Abstract
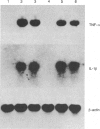
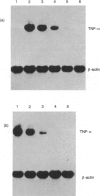
The effects of 3-deazaadenosine (DZA), 3-deaza(+/-)-aristeromycin (DZAri) and 3-deazaneplanocin (DZNep) on tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) production were examined in the mouse macrophage cell line, RAW264.7, stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The 3-deazaadenosine analogues inhibited the TNF-alpha production and the inhibition was dependent upon the concentration of the analogue. DZA reduced the level of TNF-alpha mRNA suggesting that DZA acts at a transcriptional step. In contrast, DZAri and DZNep had little effect on mRNA levels for TNF-alpha, implying that these compounds inhibit a post-transcriptional or translational biosynthetic step of TNF-alpha synthesis. The observation that homocysteine (Hcy) potentiated the DZA inhibition of TNF-alpha production and of TNF-alpha mRNA levels suggests that the inhibition of TNF-alpha production may be caused by elevated levels of 3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine (DZAHcy). The results show that the 3-deazaadenosine analogues are potent inhibitors of TNF-alpha production in the RAW264.7 cell line stimulated with LPS and suggest that these analogues may be effective agents for the treatment of diseases in which TNF-alpha plays an important pathogenic role.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit R. R., Falk W., Cantoni G. L. Inhibition of chemotaxis by S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine in a mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):621–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backlund P. S., Jr, Carotti D., Cantoni G. L. Effects of the S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitors 3-deazaadenosine and 3-deazaaristeromycin on RNA methylation and synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Richards H. H., Cantoni G. L. S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase: analogues of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine as potential inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):939–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endresen P. C., Eide T. J., Aarbakke J. Cell death initiated by 3-deazaadenosine in HL-60 cells is apoptosis and is partially inhibited by homocysteine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 3;46(11):1893–1901. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90629-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer R. I., Hartman K. D., Knode M. C., Richard M. M., Chiang P. K., Tseng C. K., Marquez V. E. 3-Deazaneplanocin: a new and potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and its effects on human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):688–694. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Thompson P., Beutler B. Dexamethasone and pentoxifylline inhibit endotoxin-induced cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis at separate points in the signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):391–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. K., Aksamit R. R., Cantoni G. L. Mechanism of the cytostatic activity of 3-deazaaristeromycin, an inhibitor of adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14726–14729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Spengler M., May M. A., Spengler R., Larrick J., Remick D. Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Sarno E. N., Galilly R., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):699–703. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. J., Silverstein S. C. Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis by methylation inhibitors. Lack of correlation of protein carboxymethylation and phospholipid methylation with phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):546–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Zimmerman T. P., Duncan G. S., Singer K. H., Elion G. B. Inhibition of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis by adenosine analogs. Biochemical studies concerning mechanism of action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 May 15;27(10):1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Zimmerman T. P., Hiemstra K., Winston M., Chu L. C. Adenosine inhibition of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: possible role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1975 Mar 14;187(4180):957–959. doi: 10.1126/science.167434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolos J. A., Frondorf K. A., Esser R. E. Immunosuppression mediated by an inhibitor of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Prevention and treatment of collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):526–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Sternsdorf T., Liese J., Belohradsky B., Weber C., Wedel A., Schreck R., Bäuerle P., Ströbel M. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits NF-kappa B mobilization and TNF production in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6986–6993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Rideout J. L., Wolberg G., Duncan G. S., Elion G. B. 2-Fluoroadenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. A metabolite of 2-fluoroadenosine in mouse cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6757–6766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]