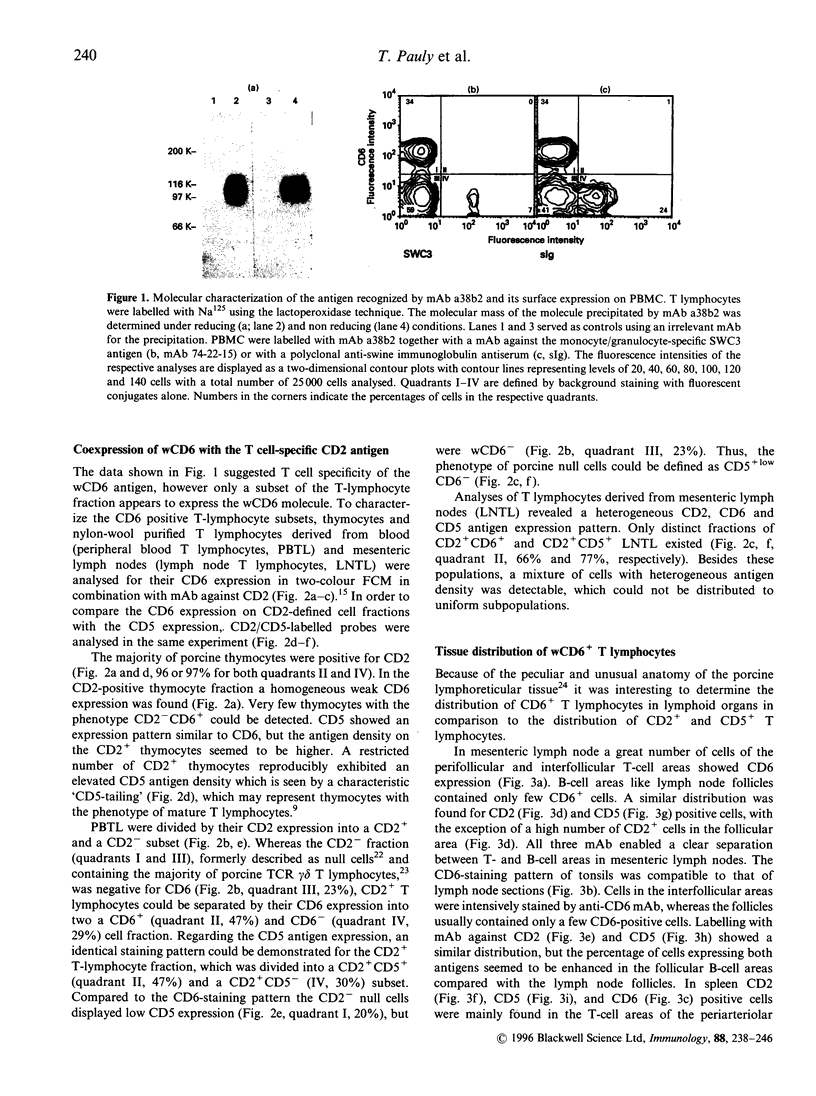
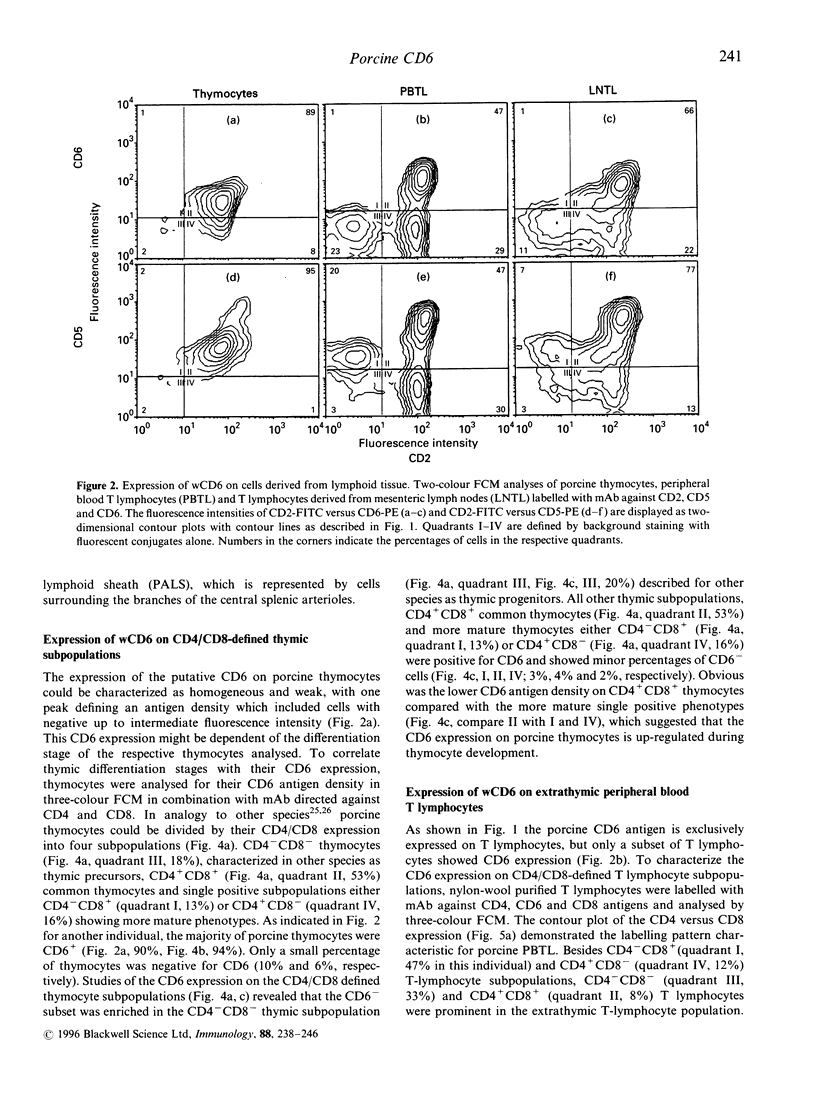
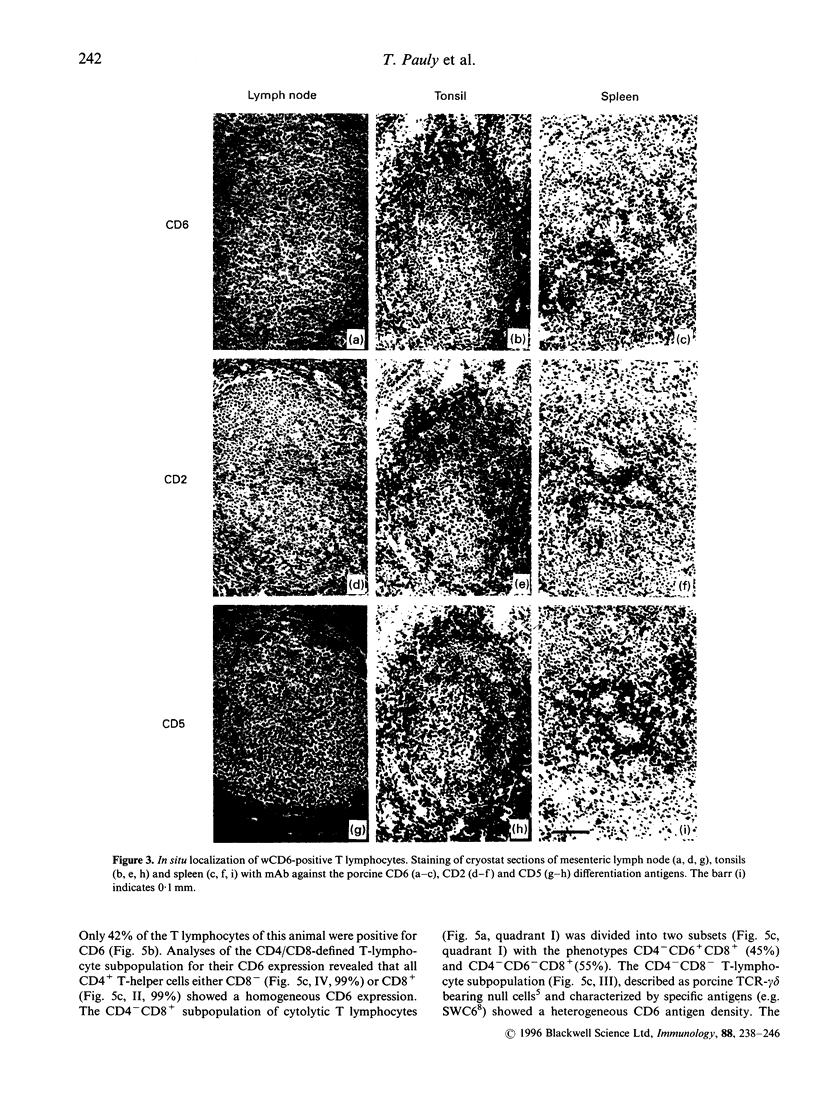
Abstract
The immune system of swine is unique in that the expression of CD4 and CD8 antigens defines four subpopulations of resting extrathymic T lymphocytes. Beyond phenotypic differences to other species, porcine T lymphocytes, particularly when derived from infected animals, are known to show high non-specific cytolytic in vitro activity. Here we describe the putative porcine CD6 antigen (workshop CD6; wCD6) which enables a phenotypic separation of T lymphocytes responsible for major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-restricted and non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity. The putative porcine CD6 analogue, wCD6, a protein with a molecular mass of 110,000, shows high specificity for T lymphocytes and is neither expressed on B lymphocytes nor on cells of the myeloid lineage. In the extrathymic T-lymphocyte compartment wCD6 characterizes two T-lymphocyte fractions: wCD6+ T lymphocytes including both CD4+ T-helper cell subpopulations (CD4+CD8- and CD4+CD8+) and within the CD4-CD8+ fraction cells with high CD8 antigen density. In contrast the CD4-CD8- gamma/delta T-cell receptor (TCR) subset and CD4-CD8+ cells with low CD8 antigen density are included in the wCD6- T-lymphocyte fraction. Functional studies with separated wCD6 fractions revealed that the wCD6- cells can be characterized by spontaneous and non-MHC restricted cytolytic activity, whereas the wCD6+ T lymphocytes are responsible for MHC-restricted T-cell functions. Thus, the porcine wCD6 is an important antigen to discriminate between MHC-restricted and non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity.
Full text
PDF

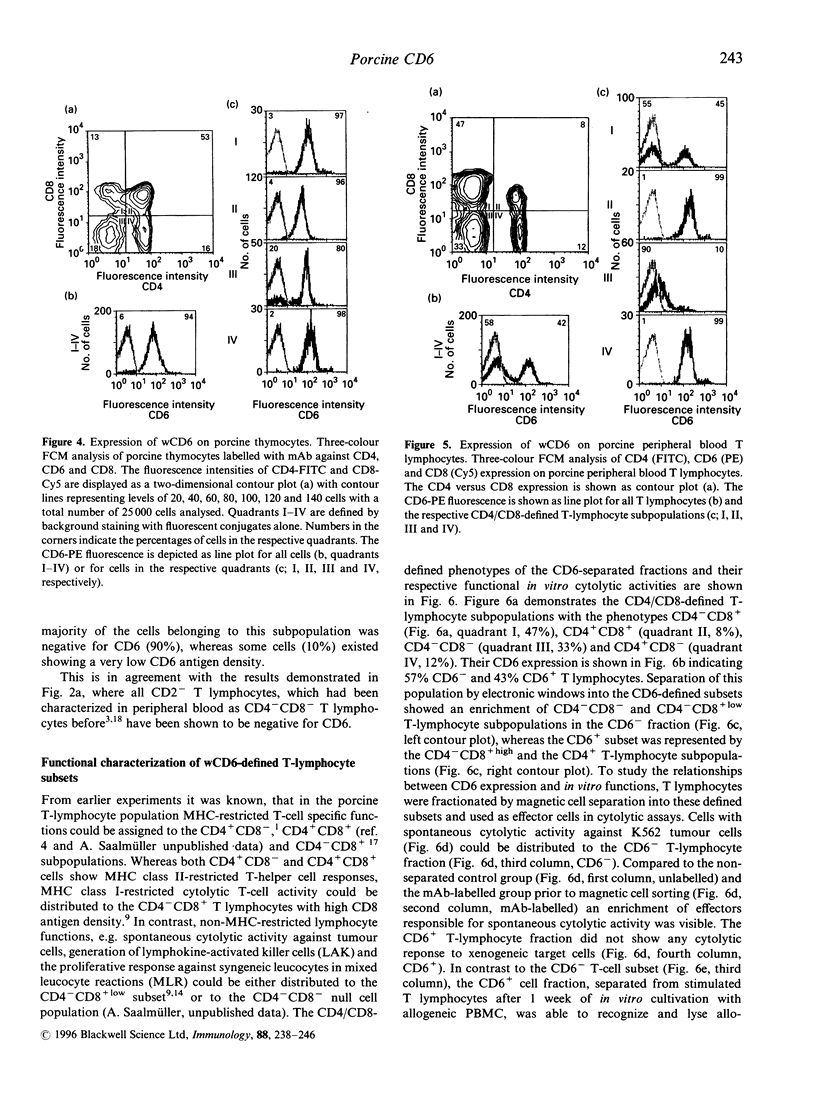
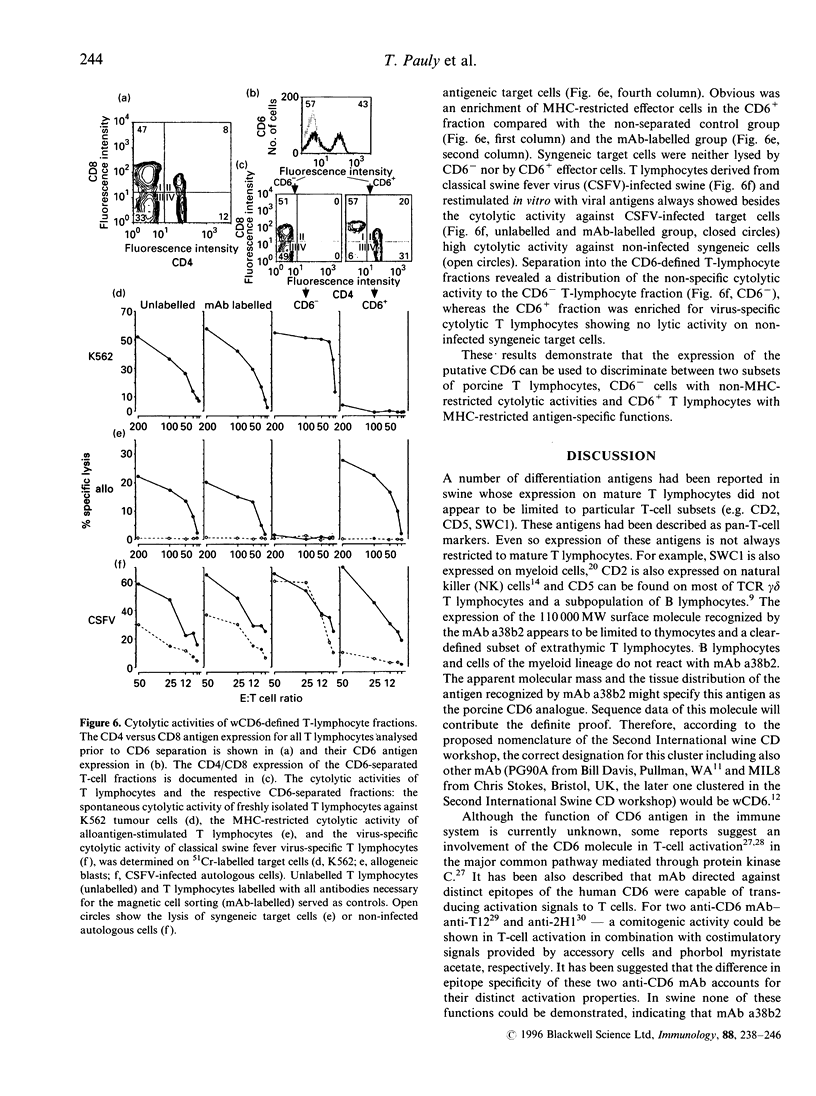


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Melnick M. B., Linsley P. S., Seed B. The lymphocyte glycoprotein CD6 contains a repeated domain structure characteristic of a new family of cell surface and secreted proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):949–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Machugh N. D., Ellis J. A., Naessens J., Newson J., Morrison W. I. Monoclonal antibodies which react with bovine T-lymphocyte antigens and induce blastogenesis: tissue distribution and functional characteristics of the target antigens. Immunology. 1988 Mar;63(3):439–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. Organisation of the lymphoreticular system and lymphocyte markers in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jan;3(1-2):95–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Pallares V., Symons D. B., Sibbons P. Effect of thymectomy on lymphocyte subpopulations in the pig. Demonstration of a thymus-dependent 'null' cell. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):96–101. doi: 10.1159/000231915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. The Null/gamma delta TCR+ T cell family in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi R. M., Swack J. A., Gaviria D. M., Romain P. L. Anti-T12, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, can activate human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2439–2447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg C., Schurig G. G. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against swine leukocytes. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Feb;11(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt W., Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J. Distinct gamma/delta T cell receptors define two subsets of circulating porcine CD2-CD4-CD8- T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):265–269. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt W., Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J. Distinct gamma/delta T cell receptors define two subsets of circulating porcine CD2-CD4-CD8- T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):265–269. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with swine lymphocytes. I. Antibodies to membrane structures that define the cytolytic T lymphocyte subset in the swine. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Allison J. P., Phillips J. H. Correlation of cell surface antigen expression on human thymocytes by multi-color flow cytometric analysis: implications for differentiation. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2501–2507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K. Characterization of swine leukocyte differentiation antigens. Immunol Today. 1993 Apr;14(4):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90227-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Rudd C. E., Letvin N. L., Hagan M., Schlossman S. F. 2H1--a novel antigen involved in T lymphocyte triggering. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2165–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly T., Elbers K., König M., Lengsfeld T., Saalmüller A., Thiel H. J. Classical swine fever virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and identification of a T cell epitope. J Gen Virol. 1995 Dec;76(Pt 12):3039–3049. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-12-3039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Aasted B., Canals A., Dominguez J., Goldman T., Lunney J. K., Maurer S., Pauly T., Pescovitz M. D., Pospisil R. Analyses of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine CD6. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Aasted B., Canals A., Dominguez J., Goldman T., Lunney J. K., Maurer S., Pescovitz M. D., Pospisil R., Salmon H. Summary of workshop findings for porcine T-lymphocyte antigens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Bryant J. Characteristics of porcine T lymphocytes and T-cell lines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Maurer S., Weiland E. Discrimination between two subsets of porcine CD8+ cytolytic T lymphocytes by the expression of CD5 antigen. Immunology. 1994 Apr;81(4):578–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Reddehase M. J. Phenotypic discrimination between thymic and extrathymic CD4-CD8- and CD4+CD8+ porcine T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2011–2016. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Reddehase M. J. Porcine gamma/delta T lymphocyte subsets differing in their propensity to home to lymphoid tissue. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2343–2346. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Jonjic S., Bühring H. J., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with swine lymphocytes. II. Detection of an antigen on resting T cells down-regulated after activation. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1852–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Maurer S. Major histocompatibility antigen class II expressing resting porcine T lymphocytes are potent antigen-presenting cells in mixed leukocyte culture. Immunobiology. 1994 Feb;190(1-2):23–34. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J., Bühring H. J., Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Simultaneous expression of CD4 and CD8 antigens by a substantial proportion of resting porcine T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1297–1301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swack J. A., Mier J. W., Romain P. L., Hull S. R., Rudd C. E. Biosynthesis and post-translational modification of CD6, a T cell signal-transducing molecule. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7137–7143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Velde H., von Hoegen I., Luo W., Parnes J. R., Thielemans K. The B-cell surface protein CD72/Lyb-2 is the ligand for CD5. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):662–665. doi: 10.1038/351662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]