Abstract
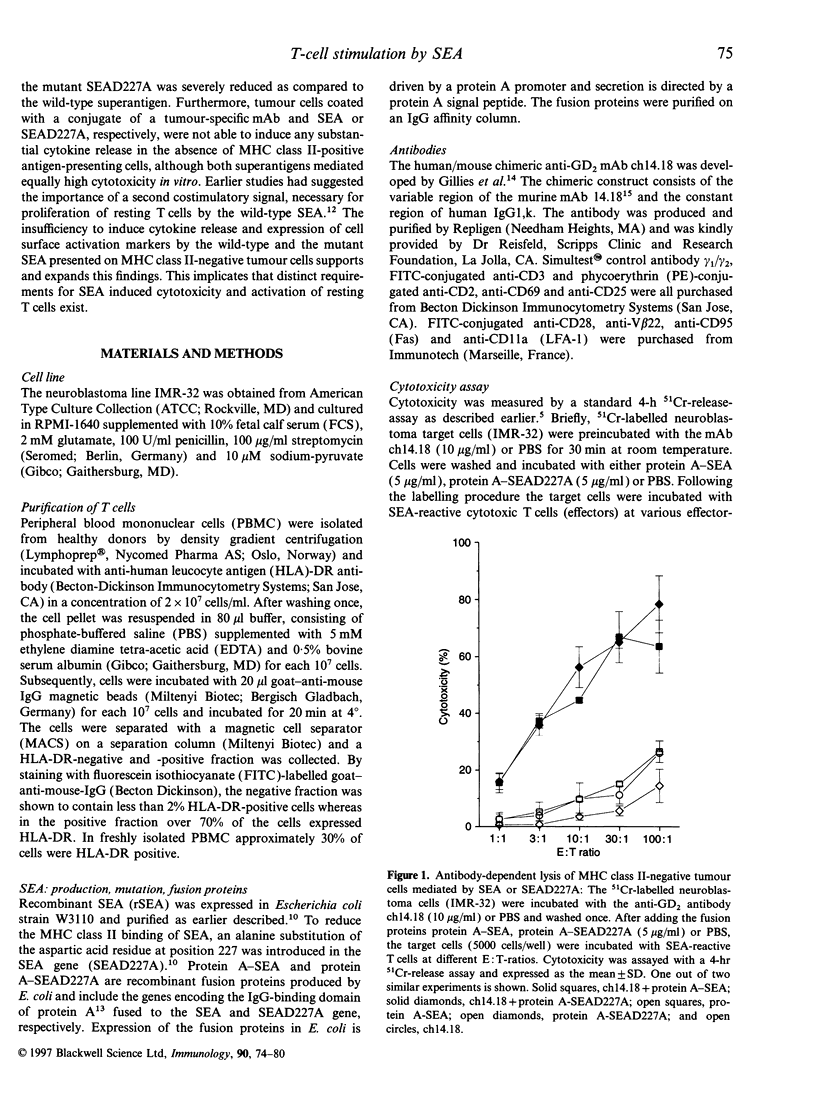
Previous work demonstrated that human cytotoxic T cells activated by superantigens can lyse major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-positive target cells as well as MHC class II-negative tumour cells coated with conjugates of monoclonal antibodies and superantigens. In order to decrease MHC class II affinity, and therefore unwanted binding of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) to MHC class II molecules, a point mutation was introduced into the SEA gene. This mutation (SEAD227A) resulted in an approximately 3-log reduction of affinity to human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DR, but cytotoxicity mediated by this mutant superantigen towards antibody-labelled tumour cells is as efficient as cytotoxicity mediated by the native superantigen. We therefore compared the T-cell activating potency of native and mutated SEA. Our data show that SEAD227A is 4- to 5-log less effective than native SEA when activation of resting T cells is assayed in terms of blast formation, expression of cell surface activation markers and cytokine release. Furthermore, presenting either SEA or SEAD227A to MHC class II-negative mononuclear cells by MHC class II-negative tumour cells did not result in significant blast formation of T cells, up-regulation of CD25 or cytokine release. This suggests that lysis of MHC class II-negative tumour cells is efficiently induced by monoclonal antibody targeted superantigen, while activation of resting T cells requires additional co-stimulatory signals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahmsén L., Dohlsten M., Segrén S., Björk P., Jonsson E., Kalland T. Characterization of two distinct MHC class II binding sites in the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 3;14(13):2978–2986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Klussman K., Leytze G., Linsley P. S. Proliferation of human T lymphocytes induced with superantigens is not dependent on costimulation by the CD28 counter-receptor B7. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hansson J., Ohlsson L., Litton M., Kalland T. Antibody-targeted superantigens are potent inducers of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9791–9795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Akerblom E., Lando P. A., Kalland T. Monoclonal antibody-targeted superantigens: a different class of anti-tumor agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9287–9291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Kalland T. Staphylococcal-enterotoxin-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunol Today. 1991 May;12(5):147–150. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80043-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Björk P., Abrahmsén L., Ohlsson L., Lind P., Kalland T. Immunotherapy of human colon cancer by antibody-targeted superantigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1995 Sep;41(3):162–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01521342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Hedlund G., Trowsdale J., Kalland T. Targeting of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes to MHC class II-expressing cells by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):96–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Sundstedt A., Björklund M., Hedlund G., Kalland T. Superantigen-induced cytokines suppress growth of human colon-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 May 28;54(3):482–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H. T cell stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Clonally variable response and requirement for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on accessory or target cells. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1697–1707. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Lo K. M., Wesolowski J. High-level expression of chimeric antibodies using adapted cDNA variable region cassettes. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. M., Turka L. A., June C. H., Thompson C. B. CD28 and staphylococcal enterotoxins synergize to induce MHC-independent T-cell proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1992 Nov;145(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J., Holzer U., Krull F., Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Niethammer D., Dannecker G. E. Antibody-targeted superantigens induce lysis of major histocompatibility complex class II-negative T-cell leukemia lines. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T. Cell adhesion molecules are co-receptors for staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced T-cell activation and cytokine production. Immunol Lett. 1994 Feb;39(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagoo A. S., Lagoo-Deenadayalan S., Lorenz H. M., Byrne J., Barber W. H., Hardy K. J. IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma gene expression versus secretion in superantigen-activated T cells. Distinct requirement for costimulatory signals through adhesion molecules. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1641–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Brodin T., Sansom D., Kalland T. Co-stimulation with B7 and targeted superantigen is required for MHC class II-independent T-cell proliferation but not cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1993 Oct;80(2):236–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Dohlsten M., Ohlsson L., Kalland T. Tumor-reactive superantigens suppress tumor growth in humanized SCID mice. Int J Cancer. 1995 Aug 9;62(4):466–471. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litton M. J., Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Kalland T., Ohlsson L., Andersson J., Andersson U. Antibody-targeted superantigen therapy induces tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, excessive cytokine production, and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jan;26(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehindate K., Thibodeau J., Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Sékaly R. P., Mourad W. Cross-linking of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules by staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen is a requirement for inflammatory cytokine gene expression. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1573–1577. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujoo K., Cheresh D. A., Yang H. M., Reisfeld R. A. Disialoganglioside GD2 on human neuroblastoma cells: target antigen for monoclonal antibody-mediated cytolysis and suppression of tumor growth. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):1098–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell K. A., Ellenhorn J. D., Bruce D. S., Bluestone J. A. In vivo T-cell activation by staphylococcal enterotoxin B prevents outgrowth of a malignant tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Moks T., Jansson B., Abrahmsén L., Elmblad A., Holmgren E., Henrichson C., Jones T. A., Uhlén M. A synthetic IgG-binding domain based on staphylococcal protein A. Protein Eng. 1987 Feb-Mar;1(2):107–113. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schad E. M., Zaitseva I., Zaitsev V. N., Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Schlievert P. M., Ohlendorf D. H., Svensson L. A. Crystal structure of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin type A. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3292–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



