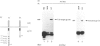Abstract
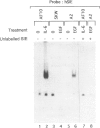
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an important B-cell growth and differentiation factor. IL-6 treatment of the human lymphoblastoid cell line, SKW6.4, leads to increased IgM production. We have previously shown that IL-6 induces activation of JAK1 and JAK2 in human B cell lines. A chimeric IL-6 receptor, comprised of the intracellular tail of the IL-6 receptor subunit gp130 fused to the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor, was stably transfected into SKW6.4 cells. EGF treatment induced IgM production in cells transfected with an intact gp130 cytoplasmic tail, but not in untransfected cells or cells transfected with a cytoplasmic tail lacking all four signal transducers and activators of transcription (Stat) binding sites. Moreover, EGF treatment induced Stat3 phosphorylation in cells transfected with the intact chimeric EGF-gp130 receptor along with induction of DNA-mobility shift of a classical interferon-gamma-activated site. To define further the relation between Stat3 activation and enhanced IgM production, we determined the effect of chimeric gp130 on the transcriptional activation of a genetic element linked to immunoglobulin production, namely the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer (IgH-enhancer). Parental as well as transfected SKW6.4 cells were transiently transfected with an IgH-enhancer-luciferase construct. The transcriptional activity of the IgH-luciferase construct was induced upon ligation of the full-length chimeric receptor but not by truncated gp130 receptors. Moreover, the gp130-induced activity of this reporter gene was abrogated by Stat3EE, a mutant Stat3 incapable of binding DNA. These results indicate that IL-6-induced B-cell differentiation, as measured by IgM production, may be controlled by Stat3 proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Oltz E. M., Young F., Gorman J., Taccioli G., Chen J. VDJ recombination. Immunol Today. 1992 Aug;13(8):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini J. N., Benson E. M. The role of human interleukin-6 in B-cell isotype regulation and differentiation. Cell Immunol. 1990 Jan;125(1):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durbin J. E., Hackenmiller R., Simon M. C., Levy D. E. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faris M., Ensoli B., Stahl N., Yancopoulos G., Nguyen A., Wang S., Nel A. E. Differential activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase, Jun kinase and Janus kinase-Stat pathways by oncostatin M and basic fibroblast growth factor in AIDS-derived Kaposi's sarcoma cells. AIDS. 1996 Apr;10(4):369–378. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199604000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein H., Koerholz D., Chesky L., Fan X. D., Ambrus J. L., Jr Divergent activities of protein kinases in IL-6-induced differentiation of a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):952–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlund A. C., Morales M. O., Viviano B. L., Yan H., Krolewski J., Schreiber R. D. Stat recruitment by tyrosine-phosphorylated cytokine receptors: an ordered reversible affinity-driven process. Immunity. 1995 Jun;2(6):677–687. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guschin D., Rogers N., Briscoe J., Witthuhn B., Watling D., Horn F., Pellegrini S., Yasukawa K., Heinrich P., Stark G. R. A major role for the protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 in the JAK/STAT signal transduction pathway in response to interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1421–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07128.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. M., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr A STAT protein domain that determines DNA sequence recognition suggests a novel DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 15;9(8):984–994. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. Cytokine receptor signalling. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):591–594. doi: 10.1038/377591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 1995 Feb;11(2):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89000-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar G., Gupta S., Wang S., Nel A. E. Involvement of Janus kinases, p52shc, Raf-1, and MEK-1 in the IL-6-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade of a growth-responsive B cell line. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4436–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy E., Kemeny M., Saxon A. Enhanced ELISA: how to measure less than 10 picograms of a specific protein (immunoglobulin) in less than 8 hours. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):3003–3009. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.3263291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Hirano T., Tang B., Matsuda T., Horii Y., Nakajima K., Kishimoto T. The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):332–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Hibi M., Nakagawa N., Nakagawa T., Yasukawa K., Yamanishi K., Taga T., Kishimoto T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.8511589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narazaki M., Witthuhn B. A., Yoshida K., Silvennoinen O., Yasukawa K., Ihle J. N., Kishimoto T., Taga T. Activation of JAK2 kinase mediated by the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Baer R., Hamlyn P. H. Transcription enhancer identified near the human C mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene is unavailable to the translocated c-myc gene in a Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):806–809. doi: 10.1038/306806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall T. D., Lund F. E., Brewer J. W., Aldridge C., Wall R., Corley R. B. Interleukin-5 (IL-5) and IL-6 define two molecularly distinct pathways of B-cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3929–3936. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal M. C., Liu Z. Y., Hirano T., Mayer L., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 induces secretion of IgG1 by coordinated transcriptional activation and differential mRNA accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer T. S., Sanders L. K., Nathans D. Cooperative transcriptional activity of Jun and Stat3 beta, a short form of Stat3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9097–9101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Wang L., Rayanade R., Pan H., Margulies L. Interleukin-6-type cytokines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 21;762:1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidell N., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Saxon A. Retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition of a human myeloma cell line via down-regulation of IL-6 receptors. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3809–3814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Farruggella T. J., Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Yancopoulos G. D. Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1349–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7871433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Yuan J., Lottspeich F., Müller-Esterl W., Schindler C., Roeb E., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The interleukin-6-activated acute-phase response factor is antigenically and functionally related to members of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) family. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3186–3196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]