Abstract
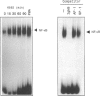
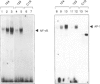
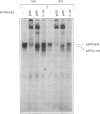
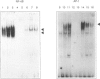
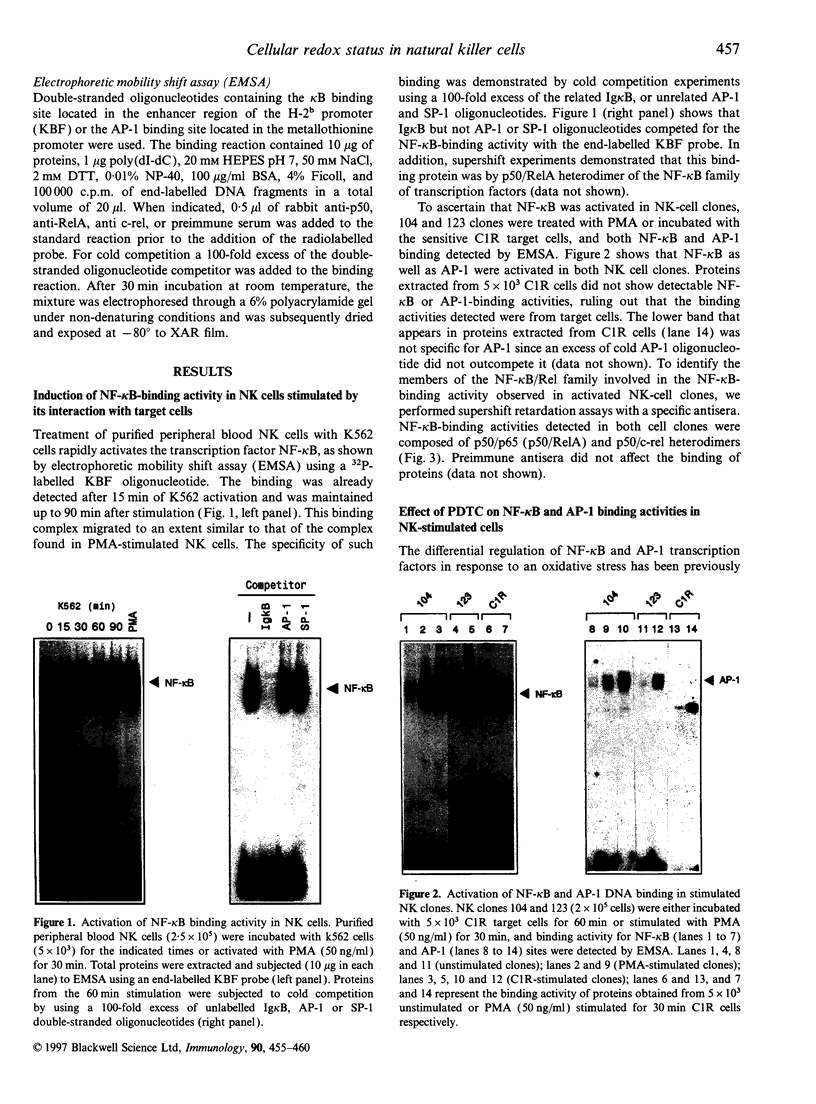
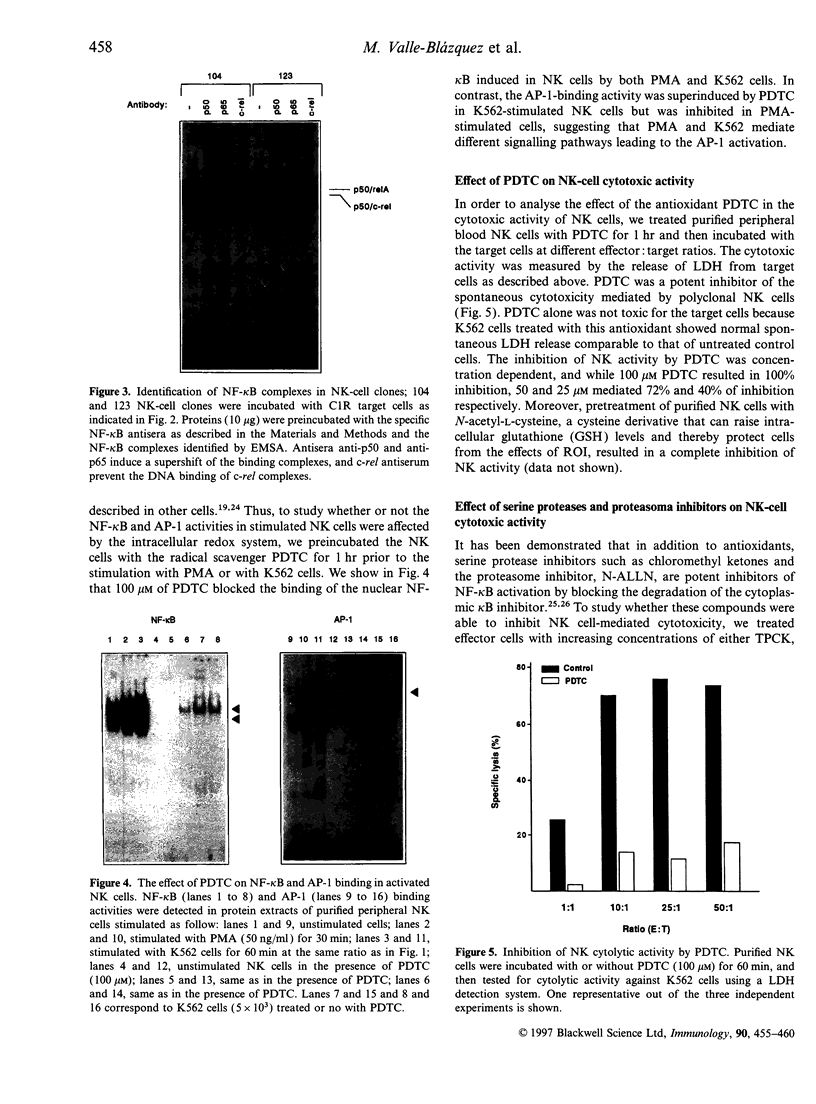
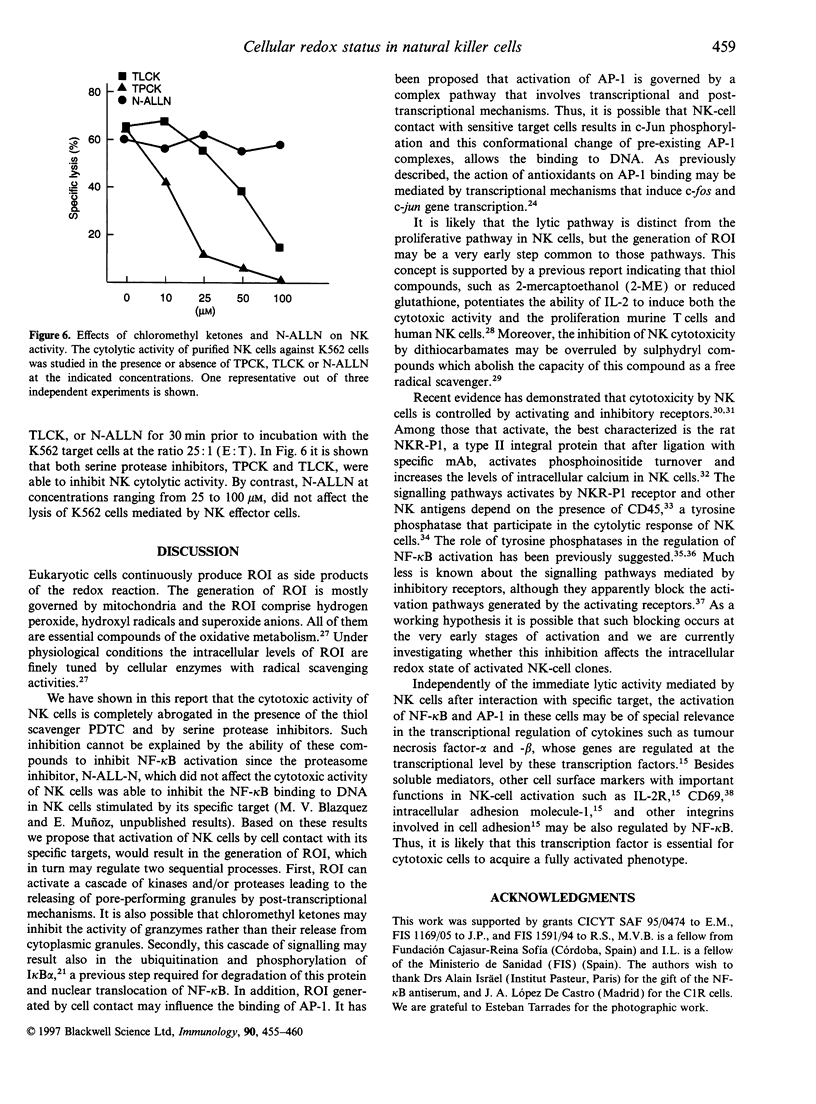
The role of cellular redox status in both cytotoxic activity and NF-kappa B activation in natural killer (NK) cells was investigated. The results indicate that stimulation of NK cells, either freshly isolated from peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) or long-term cultured NK clones, with specific cell targets results in an increased binding activity of NF-kappa B and AP-1 transcription factors measured by gel retardation. Pretreatment of NK cells with the antioxidant pyrrolidine dithiocarbarmate (PDTC) leads to the inhibition of NF-kappa B activation but the AP-1 binding to DNA was superinduced. The inhibition of NF-kappa B by PDTC paralleled with an inhibition of spontaneous cytotoxicity mediated by NK cells. Moreover, the inhibitors of serine proteases, N-alpha-tosyl-L-lysine chloromethyl ketone and N-alpha-tosyl-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone, also blocked the cytolytic activity of NK cells against the sensitive target K562. In contrast, NK activity was not affected by pretreatment of the effector cells with the proteasome inhibitor N-acetyl-leu-leu-norleucinal which selectively inhibits NF-kappa B activation. Altogether, these results support the hypothesis that the activation of NK cells involved transcriptional and post-transcriptional events, and that reactive intermediates may play an important role in the molecular processes related with the generation of a cytotoxic response by NK cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. M., Dethloff G. M., Imboden J. B. CD45-negative mutants of a rat natural killer cell line fail to lyse tumor target cells. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3646–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolhuis R. L., Roozemond R. C., van de Griend R. J. Induction and blocking of cytolysis in CD2+, CD3- NK and CD2+, CD3+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes via CD2 50 KD sheep erythrocyte receptor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):3939–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers W. H., Vujanovic N. L., DeLeo A. B., Olszowy M. W., Herberman R. B., Hiserodt J. C. Monoclonal antibody to a triggering structure expressed on rat natural killer cells and adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1373–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. J., Parent L., Maniatis T. Site-specific phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha by a novel ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity. Cell. 1996 Mar 22;84(6):853–862. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. C., NG J., Nordstedt C., Fredholm B. B., Jondal M. Phosphoinositide breakdown and evidence for protein kinase C involvement during human NK killing. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jun;114(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Hoffman R. R., Curry M. S. Calcium mobilization-associated and independent cytosolic acidification elicited in tandem with Na+/H+ exchanger activation in target cell-adherent human NK cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4766–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Merritt J. A., Jelen P. A., Borden E. C. Effects of diethyldithiocarbamate, an inhibitor of interferon antiviral activity, upon human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2868–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Nolla H. A., Hoffman R. R. Relationship between target cell recognition and temporal fluctuations in intracellular Ca2+ of human NK cells. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):1058–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Abraham R. T., Binstadt B. A., Uehara Y., Leibson P. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation provides an early and requisite signal for the activation of natural killer cell cytotoxic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6279–6283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco T. S., Baldwin A. S. Mechanistic aspects of NF-kappa B regulation: the emerging role of phosphorylation and proteolysis. Immunity. 1995 Sep;3(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A. A role for phosphorylation and degradation in the control of NF-kappa B activity. Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):203–205. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. Inhibitory MHC class I receptors on NK cells and T cells. Immunol Today. 1996 Feb;17(2):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80585-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Ruitenberg J. J., Phillips J. H. Functional and biochemical analysis of CD16 antigen on natural killer cells and granulocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3478–3485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowin B., Hahne M., Mattmann C., Tschopp J. Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):650–652. doi: 10.1038/370650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Muñoz E., Blázquez M. V., Ursa M. A., Santis A. G., Sánchez-Madrid F. Transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding the human C-type lectin leukocyte receptor AIM/CD69 and functional characterization of its tumor necrosis factor-alpha-responsive elements. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21545–21551. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon S. D., Guy G. R., Tan Y. H. Involvement of a putative protein-tyrosine phosphatase and I kappa B-alpha serine phosphorylation in nuclear factor kappa B activation by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18881–18887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ciccone E., Mingari M. C., Biassoni R., Moretta A. Human natural killer cells: origin, clonality, specificity, and receptors. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:341–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman W., Fast L. D., Rose L. M. Blockade of NK cell lysis is a property of monoclonal antibodies that bind to distinct regions of T-200. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1742–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. M., Ortaldo J. R., Shalaby M. R., Svedersky L. P., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Hass P. E., Aggarwal B. B., Herberman R. B., Goeddel D. V. Natural killer-sensitive targets stimulate production of TNF-alpha but not TNF-beta (lymphotoxin) by highly purified human peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2592–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., MacKichan M. L., Israël A. The precursor of NF-kappa B p50 has I kappa B-like functions. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90353-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Manley T. J., Donahue C., Levine H., Ritz J. Costimulatory signals are required for optimal proliferation of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1705–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk H., Klein M., Erdbrügger W., Dröge W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Distinct effects of thioredoxin and antioxidants on the activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1672–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Kraut R. P., Aebersold R., Greenberg A. H. A natural killer cell granule protein that induces DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):553–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Aggarwal B. B. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors block tumor necrosis factor-dependent activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10631–10639. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traenckner E. B., Wilk S., Baeuerle P. A. A proteasome inhibitor prevents activation of NF-kappa B and stabilizes a newly phosphorylated form of I kappa B-alpha that is still bound to NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5433–5441. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Stevenson J. K., Schwarz E. M., Van Antwerp D., Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2723–2735. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside S. T., Ernst M. K., LeBail O., Laurent-Winter C., Rice N., Israël A. N- and C-terminal sequences control degradation of MAD3/I kappa B alpha in response to inducers of NF-kappa B activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5339–5345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Bloom E. T. Requirement of thiol compounds as reducing agents for IL-2-mediated induction of LAK activity and proliferation of human NK cells. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5535–5544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M. Recognition structures on natural killer cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Hengartner H., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Purification and characterization of a cytolytic pore-forming protein from granules of cloned lymphocytes with natural killer activity. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]