Abstract
As for IgM, human IgA occurs either as soluble molecules in plasma and various other body fluids, or as membrane-bound molecules on differentiated B cells, where they are part of the B-cell receptor for antigen (BCR). We studied the structure of transcripts encoding the membrane-anchored alpha-chain of the human BCR alpha, which may be present in two different forms resulting from alternate splicing of the alpha-chain mRNA (type I or type II). The ratio of type I versus type II did not vary upon stimulation of a B-cell line with various cytokines. Rather, it differed strikingly in cells expressing either the IgA1 or IgA2 isotype of the BCR alpha, with virtually no type II alpha-chain in the latter. Co-modulation experiments also yielded different results for both isotypes, since they demonstrated a physical association of both membrane (m)IgA1 and mIgA2 with CD79b, the beta component of the BCR Ig alpha/Ig beta heterodimer, but only of mIgA1 with CD19. Whatever the isotype, the BCR of the IgA class was able to carry out signal transduction upon cross-linking by specific monoclonal antibodies but, in contrast to mIgM, it relied mainly on the entry of extracellular Ca2+ rather than on the release of intracellular stocks.
Full text
PDF


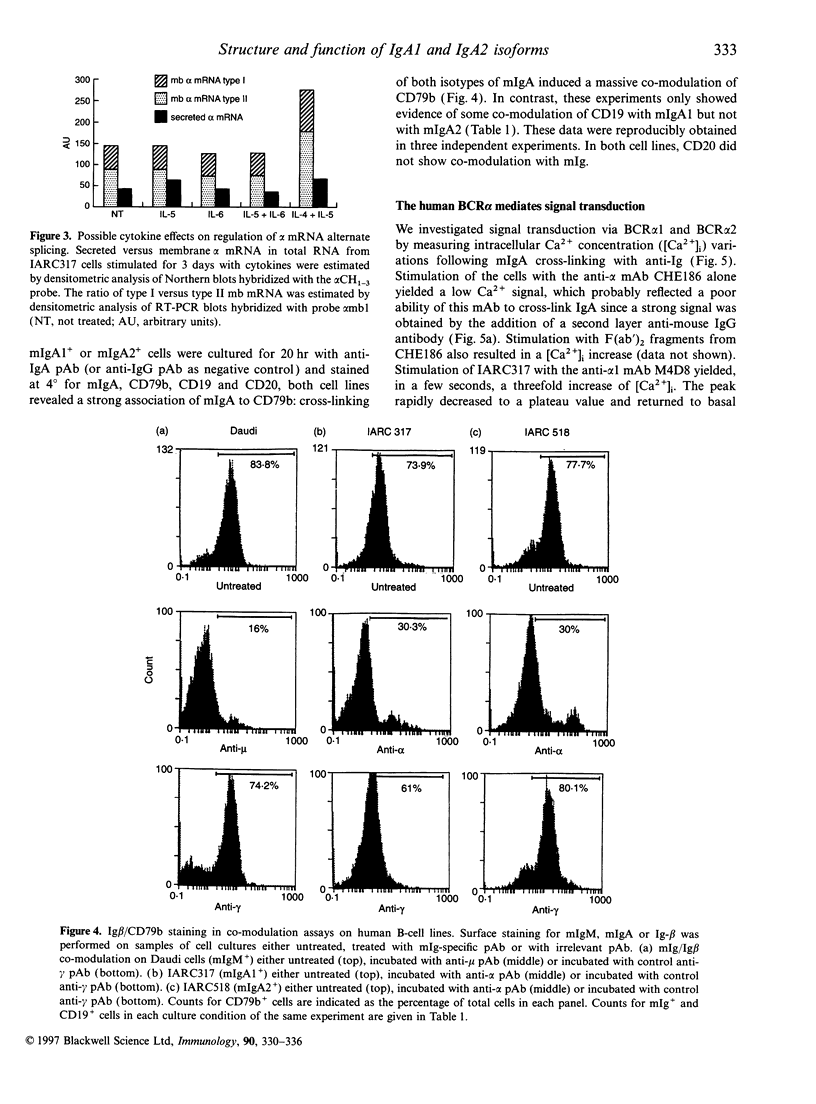
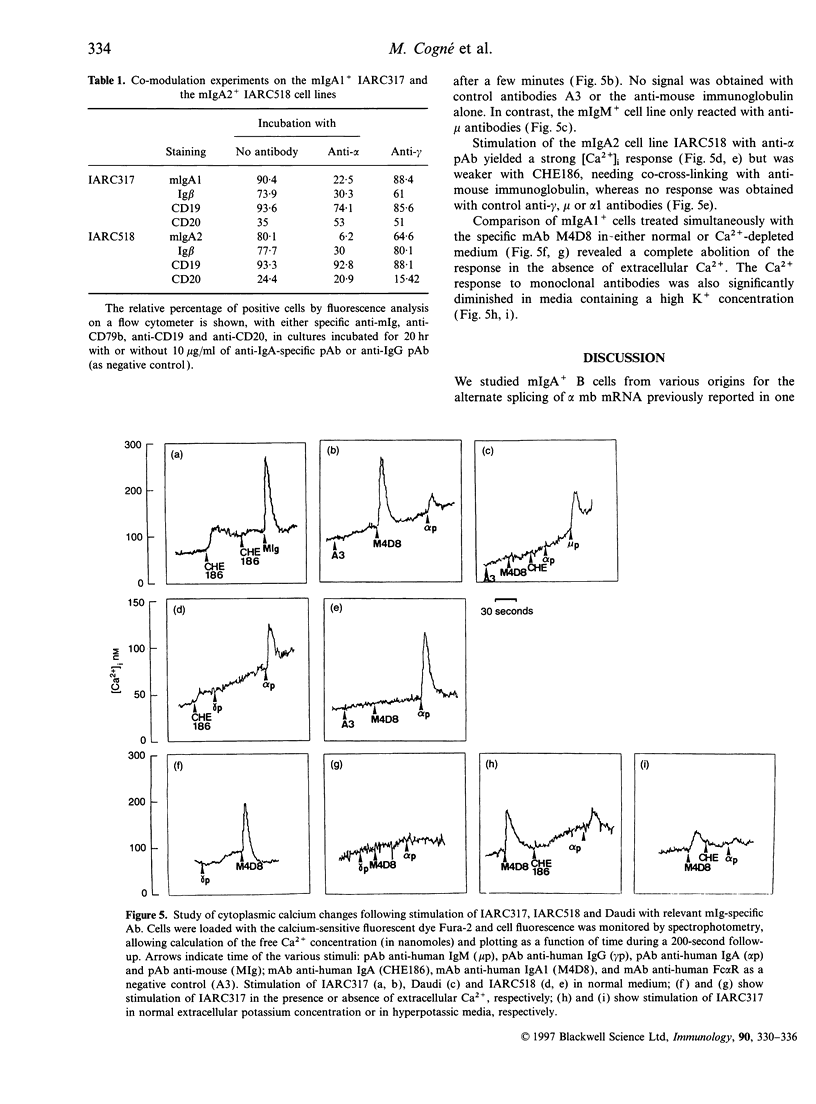


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batista F. D., Efremov D. G., Burrone O. R. Characterization and expression of alternatively spliced IgE heavy chain transcripts produced by peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini J. N., Bertolini J., Thean E., Benson E. M. Human low molecular weight B cell growth factor induces surface IgM+/A- B cells to express and secrete IgA. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1771–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Rigley K. P., Klaus G. G. Cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin on B lymphocytes induces both intracellular Ca2+ release and Ca2+ influx: analysis with indo-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):500–506. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogné M., Preud'homme J. L. Gene deletions force nonsecretory alpha-chain disease plasma cells to produce membrane-form alpha-chain only. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2455–2458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Vanbervliet B., Brière F., Durand I., Rousset F., Banchereau J. Interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor beta cooperate to induce anti-CD40-activated naive human B cells to secrete immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):671–682. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Lefranc M. P., Rabbitts T. H. Mechanisms of divergence and convergence of the human immunoglobulin alpha 1 and alpha 2 constant region gene sequences. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2240–2242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harriman G. R., Kunimoto D. Y., Elliott J. F., Paetkau V., Strober W. The role of IL-5 in IgA B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3033–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishioka C., Yoshida A., Kimata H., Mikawa H. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates immunoglobulin production and growth of human B cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Mar;87(3):504–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justement L. B., Wienands J., Hombach J., Reth M., Cambier J. C. Membrane IgM and IgD molecules fail to transduce Ca2+ mobilizing signals when expressed on differentiated B lineage cells. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3272–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A. The structure and function of human IgA. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):285–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2710285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P., Radl J., Haaijman J. J. Different subclass distribution of IgA-producing cells in human lymphoid organs and various secretory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata H., Fujimoto M. Induction of IgA1 and IgA2 production in immature human fetal B cells and pre-B cells by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Blood. 1995 Apr 15;85(8):2098–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto D. Y., Nordan R. P., Strober W. IL-6 is a potent cofactor of IL-1 in IgM synthesis and of IL-5 in IgA synthesis. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2230–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBaer J., Tsien R. Y., Fahey K. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of the antigen receptor on WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells results in a voltage-independent increase in cytoplasmic calcium. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1836–1844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebman D. A., Nomura D. Y., Coffman R. L., Lee F. D. Molecular characterization of germ-line immunoglobulin A transcripts produced during transforming growth factor type beta-induced isotype switching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3962–3966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebman D. A., Park M. J., Fatica R., Zhang Z. Regulation of usage of membrane and secreted 3' termini of alpha mRNA differs from mu mRNA. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3282–3289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc I., Preud'homme J. L., Cogné M. Structure and expression of the mb-1 transcript in human lymphoid cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(1):141–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall S. L., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Detection of ligand-activated conductive Ca2+ channels in human B lymphocytes. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T. M., Kehry M. R., Snapper C. M. Novel in vitro model for high-rate IgA class switching. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;154(7):3156–3161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiman C. M., D'Ambrosio D., Cambier J. C. The B-cell antigen receptor complex: structure and signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1994 Sep;15(9):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W. Regulation of IgA B-cell development in the mucosal immune system. J Clin Immunol. 1990 Nov;10(6 Suppl):56S–63S. doi: 10.1007/BF00918692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Moldoveanu Z., Koopman W. J., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Cellular origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA: enumeration of single cells secreting polymeric IgA1 and IgA2 in peripheral blood, bone marrow, spleen, gingiva and synovial tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Zhou L. J., Engel P. The CD19/CD21 signal transduction complex of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1994 Sep;15(9):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman A. R., Williams G. T., Dariavach P., Neuberger M. S. The B-cell antigen receptor of the five immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):777–781. doi: 10.1038/352777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe V., Helal A., Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G. Molecular analysis of the T17 immunoglobulin CH multigene deletion (del A1-GP-G2-G4-E). Hum Genet. 1994 May;93(5):520–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00202816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Word C. J., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. The murine immunoglobulin alpha gene expresses multiple transcripts from a unique membrane exon. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):887–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. M., Peng C., Starnes S. M., Liou R. S., Chang T. W. Two isoforms of human membrane-bound alpha Ig resulting from alternative mRNA splicing in the membrane segment. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3932–3936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Noesel C. J., van Lier R. A. Architecture of the human B-cell antigen receptors. Blood. 1993 Jul 15;82(2):363–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]