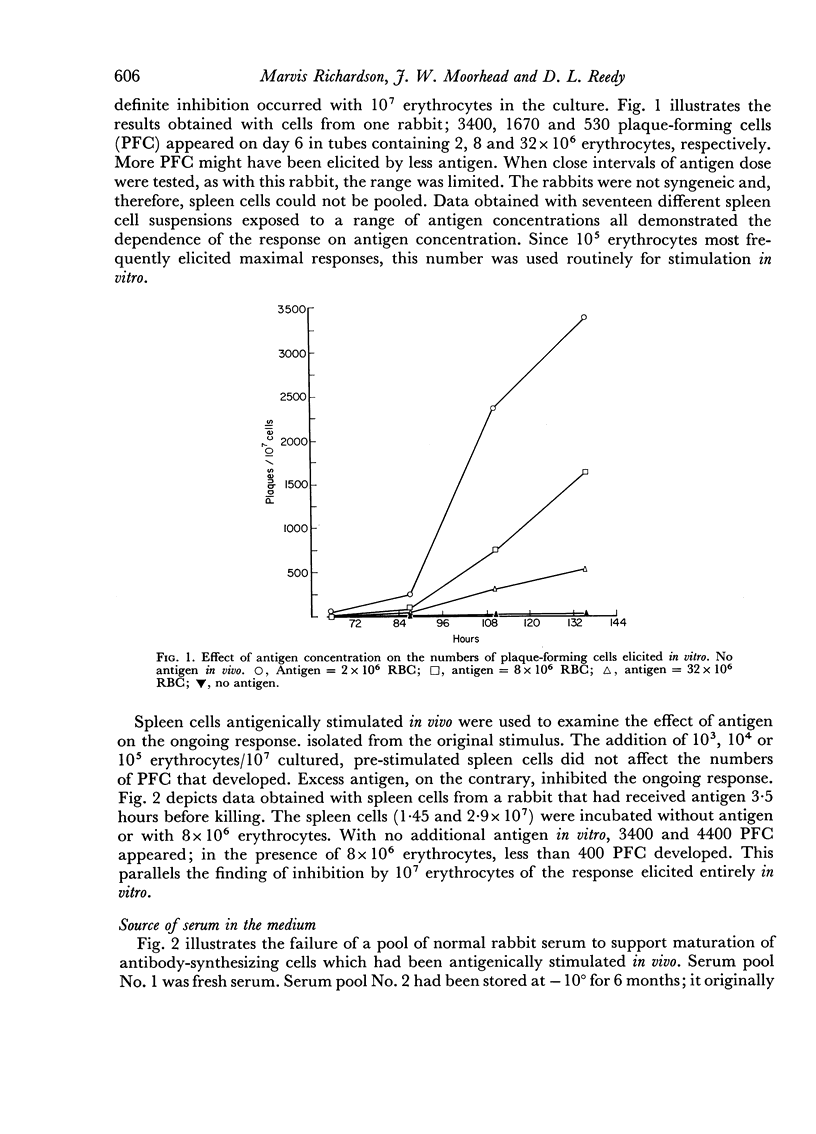
Abstract
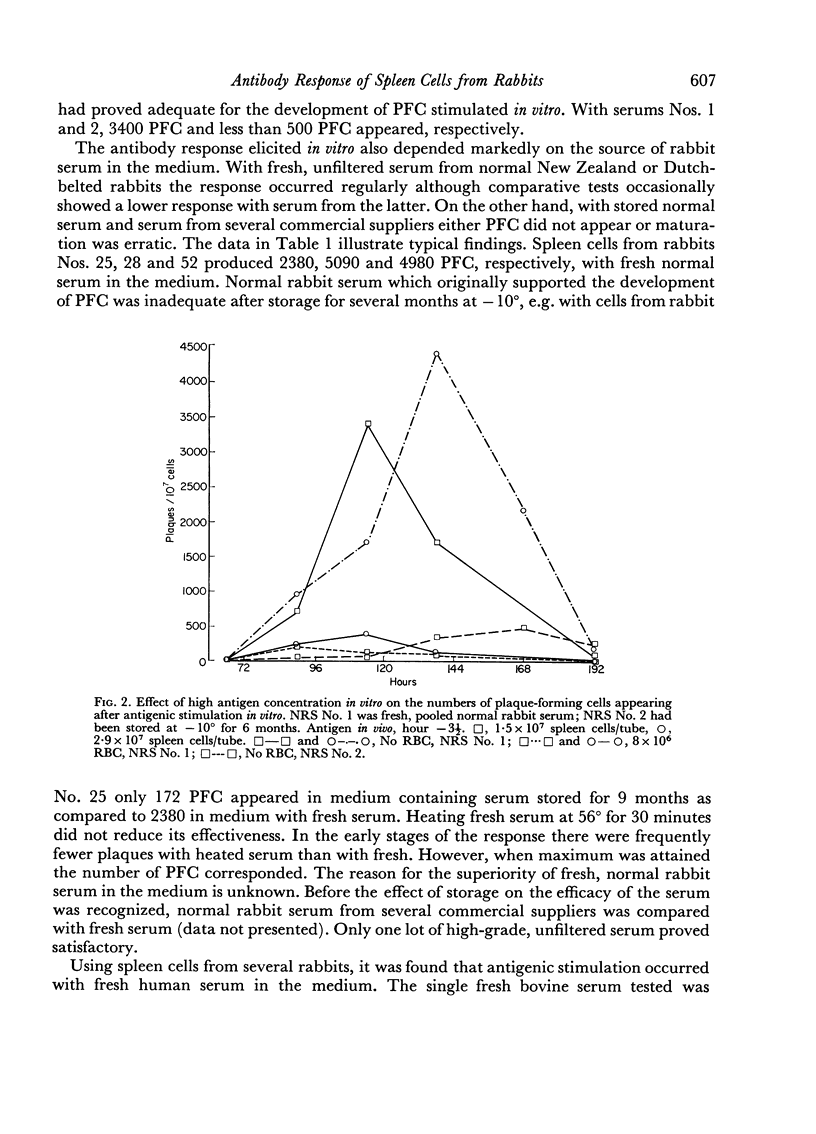
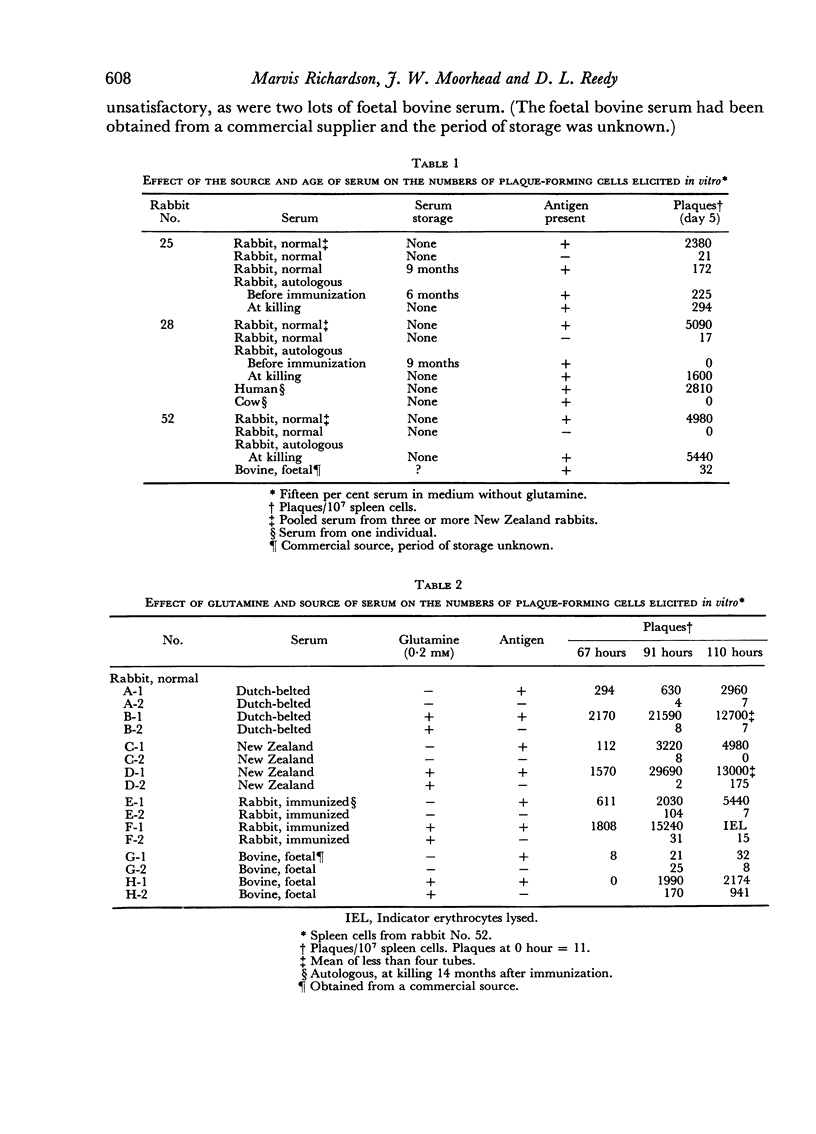
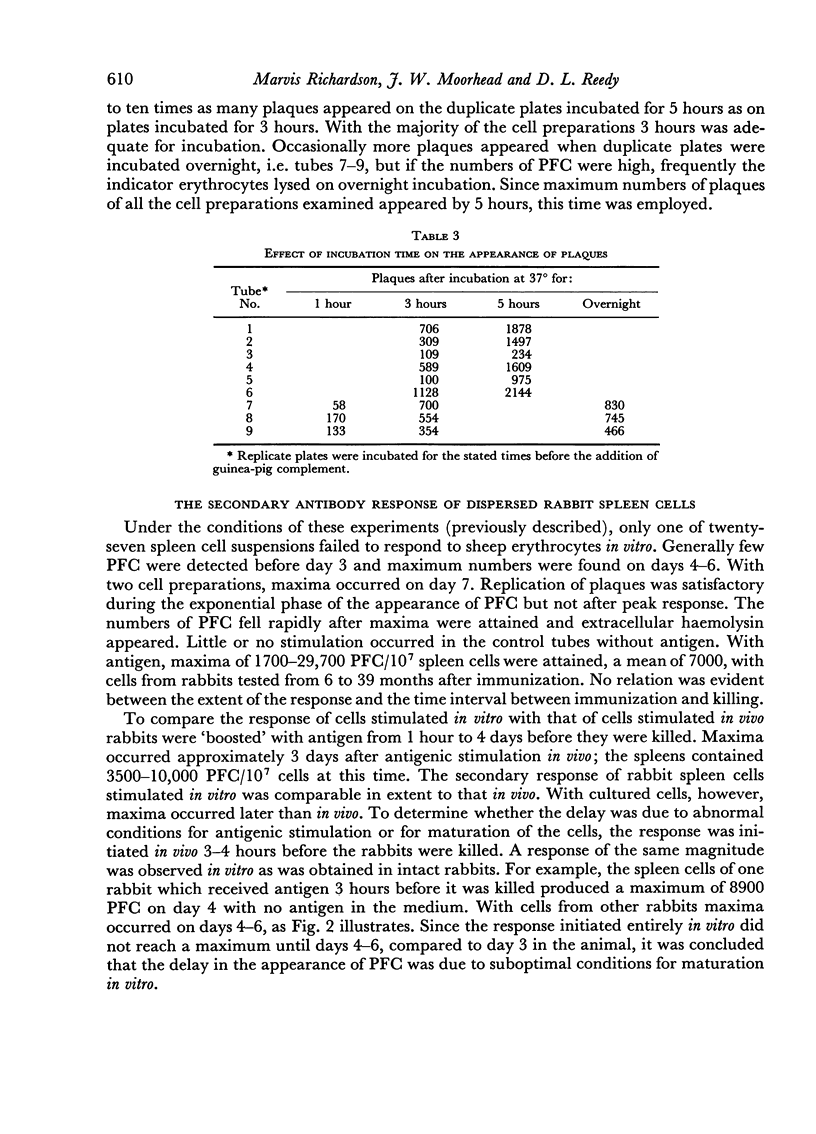
Suspensions of spleen cells from rabbits immunized to sheep erythrocytes and stimulated in vitro by the specific antigen produced high numbers of antibody-synthesizing cells. Several factors were found to affect secondary antigenic stimulation in vitro. The extent of the immune response elicited was a function of antigen concentration. Maximum was obtained by stimulation with 104 to 105 erythrocytes/107 spleen cells; 107 erythrocytes inhibited the response. The maximum usually occurred on days 4–6; glutamine increased the rate at which antibody-synthesizing cells appeared. It was found that the source of the normal serum supplement used in the growth medium markedly affected the results. Storage of rabbit serum reduced its efficacy; after 6 months storage at –10° little or no response was obtained. The addition of specific antiserum on days 1, 2 or 3 reduced the cellular response.
With cells from twenty-six rabbits tested 6–39 months after immunization, maxima of 1700–29,700 antibody-synthesizing cells/107 spleen cells were attained. No relationship was evident between the time from immunization and the extent of the response. The activity of the extracellular antibody produced by the cells correlated roughly with the number of antibody-synthesizing cells. The antibody elicited in vitro was specific and stable on storage at –10° for 2 years. On the basis of sensitivity to 2-mercaptoethanol, it was a macroglobulin. Disc electrophoresis and identification of the haemolytic component showed that the antibody synthesized in vitro migrated with the γ-globulins, at the same rate as the active component in anti-erythrocyte rabbit serum.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Flad H. D. Effect of lymphocyte stimulants on specific antibody synthesis in vitro. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):975–978. doi: 10.1038/219975a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON M., DUTTON R. W. ANTIBODY SYNTHESIZING CELLS: APPEARANCE AFTER SECONDARY ANTIGENIC STIMULATION IN VITRO. Science. 1964 Oct 30;146(3644):655–656. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3644.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. A., FITCH F. W. THE MECHANISM OF TOLERANCE PRODUCED IN RATS TO SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES. II. THE PLAQUE-FORMING CELL AND ANTIBODY RESPONSE TO MULTIPLE INJECTIONS OF ANTIGEN BEGUN AT BIRTH. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:683–695. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. Antibody elicited by Brucella abortus antigen in vitro: prolonged production by cell suspensions. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALIAFERRO W. H., TALIAFERRO L. G. THE EFFECT OF ANTIGEN DOSAGE ON THE FORSSMAN HEMOLYSIN RESPONSE IN RABBITS. J Infect Dis. 1963 Nov-Dec;113:155–169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.3.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Möller G. Regulatory effect of antibody on the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:81–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang H. Y., Neter E. Inhibtion by cardiolipin of the antibody response to bacterial antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




