Abstract
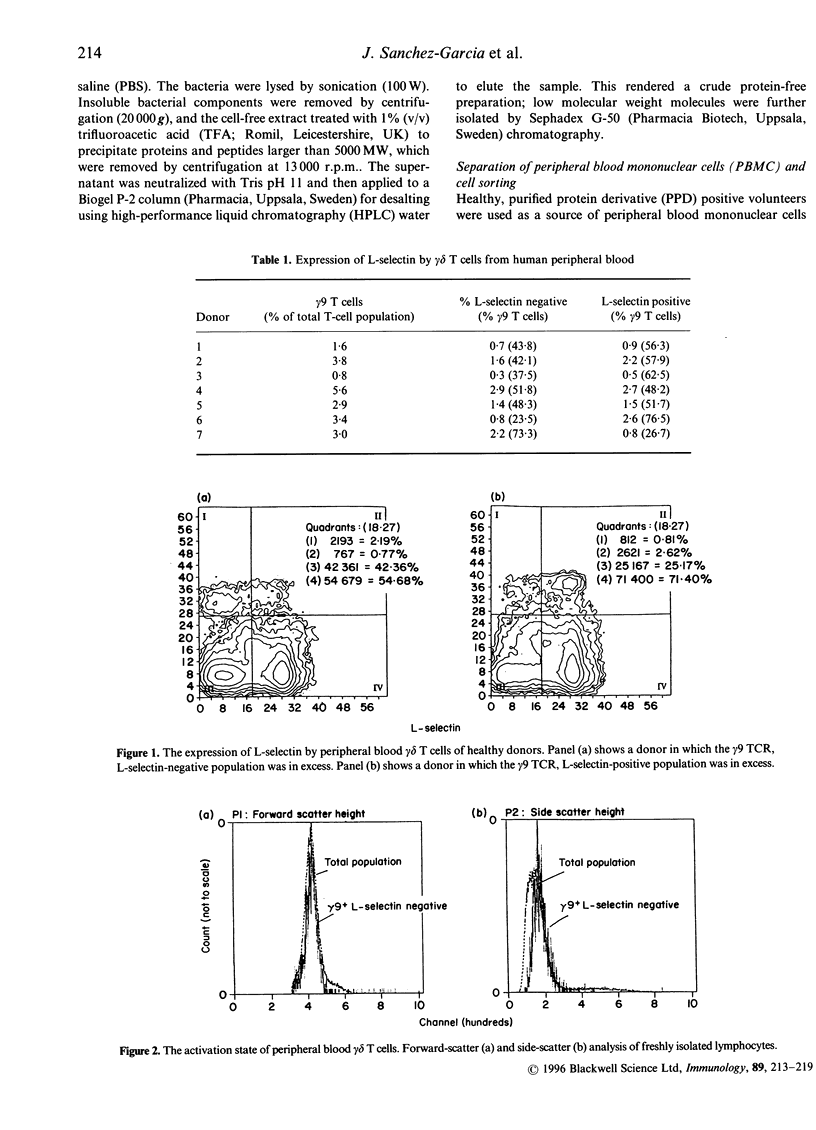
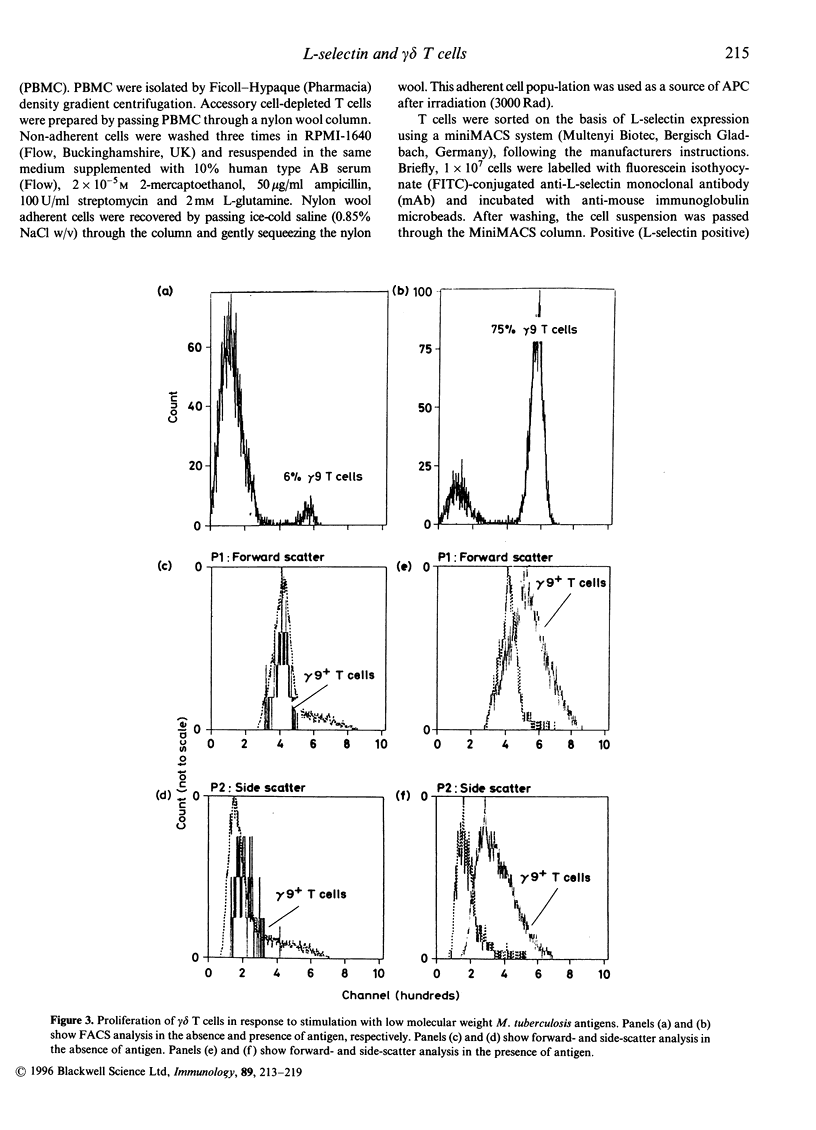
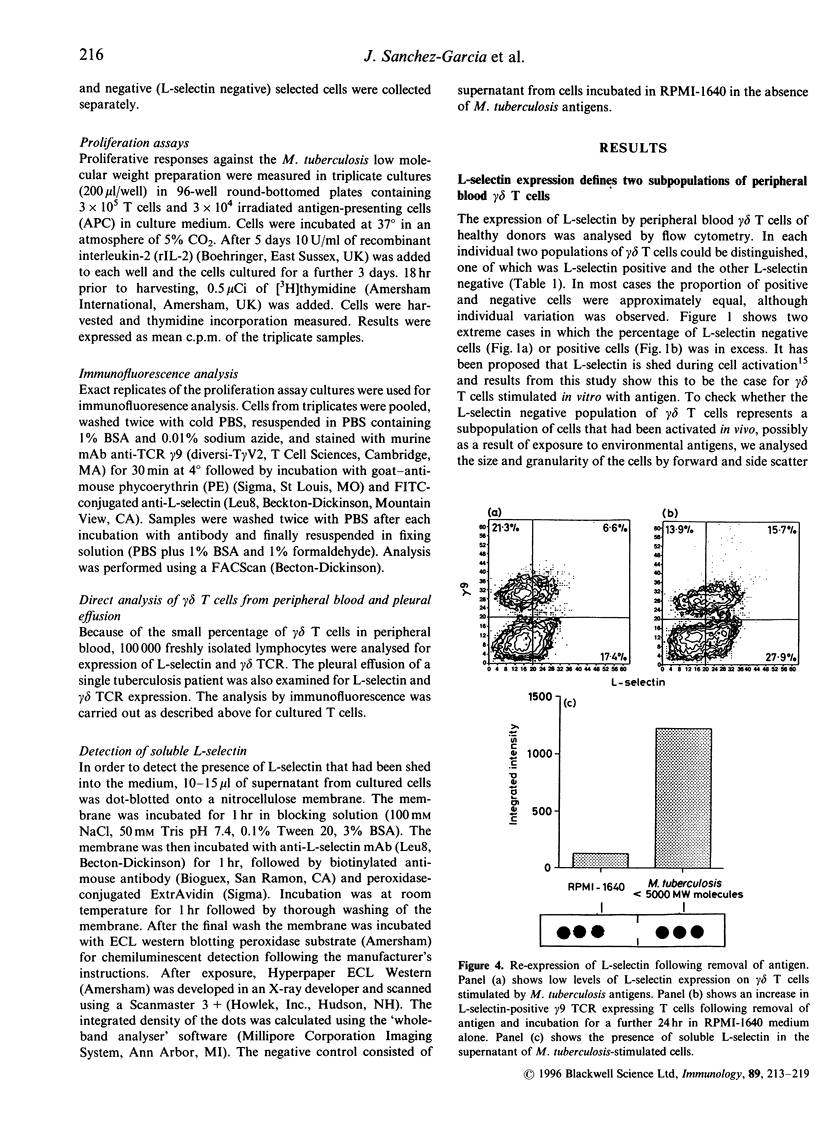
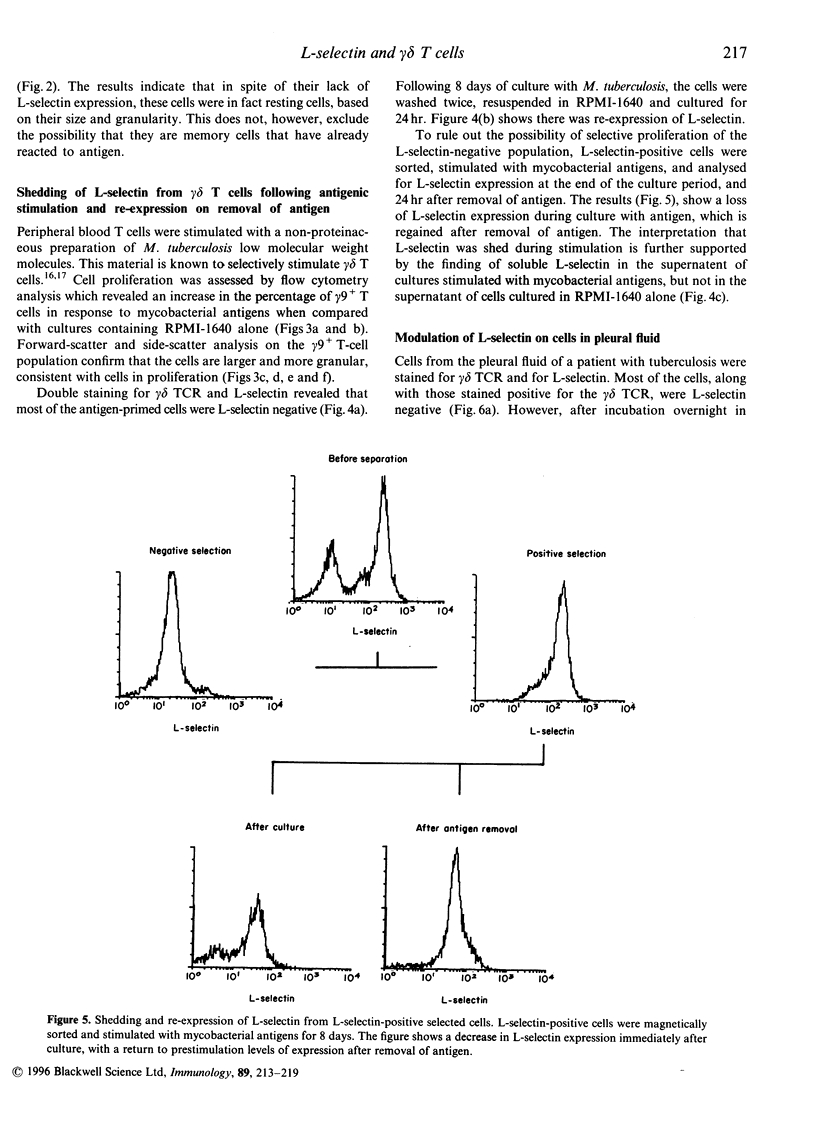
Activation of lymphocytes leads to the modulation of a number of surface molecules. We have investigated the expression of one such molecule. L-selectin, following activation of gamma delta T cells with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. L-selectin is modulated during lymphocyte entry into lymph nodes; this modulation reflects the recirculation and homing potential of lymphocytes. We find that stimulation of gamma delta T cells by M. tuberculosis antigens results in shedding of L-selectin from gamma delta T cells. Re-expression of L-selectin occurs on removal of antigen suggesting that the regulation of expression is controlled by the presence or absence of antigen. The gamma delta T-cell receptor (TCR)-positive, L-selectin negative population of peripheral blood lymphocytes appears to be resting cells, as assessed by forward- and light-scatter analysis. We further find that gamma delta T cells isolated from a site of infection, the pleural fluid of a tuberculosis patient, are L-selectin negative, and that L-selectin is re-expressed following culture of the pleural fluid gamma delta T cells in the absence of antigen. These results demonstrate that, in addition to stimulation with polyclonal mitogens, antigen stimulation can also promote the surface shedding of L-selectin and that gamma delta T cells have the potential to home to sites of infection supporting their role in the immunological defence against infectious micro-organisms.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casorati G., De Libero G., Lanzavecchia A., Migone N. Molecular analysis of human gamma/delta+ clones from thymus and peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1521–1535. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davodeau F., Peyrat M. A., Hallet M. M., Houde I., Vie H., Bonneville M. Peripheral selection of antigen receptor junctional features in a major human gamma delta subset. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):804–808. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrick D. A., Schrenzel M. D., Mulvania T., Hsieh B., Ferlin W. G., Lepper H. Differential production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in response to Th1- and Th2-stimulating pathogens by gamma delta T cells in vivo. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):255–257. doi: 10.1038/373255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galéa P., Brezinschek R., Lipsky P. E., Oppenheimer-Marks N. Phenotypic characterization of CD4-/alpha beta TCR+ and gamma delta TCR+ T cells with a transendothelial migratory capacity. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):529–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Spertini O., Ernst T. J., Belvin M. P., Levine H. B., Kanakura Y., Tedder T. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines regulate surface expression of the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 on human neutrophils, monocytes, and their precursors. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):576–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Jones B., Hayday A. Specificity and function of T cells bearing gamma delta receptors. Immunol Today. 1988 Mar;9(3):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T. M., Dailey M. O. Rapid modulation of homing receptors (gp90MEL-14) induced by activators of protein kinase C. Receptor shedding due to accelerated proteolytic cleavage at the cell surface. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3130–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanof M. E., James S. P. Leu-8 antigen expression is diminished during cell activation but does not correlate with effector function of activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3701–3706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1238–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.2551036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Butcher E. C. Identification of a human peripheral lymph node homing receptor: a rapidly down-regulated adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A. Selectins: interpreters of cell-specific carbohydrate information during inflammation. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1439808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Wahl C., Holzmann B., Heeg K., Wagner H. Bacterial superantigens induce rapid and T cell receptor V beta-selective down-regulation of L-selectin (gp90Mel-14) in vivo. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Pirmez C., Hofman F. M., Torigian V., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific gamma delta T-cell receptors accumulate in human infectious disease lesions. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):544–548. doi: 10.1038/339544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palecanda A., Walcheck B., Bishop D. K., Jutila M. A. Rapid activation-independent shedding of leukocyte L-selectin induced by cross-linking of the surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Gulle H., Kaufmann S. H., Wagner H. Primary responses of human T cells to mycobacteria: a frequent set of gamma/delta T cells are stimulated by protease-resistant ligands. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Plesnila N., Lipford G. B., Kromer S., Deusch K., Wagner H. A lectin-binding, protease-resistant mycobacterial ligand specifically activates V gamma 9+ human gamma delta T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Treer J. R., Ferguson-Darnell B., Collins P. A., Buck D., Terstappen L. W. Control of lymphocyte recirculation in man. I. Differential regulation of the peripheral lymph node homing receptor L-selectin on T cells during the virgin to memory cell transition. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1105–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Hiromatsu K., Matsuzaki G., Muramori K., Nomoto K. Peritoneal gamma delta T cells induced by Escherichia coli infection in mice. Correlation between Thy-1 phenotype and host minor lymphocyte-stimulating phenotype. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2062–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walcheck B., Jutila M. A. Bovine gamma delta T cells express high levels of functional peripheral lymph node homing receptor (L-selectin). Int Immunol. 1994 Jan;6(1):81–91. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. L., Beverley P. C. Characterization of a novel subset of T cells from human spleen that lacks L-selectin. Immunology. 1993 Apr;78(4):623–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



