Abstract
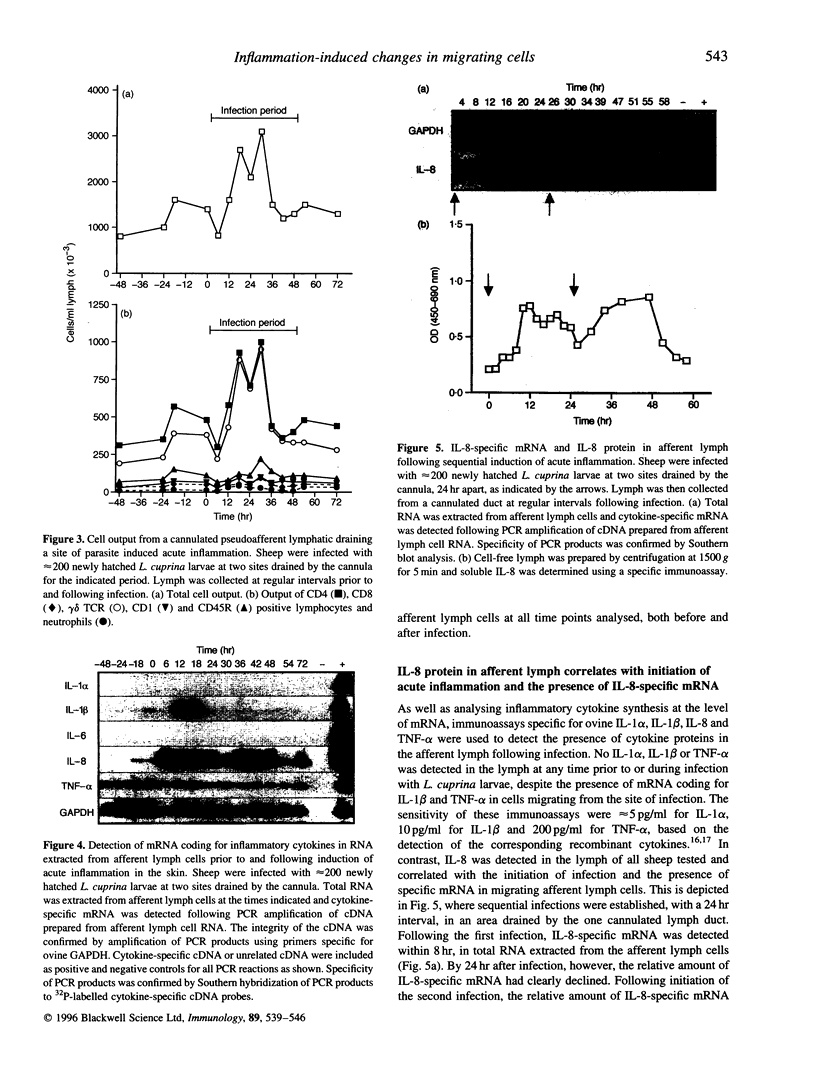
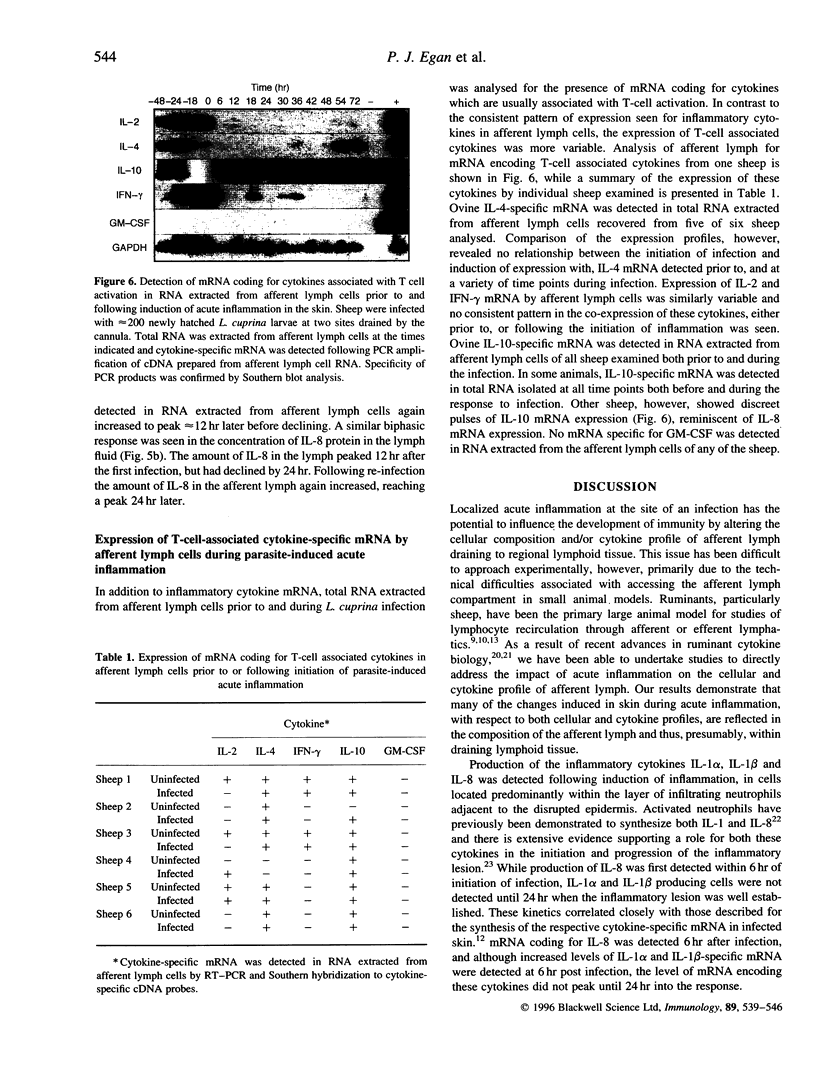
In the present study, we have localized cytokine-secreting cells within an ectoparasite-induced inflammatory lesion and monitored the phenotype and cytokine profile of cells migrating from the inflammatory lesion to the local draining lymph node via the afferent lymphatics. Interleukin (IL)-8-producing cells were first detected in skin within 6 hr of infection, with increased numbers observed at 24 and 48 hr post infection. While these cells were concentrated within the neutrophil influx, adjacent to disrupted epidermis; they were also found scattered throughout the surrounding dermis in areas where significant cellular infiltration was not apparent. IL-1 alpha- and IL-1 beta-producing cells could not be detected until 24 hr after infection and were restricted to areas of intense neutrophil accumulation. Concurrent with the onset of inflammation was a threefold increase in the total number of cells migrating through the draining afferent lymph. This increase in cellularity was due primarily to increased migration of CD4 and gamma delta T cells. Cytokine mRNA synthesis by migrating afferent lymph cells was examined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of RNA extracted prior to, and at regular intervals during the course of the inflammatory response. IL-1 beta and IL-8, but not IL-1 alpha or IL-6 mRNA, was detected in migrating afferent lymph cells. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-specific mRNA was present in migrating afferent lymph cells at all time points both prior to, and following infection. Soluble IL-8 protein, but not IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta or TNF-alpha protein, could be detected in lymph, with the amount of IL-8 detected increasing as the infection progressed. mRNA coding for cytokines associated with T-cell activation, such as IL-2, IL-4 or interferon (IFN)-gamma, was also detected in migrating cells, although the cytokine profiles of different experimental animals were extremely variable.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. E., Barcham G. J., Brandon M. R., Nash A. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of ovine IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):453–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles V. M., Grey S. T., Brandon M. R. Cellular immune responses in the skin of sheep infected with larvae of Lucilia cuprina, the sheep blowfly. Vet Parasitol. 1992 Sep;44(1-2):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(92)90153-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand C. U., Hunziker T., Limat A., Braathen L. R. Large increase of Langerhans cells in human skin lymph derived from irritant contact dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Feb;128(2):184–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb15149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujdoso R., Hopkins J., Dutia B. M., Young P., McConnell I. Characterization of sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells and their role in antigen carriage. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1285–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A. The production of cytokines by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Immunol Today. 1995 Jan;16(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch M., Kimber I. Dermal tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces dendritic cell migration to draining lymph nodes, and possibly provides one stimulus for Langerhans' cell migration. Immunology. 1992 Feb;75(2):257–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan P. J., Andrews A. E., Barcham G. J., Brandon M. R., Nash A. D. Production and application of monoclonal antibodies to ovine interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Jun;41(3-4):241–257. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan P. J., Rothel J. S., Andrews A. E., Seow H. F., Wood P. R., Nash A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to ovine tumor necrosis factor-alpha and development of a sensitive immunoassay. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Jun;41(3-4):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhay M. J., Hanrahan C. F., Bowles V. M., Seow H. F., Andrews A. E., Nash A. D. Cytokine mRNA expression in skin in response to ectoparasite infection. Parasite Immunol. 1994 Sep;16(9):451–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1994.tb00373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. N., McKeever D. J., Sileghem M., Naessens J. Modulation of the phenotype and function of bovine afferent lymph cells during infection with Trypanosoma congolense. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Jan;40(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P., Springer T. A. High endothelial venules (HEVs): specialized endothelium for lymphocyte migration. Immunol Today. 1995 Sep;16(9):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Enhancement of human B cell proliferation and differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2970–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegane H., Miyawaki T., Kato K., Yokoi T., Uehara T., Yachie A., Taniguchi N. A novel subpopulation of CD45RA+ CD4+ T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chain (CD25) and having a functionally transitional nature into memory cells. Int Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1349–1356. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.12.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Chin J., Schmidt J. A., Abbas A. K. Role of interleukin 1 in the activation of T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9699–9703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Marston W. L., Dudler L. Naive and memory T cells show distinct pathways of lymphocyte recirculation. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):801–817. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Marston W., Dudler L. Altered patterns of T cell migration through lymph nodes and skin following antigen challenge. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2205–2210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mwangi D. M., Hopkins J., Luckins A. G. Cellular phenotypes in Trypanosoma congolense infected sheep: the local skin reaction. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Nov;12(6):647–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandeman R. M., Dowse C. A., Carnegie P. R. Initial characterisation of the sheep immune response to infections of Lucilia cuprina. Int J Parasitol. 1985 Apr;15(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(85)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J. Biology of the RANTES/SIS cytokine family. Cytokine. 1991 May;3(3):165–183. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Thoma B., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K. Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: induction of TNF receptors on human T cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Davis M. M., Fazekas de St Groth B. The presence of interleukin 4 during in vitro priming determines the lymphokine-producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1091–1098. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T-cell subsets. Who does the polarizing? Curr Biol. 1995 Aug 1;5(8):849–851. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Weinberg A. D., English M., Huston G. IL-4 directs the development of Th2-like helper effectors. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3796–3806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen A. M., Brandon M. R., Nash A. D. Characterization of the ovine interleukin-2 receptor-alpha chain: differential induction on precultured alpha beta and gamma delta T cells. Immunology. 1993 Jul;79(3):471–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Coulie P. G., Wauters P., Nordan R. P., Van Snick J. B cell growth and differentiation activity of interleukin-HP1 and related murine plasmacytoma growth factors. Synergy with interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):607–612. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]