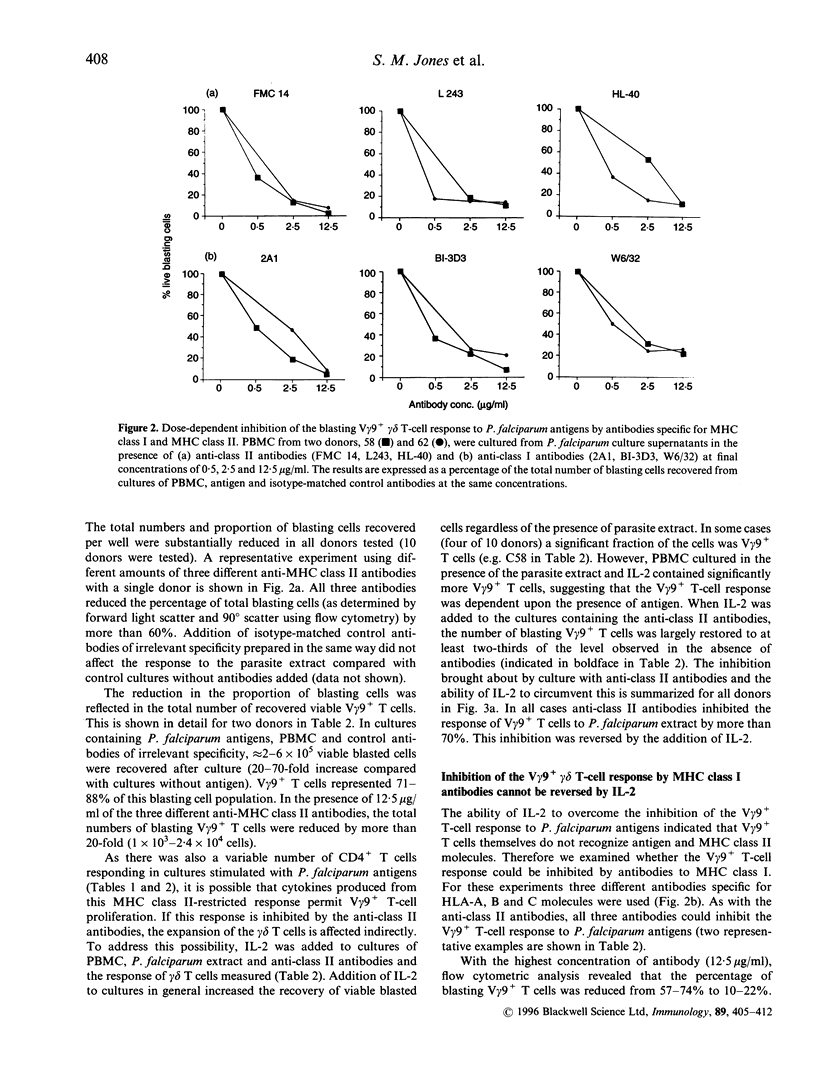
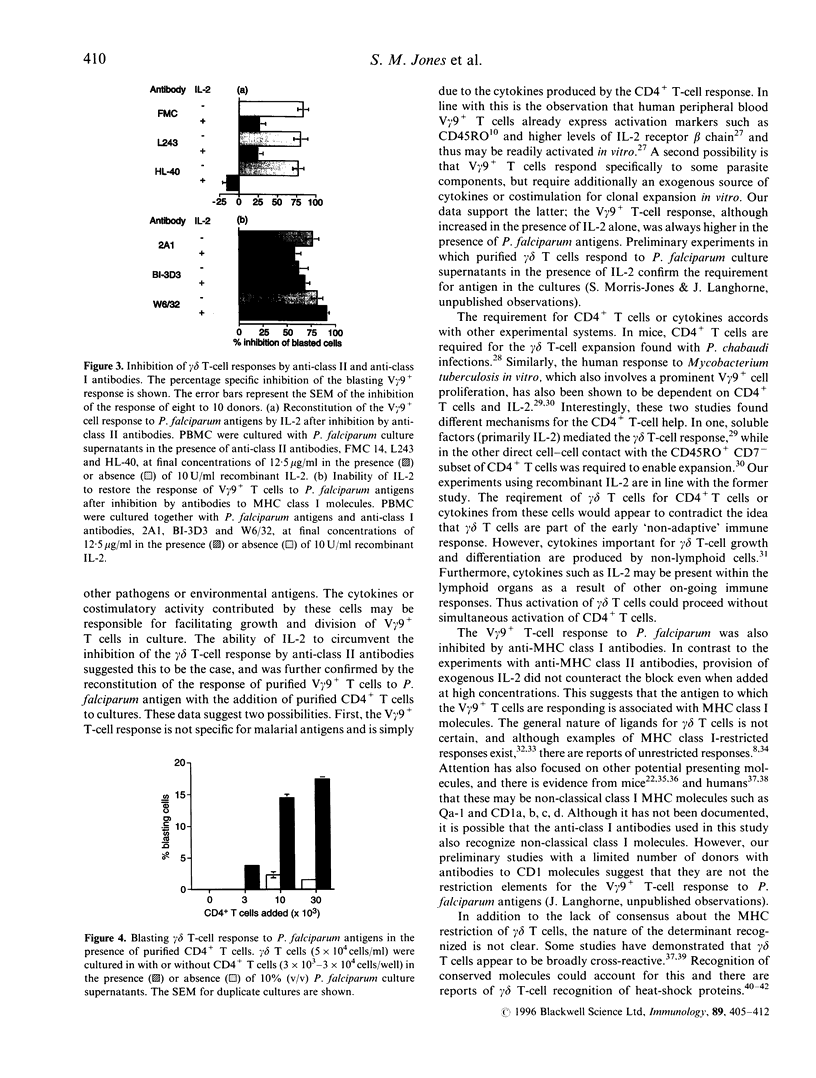
Abstract
Peripheral blood gamma delta T cells from non-exposed individuals respond to antigens of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, in vitro. This response, largely caused by T cells bearing the V gamma 9+ chain of the T-cell receptor, is stimulated by components of the parasite expressed on the schizont stage and released at schizont rupture. The response of V gamma 9+ T cells to parasite components is inhibited by antibodies to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II. However, the inhibition by anti-MHC class II antibodies can be overcome by the addition of interleukin-2 (IL-2) to the cultures, suggesting that gamma delta T cells themselves do not recognize MHC class II molecules but require an MHC class II-dependent response taking place in the culture. In contrast, the inhibition by anti-class I antibodies cannot be reversed by addition of IL-2. Since an accompanying CD4+ T-cell response occurred in peripheral blood mononuclear cells cultured with P falciparum antigens, it was considered that these cells provide the cytokines necessary for the subsequent activation and expansion of V gamma 9+ T cells recognizing components of the parasite and MHC class I molecules. This was confirmed by reconstituting the response of enriched gamma delta T cells to P falciparum schizont extract by addition of purified CD4+ T cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman E. M., Brenner M. B. MHC class I-like, class II-like and CD1 molecules: distinct roles in immunity. Immunol Today. 1995 Jul;16(7):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman E. M., Porcelli S. A., Morita C. T., Behar S. M., Furlong S. T., Brenner M. B. Recognition of a lipid antigen by CD1-restricted alpha beta+ T cells. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):691–694. doi: 10.1038/372691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behr C., Dubois P. Preferential expansion of V gamma 9 V delta 2 T cells following stimulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes with extracts of Plasmodium falciparum. Int Immunol. 1992 Mar;4(3):361–366. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A. CD1: presenting unusual antigens to unusual T lymphocytes. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):185–186. doi: 10.1126/science.7542402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Heckl-Ostreicher B., Grondal E. J., Kabelitz D. Clonal specificity of human gamma delta T cells: V gamma 9+ T-cell clones frequently recognize Plasmodium falciparum merozoites, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and group-A streptococci. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993;100(1):12–18. doi: 10.1159/000236381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertotto A., Gerli R., Spinozzi F., Muscat C., Scalise F., Castellucci G., Sposito M., Candio F., Vaccaro R. Lymphocytes bearing the gamma delta T cell receptor in acute Brucella melitensis infection. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1177–1180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürk M. R., Mori L., De Libero G. Human V gamma 9-V delta 2 cells are stimulated in a cross-reactive fashion by a variety of phosphorylated metabolites. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jul;25(7):2052–2058. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño A. R., Tangri S., Miller J. E., Holcombe H. R., Jackson M. R., Huse W. D., Kronenberg M., Peterson P. A. Peptide binding and presentation by mouse CD1. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.7542403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier J., Beck H. P., Currie B., Good M. F. Antigens released at schizont burst stimulate Plasmodium falciparum-specific CD4+ T cells from non-exposed donors: potential for cross-reactive memory T cells to cause disease. Int Immunol. 1995 May;7(5):821–833. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Cavarzerani V., Comoretto R., Santini G. Gamma delta T cell receptor-bearing lymphocytes during Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1013–1016. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elloso M. M., van der Heyde H. C., vande Waa J. A., Manning D. D., Weidanz W. P. Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro by human gamma delta T cells. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 1;153(3):1187–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure F., Jitsukawa S., Miossec C., Hercend T. CD1c as a target recognition structure for human T lymphocytes: analysis with peripheral blood gamma/delta cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):703–706. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerlich R., Häcker G., Pfeffer K., Heeg K., Wagner H. Plasmodium falciparum merozoites primarily stimulate the V gamma 9 subset of human gamma/delta T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2613–2616. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodier M. R., Lundqvist C., Hammarström M. L., Troye-Blomberg M., Langhorne J. Cytokine profiles for human V gamma 9+ T cells stimulated by Plasmodium falciparum. Parasite Immunol. 1995 Aug;17(8):413–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1995.tb00909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodier M., Fey P., Eichmann K., Langhorne J. Human peripheral blood gamma delta T cells respond to antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Int Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodier M., Krause-Jauer M., Langhorne J. Quantitative analysis of the response of human T cell receptor V gamma 9+ cells to Plasmodium falciparum. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2757–2760. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groh V., Porcelli S., Fabbi M., Lanier L. L., Picker L. J., Anderson T., Warnke R. A., Bhan A. K., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Human lymphocytes bearing T cell receptor gamma/delta are phenotypically diverse and evenly distributed throughout the lymphoid system. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1277–1294. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Webster H. K., Tongtawe P., Pattanapanyasat K., Weidanz W. P. Increased gamma delta T cells in acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90105-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Romzek N. C., Jia Y., Wagner L., Vila L. M., Chen S. J., Wilson J. M., Karp D. R. MHC-independent presentation of mycobacteria to human gamma delta T cells. Int Immunol. 1993 Nov;5(11):1437–1443. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.11.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Quayle A. J., Skålhegg B. S., Sioud M., Førre O. Selective activation of resting human gamma delta T lymphocytes by interleukin-2. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2092–2099. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Hill A. V., Sambou I., Twumasi P., Castracane J., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Brewster D. R., Greenwood B. M. TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1201–1204. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorne J., Morris-Jones S., Casabo L. G., Goodier M. The response of gamma delta T cells in malaria infections: a hypothesis. Res Immunol. 1994 Jul-Aug;145(6):429–436. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2494(94)80173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Kasahara Y., Taga K., Yachie A., Taniguchi N. Differential expression of CD45RO (UCHL1) and its functional relevance in two subpopulations of circulating TCR-gamma/delta+ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1833–1838. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Pirmez C., Hofman F. M., Torigian V., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific gamma delta T-cell receptors accumulate in human infectious disease lesions. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):544–548. doi: 10.1038/339544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Soboslay P. T., Arnoldi J., Brattig N., Schulz-Key H., Kaufmann S. H. Onchocerca volvulus provides ligands for the stimulation of human gamma/delta T lymphocytes expressing V delta 1 chains. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1241–1247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Fu Y. X., Cranfill R., Dallas A., Ellis C., Reardon C., Lang J., Carding S. R., Kubo R., Born W. Heat shock protein Hsp60-reactive gamma delta cells: a large, diversified T-lymphocyte subset with highly focused specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4348–4352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechhold K., Wesch D., Schondelmaier S., Kabelitz D. Primary activation of V gamma 9-expressing gamma delta T cells by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Requirement for Th1-type CD4 T cell help and inhibition by IL-10. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):4984–4992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussilhon C., Agrapart M., Ballet J. J., Bensussan A. T lymphocytes bearing the gamma delta T cell receptor in patients with acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):283–285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.283-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussilhon C., Agrapart M., Guglielmi P., Bensussan A., Brasseur P., Ballet J. J. Human TcR gamma delta+ lymphocyte response on primary exposure to Plasmodium falciparum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Jan;95(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild H., Mavaddat N., Litzenberger C., Ehrich E. W., Davis M. M., Bluestone J. A., Matis L., Draper R. K., Chien Y. H. The nature of major histocompatibility complex recognition by gamma delta T cells. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieling P. A., Chatterjee D., Porcelli S. A., Prigozy T. I., Mazzaccaro R. J., Soriano T., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B., Kronenberg M., Brennan P. J. CD1-restricted T cell recognition of microbial lipoglycan antigens. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.7542404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Paliard X., Engelhard V. H., de Vries J. E. Cytotoxic activity and lymphokine production of T cell receptor (TCR)-alpha beta+ and TCR-gamma delta+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) clones recognizing HLA-A2 and HLA-A2 mutants. Recognition of TCR-gamma delta+ CTL clones is affected by mutations at positions 152 and 156. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4156–4162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya Y., Bamford R. N., DeFilippis A. P., Waldmann T. A. IL-15: a pleiotropic cytokine with diverse receptor/signaling pathways whose expression is controlled at multiple levels. Immunity. 1996 Apr;4(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Morita C. T., Tanaka Y., Nieves E., Brenner M. B., Bloom B. R. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):155–158. doi: 10.1038/375155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila L. M., Haftel H. M., Park H. S., Lin M. S., Romzek N. C., Hanash S. M., Holoshitz J. Expansion of mycobacterium-reactive gamma delta T cells by a subset of memory helper T cells. Infect Immun. 1995 Apr;63(4):1211–1217. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.4.1211-1217.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyde H. C., Manning D. D., Weidanz W. P. Role of CD4+ T cells in the expansion of the CD4-, CD8- gamma delta T cell subset in the spleens of mice during blood-stage malaria. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6311–6317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]