Abstract
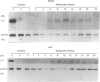
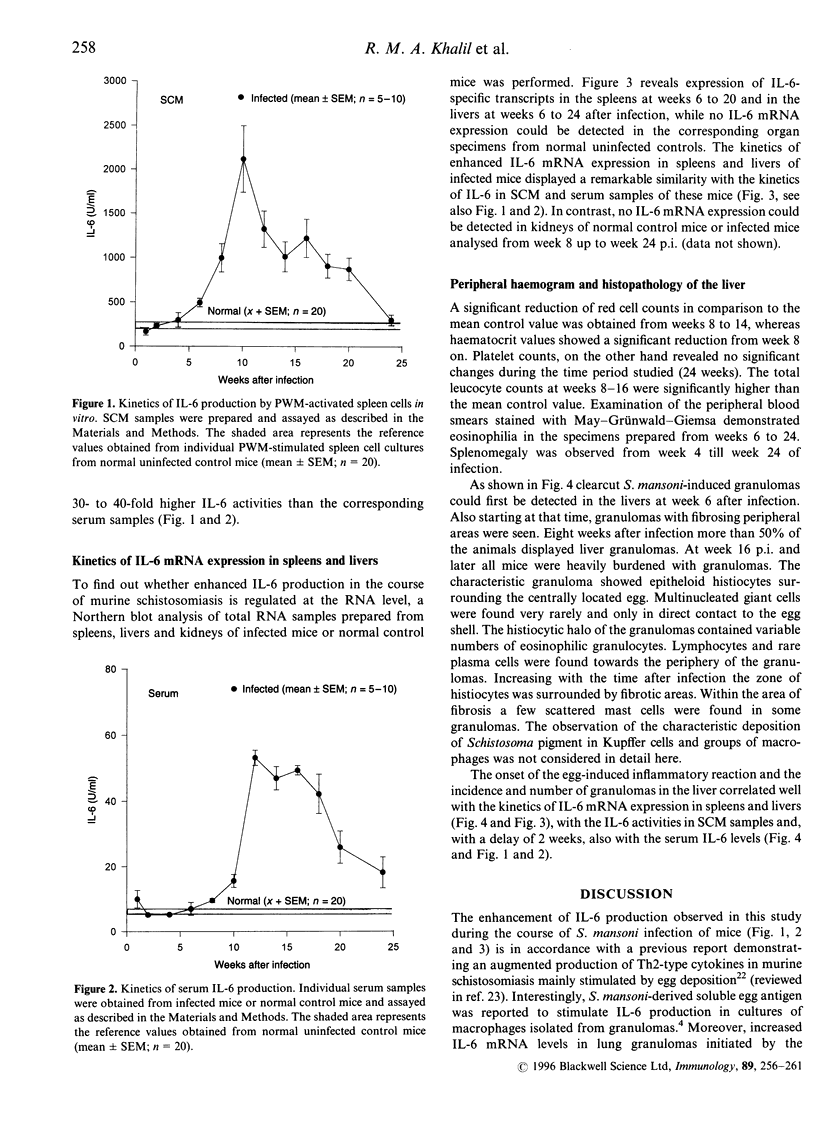
It has been reported that interleukin-6 (IL-6) is expressed in cells of acute inflammatory granulomas experimentally induced in mice by eggs of Schistosoma mansoni. Moreover, in vitro IL-6 was shown to enhance the cytotoxic activity of human platelets against larvae of S. mansoni. To elucidate further a proposed biological significance of this cytokine during the course of schistosomiasis, we studied the kinetics of IL-6 production and concomitantly performed a histopathological analysis of the livers in BALB/c mice subcutaneously infected with S. mansoni cercariae. Over a period of 24 weeks postinfection (p.i.) we monitored serum IL-6 levels, IL-6 production in vitro by pokeweed mitogen (PWM)-stimulated spleen cells as well as IL-6 mRNA expression in livers, spleens and kidneys. We found significantly elevated IL-6 levels in PWM-stimulated spleen cell-conditioned media (SCM) at weeks 6 to 20 p.i., peaking at week 10 p.i. In contrast, serum IL-6 concentrations started to rise not before week 8 but remained significantly elevated above normal control values until week 24 p.i. The time pattern of enhanced IL-6 mRNA expression detected in spleens and livers, but not in kidneys, as well as the rises of IL-6 in SCM and with a delay of 2 weeks in serum samples correlated with the onset of the egg-induced inflammatory reactions as well as the incidence and the number of the granulomas observed histopathologically in the livers of infected mice. Our data emphasize both a local and a systemic role of IL-6 in the host immune response following infection of mice with S. mansoni.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiri P., Locksley R. M., Parslow T. G., Sadick M., Rector E., Ritter D., McKerrow J. H. Tumour necrosis factor alpha restores granulomas and induces parasite egg-laying in schistosome-infected SCID mice. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):604–607. doi: 10.1038/356604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attallah A. M., Abdul-Aal G. M., Urritia-Shaw A., Murrell K. D., Fleisher T. A., Vannier W. E. Parasitic modulation of host immune mechanisms in schistosomiasis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;84(1):1–9. doi: 10.1159/000234391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbernou N., Matsiota-Bernard P., Jolivet C., Ougen P., Guenounou M. Tumour necrosis factor, IL-1 and IL-6 in bronchoalveolar washings and their in vitro production during Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 May;88(2):264–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Warmington K., Ruth J., Lincoln P., Kuo M. C., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine responses during mycobacterial and schistosomal antigen-induced pulmonary granuloma formation. Production of Th1 and Th2 cytokines and relative contribution of tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1105–1113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E. O., Warren K. S., Stenger R. J. Increased incidence of hepatoma in mice with chronic schistosomiasis mansoni treated with a carcinogen. Am J Pathol. 1967 Sep;51(3):307–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzych J. M., Pearce E., Cheever A., Caulada Z. A., Caspar P., Heiny S., Lewis F., Sher A. Egg deposition is the major stimulus for the production of Th2 cytokines in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1322–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hültner L., Moeller J., Schmitt E., Jäger G., Reisbach G., Ring J., Dörmer P. Thiol-sensitive mast cell lines derived from mouse bone marrow respond to a mast cell growth-enhancing activity different from both IL-3 and IL-4. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3440–3446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hültner L., Szöts H., Welle M., Van Snick J., Moeller J., Dörmer P. Mouse bone marrow-derived IL-3-dependent mast cells and autonomous sublines produce IL-6. Immunology. 1989 Jul;67(3):408–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuo G., Akao N., Kohsaka H., Saito I., Miyasaka N., Fujita K. Toxocara canis adult worm antigen induces proliferative response of healthy human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasite Immunol. 1995 Feb;17(2):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1995.tb00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopf M., Baumann H., Freer G., Freudenberg M., Lamers M., Kishimoto T., Zinkernagel R., Bluethmann H., Köhler G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):339–342. doi: 10.1038/368339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A. Schistosomiasis: clinical features and relevance to hematology. Semin Hematol. 1982 Apr;19(2):132–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S., Graham R. C., Jr Antieosinophil serum and the kinetics of eosinophilia in Schistosomiasis mansoni. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):560–574. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeller J., Hültner L., Schmitt E., Breuer M., Dörmer P. Purification of MEA, a mast cell growth-enhancing activity, to apparent homogeneity and its partial amino acid sequencing. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4231–4234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. P., Ruffier J. J., Warren K. S. Suppressive effect of a chronic helminth infection, schistosomiasis mansoni, on the in vitro responses of spleen and lymph node cells to the T cell mitogens phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1176–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1176-1183.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L., Musallam R., Doenhoff M. J. Serum protein concentrations during Schistosoma mansoni infection in intact and T-cell deprived mice. I. The acute phase proteins, C3 and serum amyloid P-component (SAP). Immunology. 1980 Feb;39(2):249–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Szikora J. P., Renauld J. C., Van Roost E., Boon T., Simpson R. J. cDNA cloning of murine interleukin-HP1: homology with human interleukin 6. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):193–197. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The pathogenesis of "clay-pipe stem cirrhosis" in mice with chronic schistosomiasis mansoni, with a note on the longevity of the schistosomes. Am J Pathol. 1966 Sep;49(3):477–489. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J. V., Boros D. L. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. VI. T lymphocyte subsets influence mast cell density in liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):959–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynn T. A., Cheever A. W. Cytokine regulation of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Aug;7(4):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynn T. A., Eltoum I., Cheever A. W., Lewis F. A., Gause W. C., Sher A. Analysis of cytokine mRNA expression during primary granuloma formation induced by eggs of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1430–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynn T. A., Eltoum I., Oswald I. P., Cheever A. W., Sher A. Endogenous interleukin 12 (IL-12) regulates granuloma formation induced by eggs of Schistosoma mansoni and exogenous IL-12 both inhibits and prophylactically immunizes against egg pathology. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1551–1561. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K. A., Kolb J. P., Miyasaka N., Inuo G., Fujita K. Purified excretory-secretory component of filarial parasite enhances Fc epsilon RII/CD23 expression on human splenic B and T cells and IgE synthesis while potentiating T-helper type 2-related cytokine generation from T cells. Immunology. 1994 Apr;81(4):507–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarinsky A., Drobeck H. P., Freele H., Wiland J., Gumaer K. I. An 18-month study of the parasitologic and tumorigenic effects of hycanthone in Schistosoma mansoni-infected and noninfected mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;27(1):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von LICHTENBERG Host response to eggs of S. mansoni. I. Granuloma formation in the unsensitized laboratory mouse. Am J Pathol. 1962 Dec;41:711–731. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]