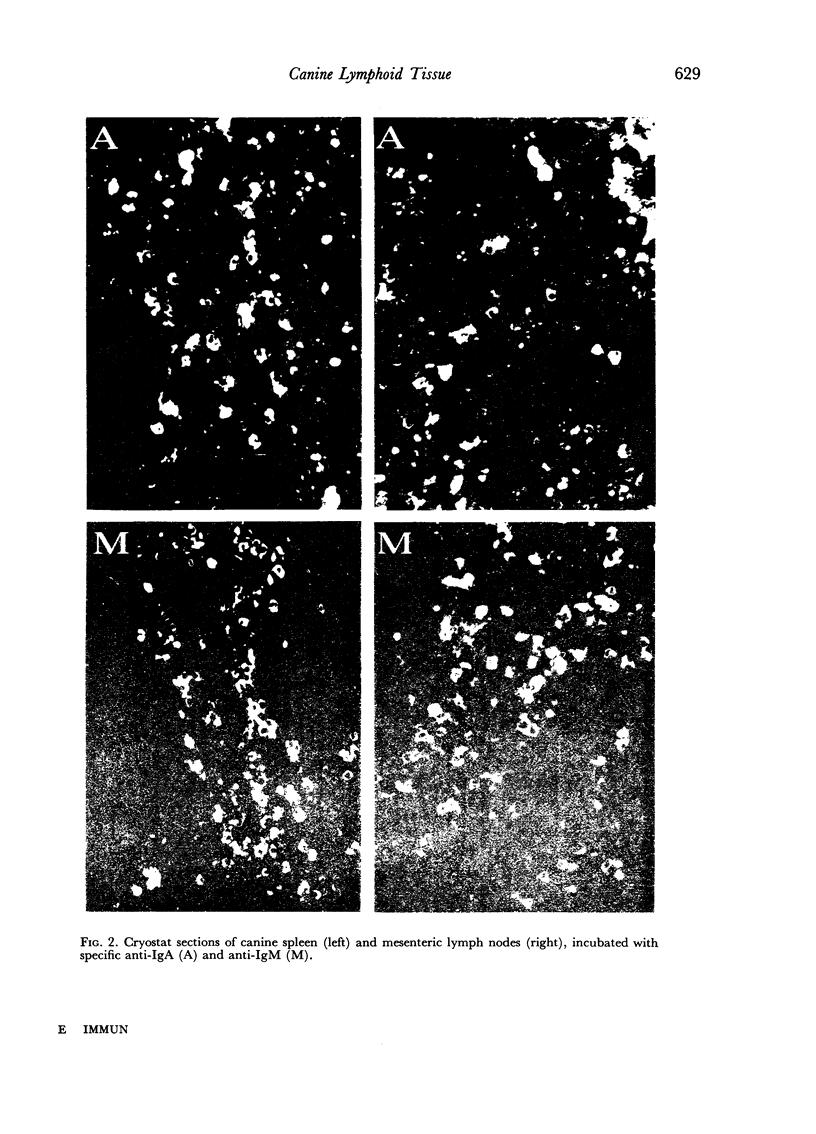
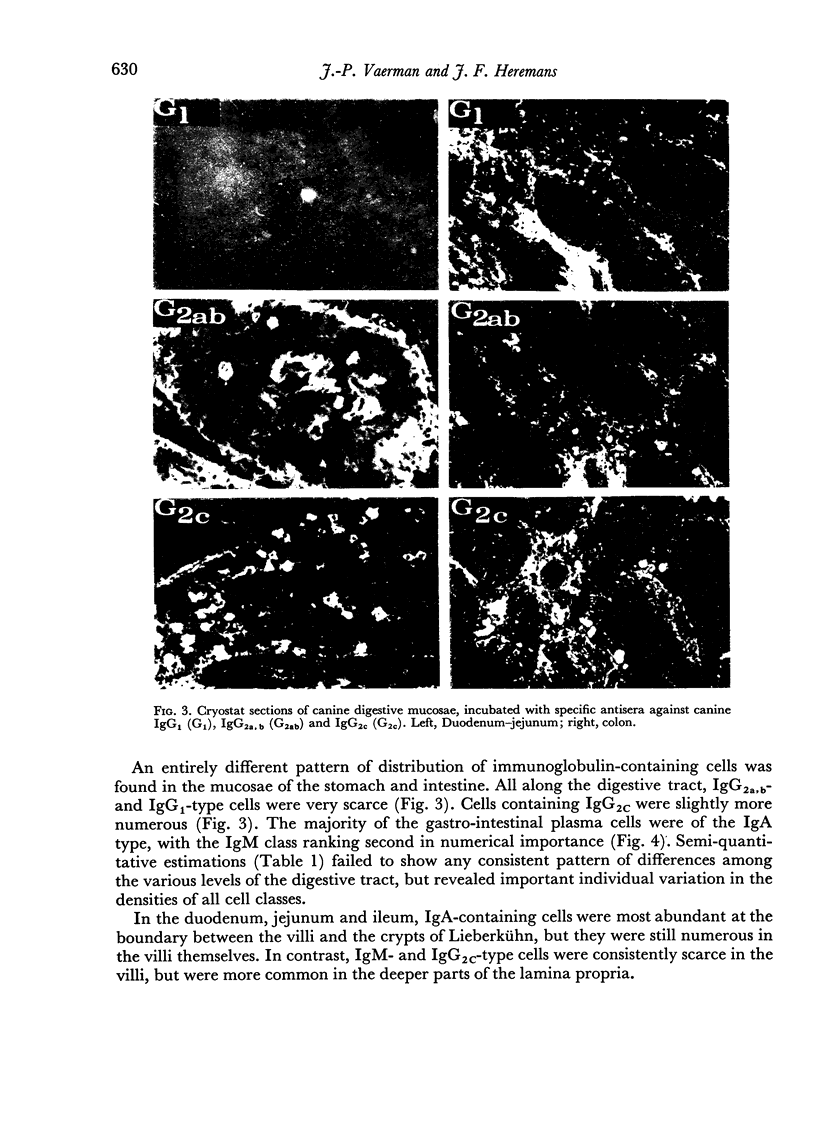
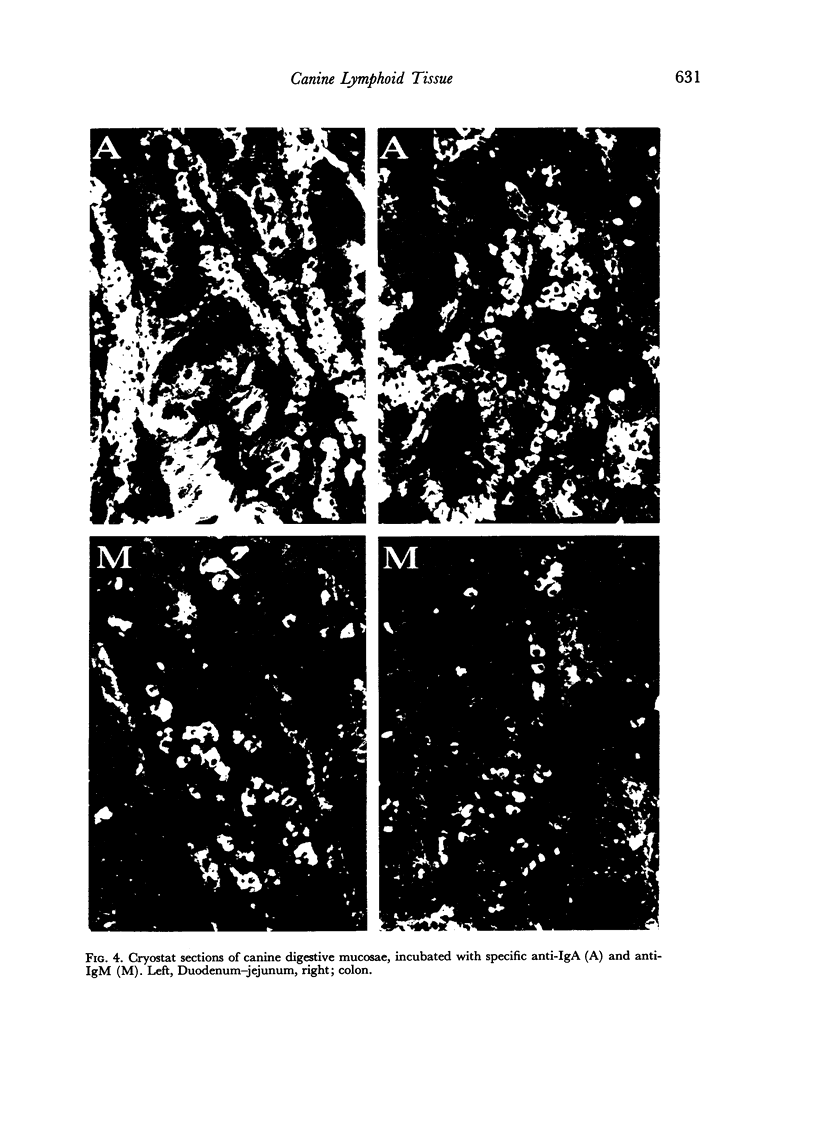

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRABBE P. A., CARBONARA A. O., HEREMANS J. F. THE NORMAL HUMAN INTESTINAL MUCOSA AS A MAJOR SOURCE OF PLASMA CELLS CONTAINING GAMMA-A-IMMUNOGLOBULIN. Lab Invest. 1965 Mar;14:235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Bazin H., Eyssen H., Heremans J. F. The normal microbial flora as a major stimulus for proliferation of plasma cells synthesizing IgA in the gut. The germ-free intestinal tract. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(4):362–375. doi: 10.1159/000230130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall R. B., Cebra J. J., Crandall C. A. The relative proportions of IgG-, IgAand IgM-containing cells in rabbit tissues during experimental trichinosis. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):147–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







