Abstract
The CD27 molecule is expressed on a portion of natural killer (NK) cells as well as T and B cells. To provide the functional capacity of CD27 molecule on NK cells, we here highly purified CD3- CD56+ NK cells by flow cytometry (purity > 98%), and investigated their NK cell activity via CD27/CD70 interaction using a CD70-transfectant by a 4 h 51Cr-release assay. The enhancement of NK activity by purified NK cells in the presence of interleukin-2 (IL-2) or interleukin-12 (IL-12) against CD70/Nalm-6 was not recognized as compared to against mock/Nalm-6. However, after a coculture with the fixed CD70/300-19, the purified NK cells increased the NK cell activity against K562, the value being 10 to 20% higher than coculture with the mock/300-19 in the presence of IL-2 or IL-12. The enhancement of NK activity was blocked by the addition of anti-CD70 monoclonal antibody (mAb). In addition, conjugation of NK cells to the target was increased by coculture with the CD70/300-19 without increased expression of adhesion molecules. In the parallel experiment, there was no increase in the killing capacity of NK cells. These results strongly show that CD27/CD70 interaction directly enhances NK activity in the presence of IL-2 or IL-12 by increasing the effector and target conjugate formation, indicating that CD27/CD70 interaction plays an important role in the cytotoxic function of NK cells.
Full text
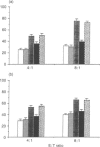
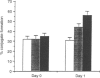
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agematsu K., Kobata T., Sugita K., Hirose T., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Direct cellular communications between CD45R0 and CD45RA T cell subsets via CD27/CD70. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3627–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma M., Cayabyab M., Buck D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. CD28 interaction with B7 costimulates primary allogeneic proliferative responses and cytotoxicity mediated by small, resting T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):353–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman M. R., Crimmins M. A., Yetz-Aldape J., Kriz R., Kelleher K., Herrmann S. The cloning of CD70 and its identification as the ligand for CD27. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1756–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galandrini R., De Maria R., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. CD44 triggering enhances human NK cell cytotoxic functions. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4399–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Alderson M. R., Smith C. A., Armitage R. J., VandenBos T., Jerzy R., Tough T. W., Schoenborn M. A., Davis-Smith T., Hennen K. Molecular and biological characterization of a ligand for CD27 defines a new family of cytokines with homology to tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90133-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata T., Agematsu K., Kameoka J., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD27 is a signal-transducing molecule involved in CD45RA+ naive T cell costimulation. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 15;153(12):5422–5432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata T., Jacquot S., Kozlowski S., Agematsu K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD27-CD70 interactions regulate B-cell activation by T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 21;92(24):11249–11253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.11249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama A., Kawai H., Yamada S., Aoyama K., Yamazaki M., Saitoh H., Miyagawa Y., Akabane T., Uehara Y. Impaired natural killer cell recycling in childhood chronic neutropenia with morphological abnormalities and defective chemotaxis of neutrophils. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallett S., Barclay A. N. A new superfamily of cell surface proteins related to the nerve growth factor receptor. Immunol Today. 1991 Jul;12(7):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90033-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Holter W., Majdic O., Fischer G. F., Knapp W. CD27 expression by a distinct subpopulation of human B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2679–2684. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Cwirla S., Phillips J. H. Comparative studies of human FcRIII-positive and negative natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3183–3191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naume B., Gately M., Espevik T. A comparative study of IL-12 (cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor)-, IL-2-, and IL-7-induced effects on immunomagnetically purified CD56+ NK cells. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Fox F. E., Oleszak E., Fong K., Nanno M., Ioannides C. G., Trotta P. P. Regulation of natural killer cytotoxicity by recombinant alpha interferons. Augmentation by IFN-alpha 7, an interferon similar to IFN-alpha J. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):849–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Soiffer R. J., Wolf S. F., Manley T. J., Donahue C., Young D., Herrmann S. H., Ritz J. Response of human natural killer (NK) cells to NK cell stimulatory factor (NKSF): cytolytic activity and proliferation of NK cells are differentially regulated by NKSF. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):779–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Caulfield J. P., Michon J., Hein A., Kamada M. M., MacDermott R. P., Stevens R. L., Ritz J. T11/CD2 activation of cloned human natural killer cells results in increased conjugate formation and exocytosis of cytolytic granules. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):991–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Carpén O., Hibbs M. L., Springer T. A. Natural killer cell and granulocyte Fc gamma receptor III (CD16) differ in membrane anchor and signal transduction. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3283–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Robertson M. J., Torimoto Y., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Participation of the CD27 antigen in the regulation of IL-2-activated human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1199–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Torimoto Y., Nojima Y., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The 1A4 molecule (CD27) is involved in T cell activation. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Patarroyo M., Gahmberg C. G. CD11a-c/CD18 and GP84 (LB-2) adhesion molecules on human large granular lymphocytes and their participation in natural killing. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1041–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lier R. A., Borst J., Vroom T. M., Klein H., Van Mourik P., Zeijlemaker W. P., Melief C. J. Tissue distribution and biochemical and functional properties of Tp55 (CD27), a novel T cell differentiation antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1589–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]