Abstract
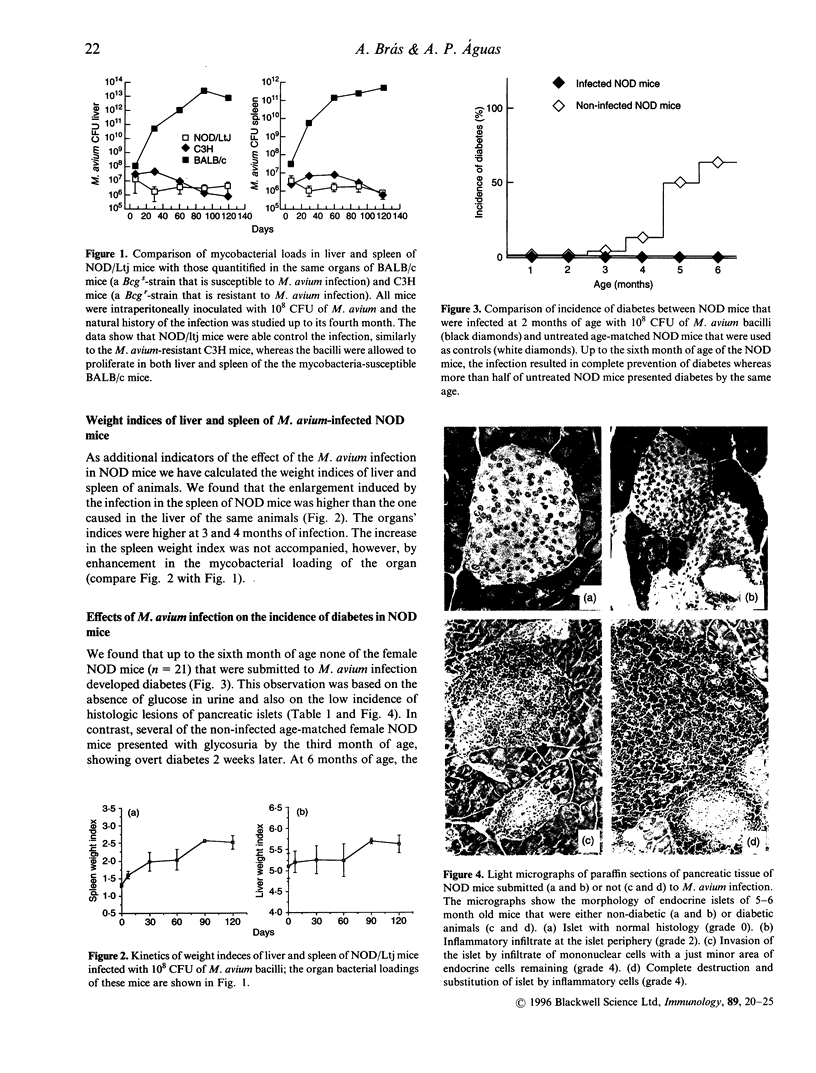
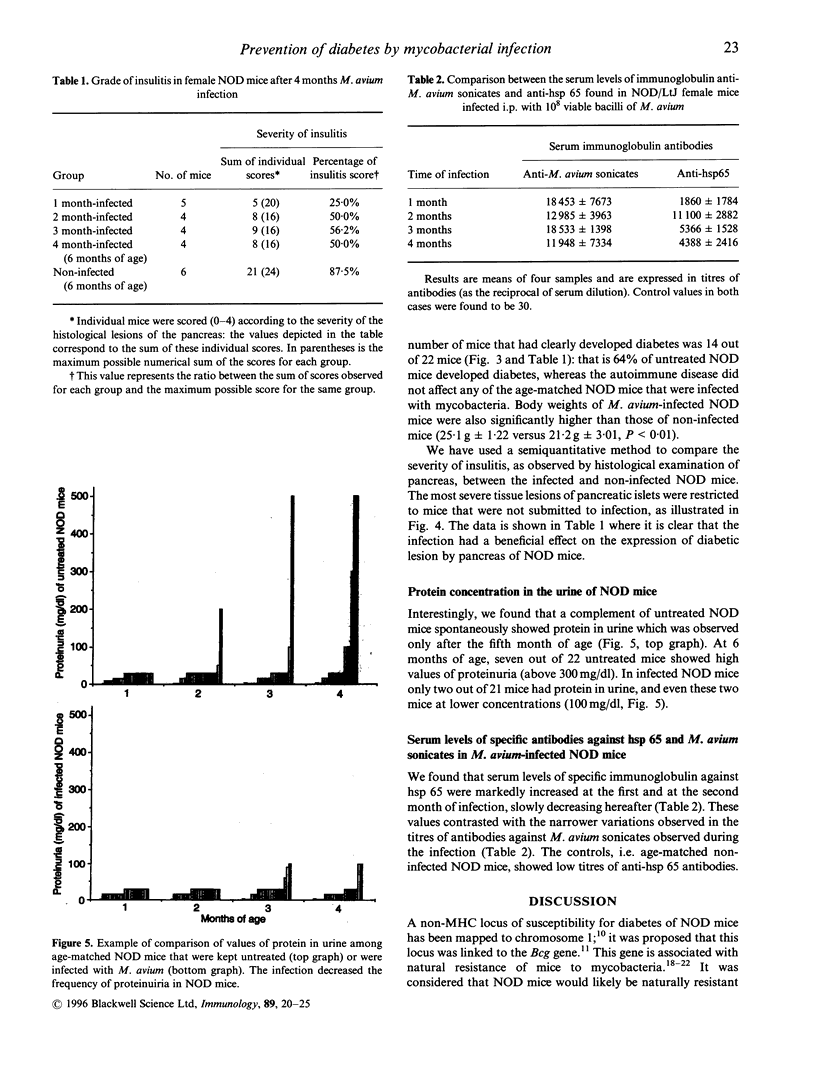
It was recently proposed that the diabetes genes of non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice are linked to the Bcg gene that is associated with resistance to infection by mycobacteria; however, it has not been established whether NOD mice are resistant or susceptible to the infection, although there are previous investigations on response of NOD mice to other intracellular parasites (e.g. Kaye et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 22: 357-364). We have investigated here this question, as well as the consequences of mycobacterial infection on the natural history of murine diabetes. Female NOD mice were intraperitoneally infected with 10(8) viable bacilli of Mycobacterium avium at 2 months of age, i.e. before the mice show diabetes; they were studied up to the sixth month of age (when more than half of untreated female NOD mice show glycosuria). To determine whether NOD mice were susceptible or resistant to M. avium infection, we have compared the kinetics of bacterial growths in liver and spleen of the mice with those determined in M. avium-susceptible (BALB/c) and resistant (C3H) strains of mice. NOD mice were able to control the M. avium infection, following a pattern similar to that observed in infected C3H mice. The mycobacterial infection prevented the expression of diabetes in all of the infected NOD mice and it also decreased the incidence of proteinuria in the treated mice. The infected NOD mice showed a marked enhancement in antibodies against the 65,000 mycobacteria antigen (heat-shock protein (hsp) 65) up to the second month of infection and these elevated titres slowly decreased in the following months; anti-hsp 65 antibodies were not detected in age-matched controls. This is the first demonstration that NOD mice are naturally resistant to mycobacterial infection, and we reinforce evidence on the role of immune response triggered by mycobacteria and its hsp 65 antigen in prevention of diabetes in NOD mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguas A., Esaguy N., Sunkel C. E., Silva M. T. Cross-reactivity and sequence homology between the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial heat shock protein and human lactoferrin, transferrin, and DR beta subsets of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1461–1470. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1461-1470.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg R., Sarmento A. M. The role of macrophage activation and of Bcg-encoded macrophage function(s) in the control of Mycobacterium avium infection in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):324–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F. Immunosuppressive therapy of autoimmune diseases. Immunol Today. 1993 Jun;14(6):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90053-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter A. G., Healey D., Cooke A. Mycobacteria precipitate autoimmune rheumatic disease in NOD mice via an adjuvant-like activity. Scand J Immunol. 1994 Jun;39(6):602–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk O. S., Cohen I. R. T-cell autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Dec;5(6):903–909. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90104-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Autoimmunity to chaperonins in the pathogenesis of arthritis and diabetes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:567–589. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornall R. J., Prins J. B., Todd J. A., Pressey A., DeLarato N. H., Wicker L. S., Peterson L. B. Type 1 diabetes in mice is linked to the interleukin-1 receptor and Lsh/Ity/Bcg genes on chromosome 1. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):262–265. doi: 10.1038/353262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Markovits D., Reshef T., van der Zee R., Cohen I. R. Induction and therapy of autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic (NOD/Lt) mouse by a 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Reshef T., Birk O. S., van der Zee R., Walker M. D., Cohen I. R. Vaccination against autoimmune mouse diabetes with a T-cell epitope of the human 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3088–3091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esaguy N., Aguas A. P. Prevention of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by neonatal bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Apr;104(1):103–107. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.d01-655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esaguy N., Freire O., Van Embden J. D., Aguas A. P. Lactoferrin triggers in vitro proliferation of T cells of Lewis rats submitted to mycobacteria-induced adjuvant arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Aug;38(2):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esaguy N., Macedo P. M., Castro A. P., Aguas A. P. Acquisition of autoimmunity genes by New Zealand mice is associated with natural resistance to infection by mycobacteria. J Autoimmun. 1992 Oct;5(5):641–651. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90160-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garchon H. J., Bedossa P., Eloy L., Bach J. F. Identification and mapping to chromosome 1 of a susceptibility locus for periinsulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):260–262. doi: 10.1038/353260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Yates M. D. Infections caused by opportunist mycobacteria: a review. J R Soc Med. 1986 Apr;79(4):226–229. doi: 10.1177/014107688607900411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Genetic control of natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2417–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Hopewell P. C., Yajko D. M., Hadley W. K., Lazarus E., Mohanty P. K., Modin G. W., Feigal D. W., Cusick P. S., Sande M. A. Natural history of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Cooke A., Lund T., Wattie M., Blackwell J. M. Altered course of visceral leishmaniasis in mice expressing transgenic I-E molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):357–364. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston A. E., Hicks C. A., Colston M. J., Billingham M. E. A 71-kD heat shock protein (hsp) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis has modulatory effects on experimental rat arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Jan;103(1):77–82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.929628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo D., Vogan K., Vidal S., Hu J., Cellier M., Schurr E., Fuks A., Bumstead N., Morgan K., Gros P. Haplotype mapping and sequence analysis of the mouse Nramp gene predict susceptibility to infection with intracellular parasites. Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):51–61. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale S. D., Byrd L. T., Southern P. M., Jockusch J. D., Cal S. X., Wynne B. A. Incidence of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex bacteremia in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1082–1085. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Genetic control of natural resistance to nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.56-62.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin H. Y., Sadelain M. W., Hitchon C., Lauzon J., Singh B. Complete Freund's adjuvant-induced T cells prevent the development and adoptive transfer of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):2072–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragno S., Winrow V. R., Mascagni P., Lucietto P., Di Pierro F., Morris C. J., Blake D. R. A synthetic 10-kD heat shock protein (hsp10) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis modulates adjuvant arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Mar;103(3):384–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1996.tb08291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadelain M. W., Qin H. Y., Lauzon J., Singh B. Prevention of type I diabetes in NOD mice by adjuvant immunotherapy. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):583–589. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Appelberg R., Silva M. N., Macedo P. M. In vivo killing and degradation of Mycobacterium aurum within mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2006–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2006-2016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Macedo P. M. The interpretation of the ultrastructure of mycobacterial cells in transmission electron microscopy of ultrathin sections. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1983 Jun;51(2):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Matsumoto M., Kishimoto Y., Makino S., Harada M. Possible mechanism of the preventive effect of BCG against diabetes mellitus in NOD mouse. II. Suppression of pathogenesis by macrophage transfer from BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1991 Nov;138(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Matsumoto M., Suzuki S., Misaki R., Suzuki R., Makino S., Harada M. Possible mechanism of the preventive effect of BCG against diabetes mellitus in NOD mouse. I. Generation of suppressor macrophages in spleen cells of BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1991 Nov;138(1):130–141. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Cohen I. Antigenic mimicry between mycobacteria and cartilage proteoglycans: the model of adjuvant arthritis. Concepts Immunopathol. 1987;4:144–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]