Abstract
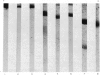
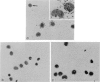
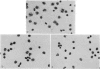
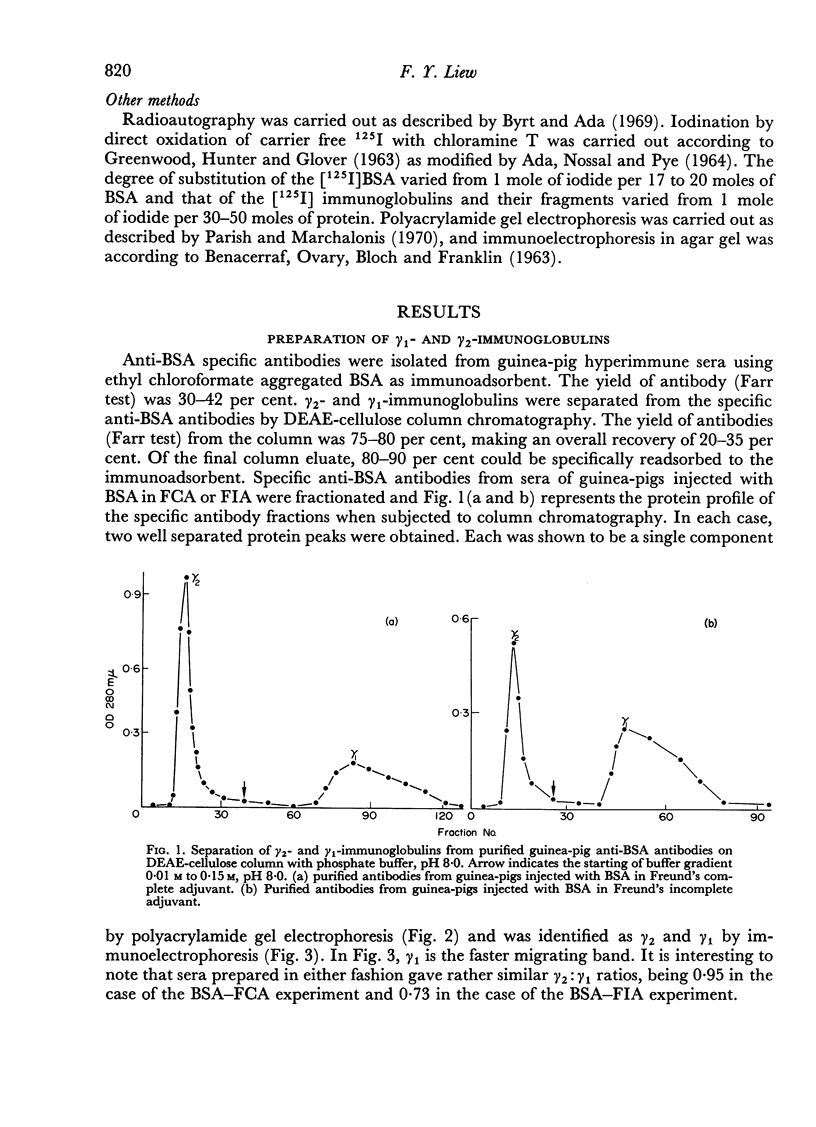
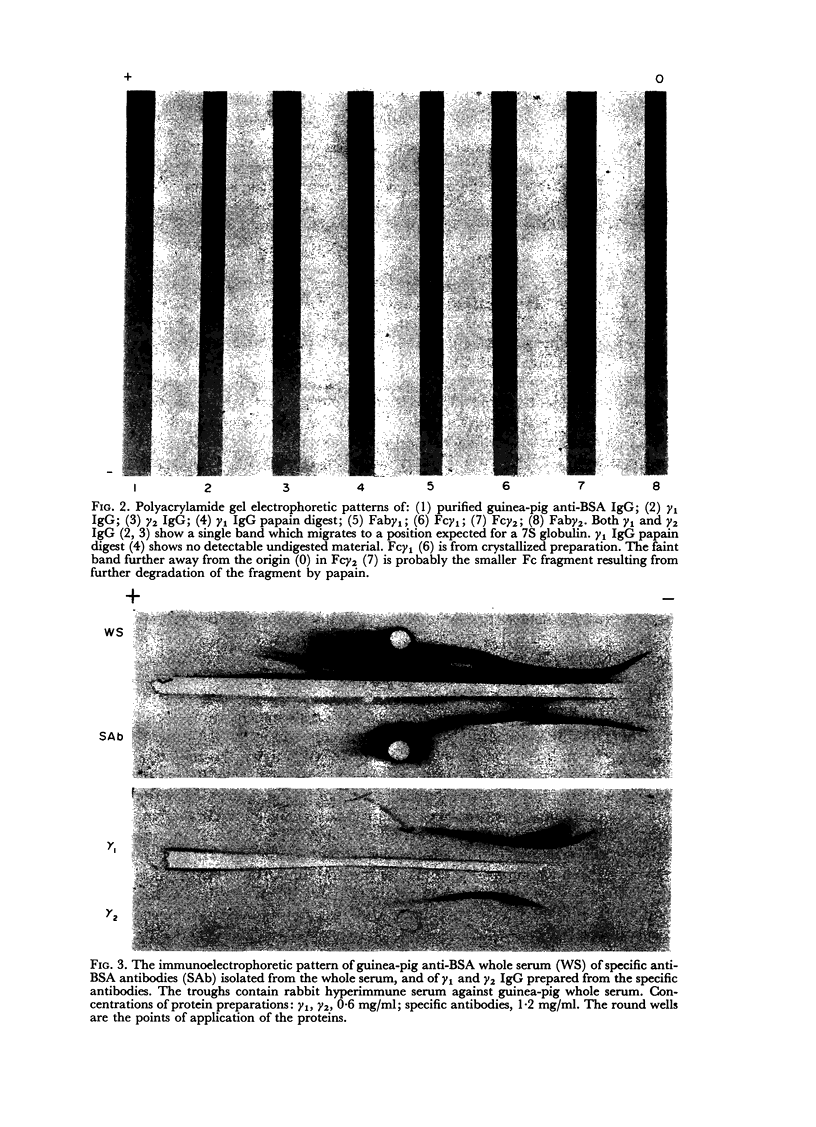
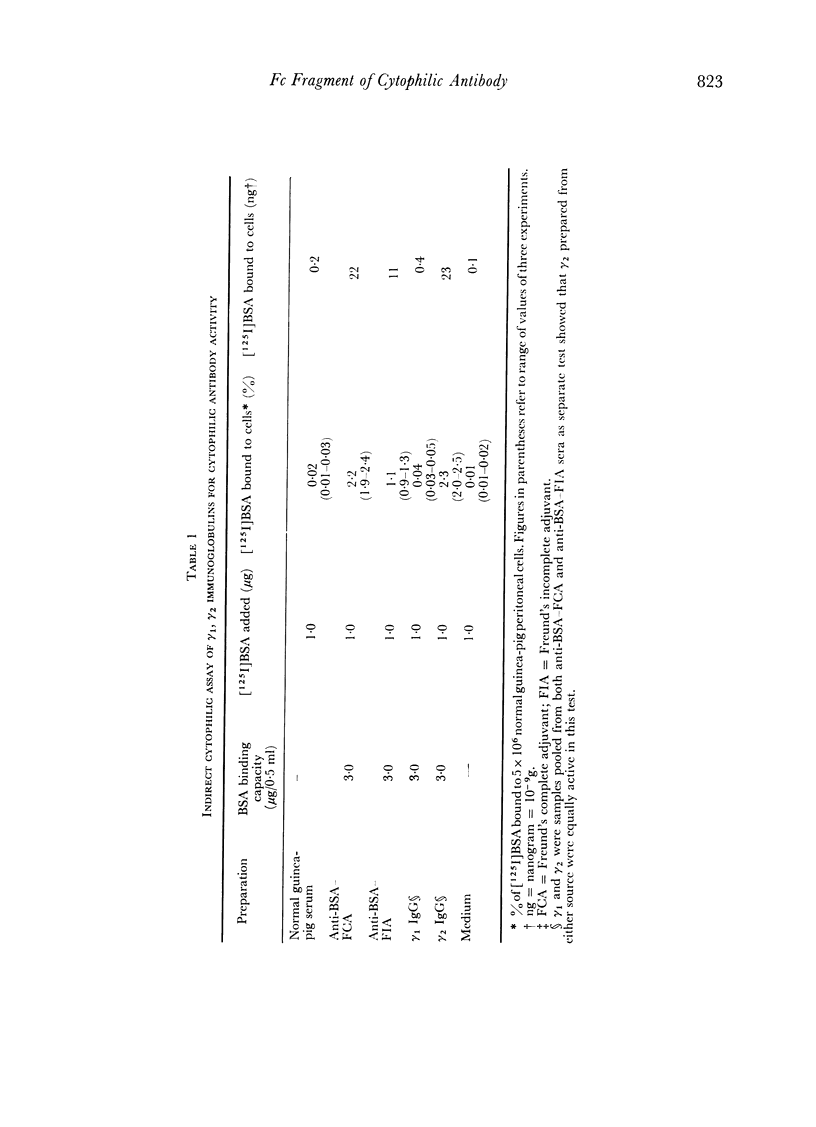
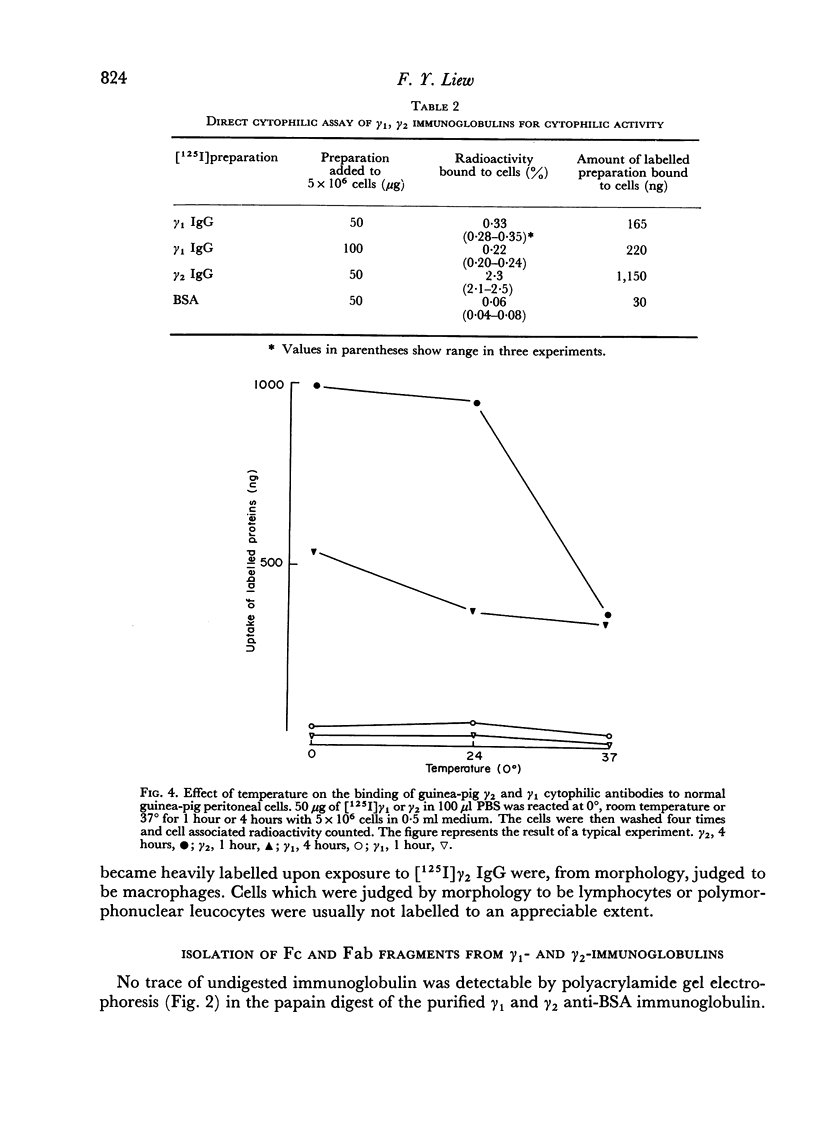
Using radioactivity assays and radioautography, it has been confirmed that the majority of the guinea-pig anti-BSA cytophilic antibodies are found in the γ2 IgG fraction. The cytophilic activity was directly demonstrated to be present in the Fc portion of the IgG molecule. Furthermore, the Fc portion quantitatively accounts for the cytophilic activity of the whole IgG molecule.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. III. DISTRIBUTION OF IODINATED ANTIGENS FOLLOWING INJECTION INTO RATS VIA THE HIND FOOTPADS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:295–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ada G. L., Byrt P. Specific inactivation of antigen-reactive cells with 125I-labelled antigen. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1291–1292. doi: 10.1038/2221291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Biologically active water-insoluble protein polymers. I. Their use for isolation of antigens and antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., OVARY Z., BLOCH K. J., FRANKLIN E. C. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. I. Electrophoretic separation of two types of guinea pig 7S antibodies. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:937–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. CYTOPHILIC ANTIBODY IN GUINEA-PIGS WITH DELAYED-TYPE HYPERSENSITIVITY. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:474–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBELL F. W., HEMMINGS W. A., OAKLEY C. L., PORTER R. R. The relative transmission of the fractions of papain hydrolyzed homologous gamma-globulin from the uterine cavity to the foetal circulation in the rabbit. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1960 Mar 1;151:478–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1960.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazkovec A. A., Sorkin E. Antigen binding properties of spleen cell suspensions coated with rabbit cytophilic antibody. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):151–166. doi: 10.1159/000229696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowland E. The physico-chemical properties of cytophilic antibody. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Feb;46(1):73–81. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herd Z. L., Ada G. L. Distribution of 125I-immunoglobulins, IgG subunits and antigen-antibody complexes in rat lymph nodes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Feb;47(1):73–80. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Benacerraf B. Properties of macrophage receptors for cytophilic antibodies. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Apr;47(2):193–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., BENACERRAF B. STUDIES ON THE PROPERTIES OF FRAGMENTS OF GUINEA PIG GAMMA-1 AND GAMMA-2 ANTIBODIES OBTAINED BY PAPAIN DIGESTION AND MILD REDUCTION. J Immunol. 1964 Dec;93:1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S., Mildenhall P. Studies on cytophilic antibodies. II. The production by guinea-pigs of macrophage cytophilic antibodies to sheep erythrocytes and human serum albumin: relationship to the production of other antibodies and the development of delayed-type hypersensitivity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Feb;46(1):33–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OETTGEN H. F., BINAGHI R. A., BENACERRAF B. HEXOSE CONTENT OF GUINEA PIG GAMMA-1 AND GAMMA-2 IMMUNOGLOBULINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., KARUSH F. Studies on the immunologic mechanism of anaphylaxis. II. Sensitizing and combining capacity in vivo of fractions separated from papain digests of antihapten antibody. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Marchalonis J. J. A simple and rapid acrylamide gel method for estimating the molecular weights of proteins and protein subunits. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):436–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage cytophilic antibody in mice. Differentiation between antigen adherence due to these antibodies and opsoni adherence. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(4):332–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]