Abstract
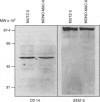
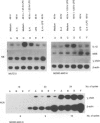
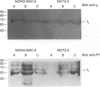
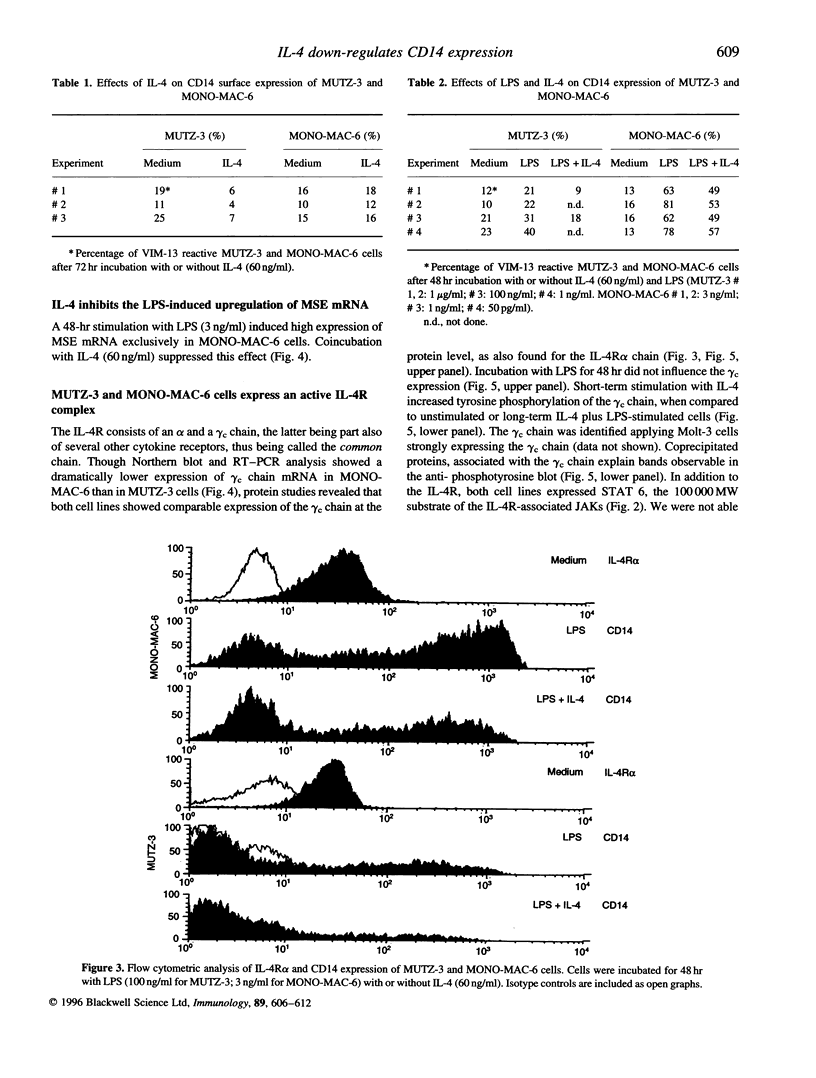
The human monocytic cell lines MUTZ-3 and MONO-MAC-6 express the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) receptor CD14. Paralleling the situation in peripheral blood monocytes (PBMo), recombinant human interleukin-4 (IL-4) down-regulated the expression of CD14 on the cell surface of MUTZ-3, but not that of MONO-MAC-6 cells. In addition, preincubation with IL-4 prevented the LPS-induced up-regulation of IL-1 beta mRNA levels in MUTZ-3, but not in MONO-MAC-6 cells. We examined whether the differential responsiveness of the cell lines was due to the missing expression of the IL-4 receptor (IL-4R) alpha or gamma c chain in MONO-MAC-6 cells. Flow cytometric and immunoprecipitation analysis revealed expression of both IL-4R chains in both cell lines. In addition, short-term stimulation with IL-4 induced tyrosine-phosphorylation of the gamma c chain. As both cell lines also expressed signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT 6), our data suggested that the differential reaction patterns of MUTZ-3 and MONO-MAC-6 cells were not due to a generally defective IL-4R complex. Interestingly, long-term (48 hr) treatment with LPS rendered MONO-MAC-6 cells sensitive to IL-4. LPS up-regulated expression of monocyte-specific esterase (MSE) mRNA as well as CD14 protein in MONO-MAC-6 cells; both effects were inhibited by IL-4. This stimulation was not paralleled by an increase of IL-4R mRNA or protein expression supporting the above hypothesis of a constitutively present and active IL-4R. We discuss possible causes for the differential reaction patterns of MUTZ-3 and MONO-MAC-6 cells to IL-4.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dokter W. H., Esselink M. T., Halie M. R., Vellenga E. Interleukin-4 inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of c-jun and c-fos messenger RNA and activator protein-1 binding activity in human monocytes. Blood. 1993 Jan 15;81(2):337–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. P., Crofford L. J., Freeman S. L., Buras J., Remmers E., Wilder R. L., Fenton M. J. Tissue-specific regulation of IL-6 production by IL-4. Differential effects of IL-4 on nuclear factor-kappa B activity in monocytes and fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5603–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner R., Rhoades K., McBride W. H., Morton D. L., Economou J. S. IL-4 down-regulates IL-1 and TNF gene expression in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3857–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. B., Ma W., Zaborski M., MacLeod R., Quentmeier H., Drexler H. G. Establishment and characterization of two novel cytokine-responsive acute myeloid and monocytic leukemia cell lines, MUTZ-2 and MUTZ-3. Leukemia. 1996 Jun;10(6):1025–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Silvennoinen O. Signaling through the hematopoietic cytokine receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:369–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. H., Fibbe W. E., Wientjens G. J., Van Damme J., Landegent J. E., Willemze R., Kluin-Nelemans J. C. Interleukin 4 down-regulates the expression of CD14 and the production of interleukin 6 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991 Dec;10(6):457–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann R., Ludwig C., Obrist R., Obrecht J. P. Effect of cytokines and lipopolysaccharide on CD14 antigen expression in human monocytes and macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Dec;47(4):317–329. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann R., Zimmerli W., Sansano S., Link S., Hahn A., Glauser M. P., Calandra T. Increased circulating soluble CD14 is associated with high mortality in gram-negative septic shock. J Infect Dis. 1995 Mar;171(3):639–644. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauener R. P., Goyert S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Interleukin 4 down-regulates the expression of CD14 in normal human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2375–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso T., Johnston J. A., Linnekin D., Varesio L., Rowe T. K., O'Shea J. J., McVicar D. W. Regulation of JAK3 expression in human monocytes: phosphorylation in response to interleukins 2, 4, and 7. J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1425–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J., Friedrichs D., Xu H., Peters J. H. IL-4 decreases the expression of the monocyte differentiation marker CD14, paralleled by an increasing accessory potency. Immunobiology. 1991 Aug;182(5):449–464. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Keegan A., Frankel M., Paul W. E., Pierce J. H. Signal transduction through the IL-4 and insulin receptor families. Stem Cells. 1995 Jul;13(4):360–368. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530130407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Aaronson S. A., White M., Pierce J. H. IRS-1: essential for insulin- and IL-4-stimulated mitogenesis in hematopoietic cells. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1591–1594. doi: 10.1126/science.8372354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Velde A. A., Huijbens R. J., Heije K., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Interleukin-4 (IL-4) inhibits secretion of IL-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IL-6 by human monocytes. Blood. 1990 Oct 1;76(7):1392–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]