Abstract
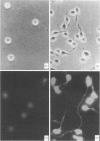
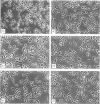
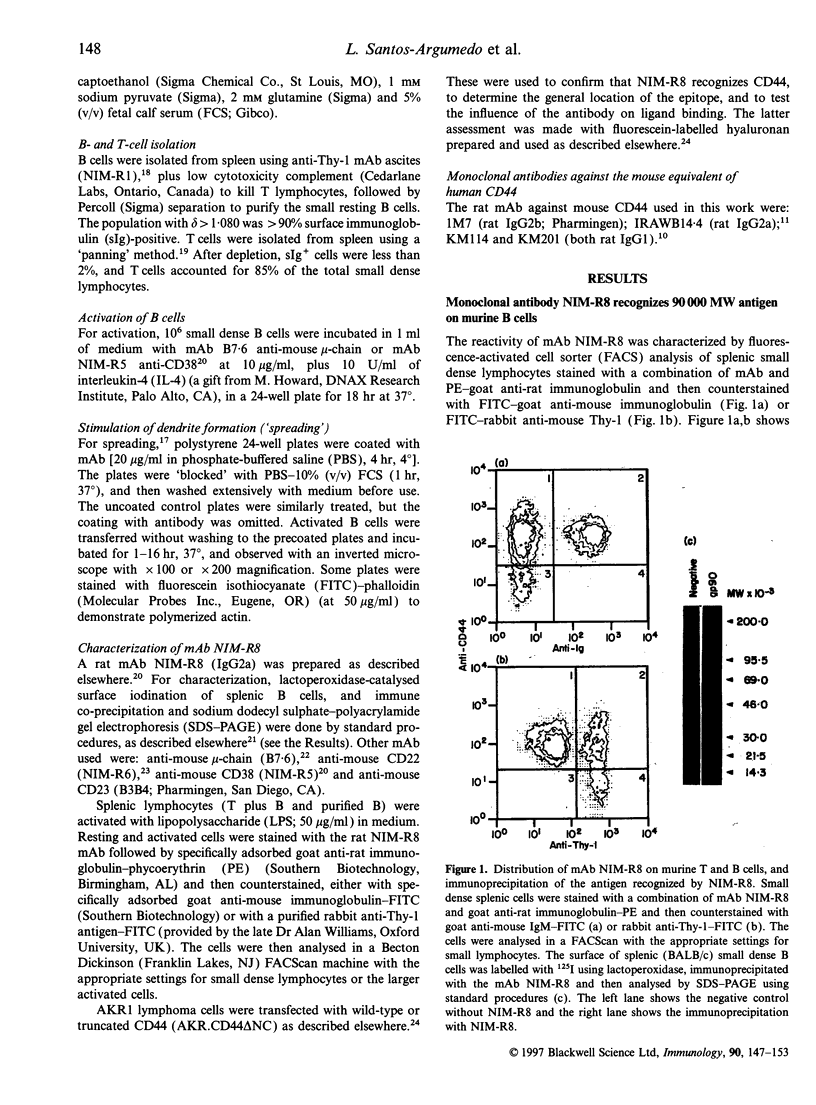
A rat monoclonal antibody (mAb) (NIM-R8), insolubilized by binding to plastic plates, induced a rapid and extensive formation of dendrite processes ('spreading') in B lymphocytes activated by anti-IgM and interleukin-4 (IL-4) or anti-CD38 and IL-4. In contrast, resting B cells were unable to spread similarly on the NIM-R8-coated plates. The NIM-R8 antibody recognized a 90,000 MW surface glycoprotein (gp90) present on both B and T lymphocytes. The expression of this molecule was greatly increased after polyclonal (lipopolysaccharide, anti-IgM plus IL-4 or concanavalin A) activation. The NIM-R8 mAb with or without IL-2 or IL-4 was unable to induce proliferation of splenic lymphocytes. Following the demonstration that the NIM-R8 mAb recognizes the murine equivalent of human CD44, the induction of spreading of activated B lymphocytes was studied using a panel of mAb recognizing different epitopes of murine CD44. All of these different mAb induced similar spreading of activated B cells. The ligand-inducible spreading of activated B lymphocytes may be an important mechanism for providing an increased cell-surface area for cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions, and thus may be an important factor controlling the response of activated lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abney E. R., Hunter I. R., Parkhouse R. M. Preparation and characterisation of an antiserum to the mouse candidate for immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):404–406. doi: 10.1038/259404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolazzi A., Peach R., Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I. Interaction between CD44 and hyaluronate is directly implicated in the regulation of tumor development. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):53–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Lehmann K. R. Ia-mediated signal transduction leads to proliferation of primed B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):877–886. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chayen A., Parkhouse R. M. Preparation and properties of a cytotoxic monoclonal rat anti-mouse Thy-1 antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1982;49(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. How B and T cells talk to each other. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):425–428. doi: 10.1038/367425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinchy B., Elenström C., Severinson E., Möller G. T and B cell collaboration: induction of motility in small, resting B cells by interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1445–1451. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock K. S., Hirano H., Murakami S., Hodes R. J. CD44 expression on activated B cells. Differential capacity for CD44-dependent binding to hyaluronic acid. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6712–6722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Q., Lesley J., Hyman R., Ishihara K., Kincade P. W. Molecular isoforms of murine CD44 and evidence that the membrane proximal domain is not critical for hyaluronate recognition. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horst E., Meijer C. J., Radaskiewicz T., van Dongen J. J., Pieters R., Figdor C. G., Hooftman A., Pals S. T. Expression of a human homing receptor (CD44) in lymphoid malignancies and related stages of lymphoid development. Leukemia. 1990 May;4(5):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M. The role of the cytoplasmic domain in regulating CD44 function. J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107(Pt 9):2353–2359. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Heusser C. H., Hartmann K. U. Induction of resting B cells to DNA synthesis by soluble monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Aug;14(8):753–757. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Muirhead M. J., Dailey M. O. Expression of the CD11/CD18, leukocyte adhesion molecule 1, and CD44 adhesion molecules during normal myeloid and erythroid differentiation in humans. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelner G. S., Kennedy J., Bacon K. B., Kleyensteuber S., Largaespada D. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Bazan J. F., Moore K. W., Schall T. J. Lymphotactin: a cytokine that represents a new class of chemokine. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1395–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.7973732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman G., Heider K. H., Horst E., Adolf G. R., van den Berg F., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Pals S. T. Activated human lymphocytes and aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas express a homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):897–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremmidiotis G., Zola H. Changes in CD44 expression during B cell differentiation in the human tonsil. Cell Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;161(2):147–157. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., He Q., Miyake K., Hamann A., Hyman R., Kincade P. W. Requirements for hyaluronic acid binding by CD44: a role for the cytoplasmic domain and activation by antibody. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):257–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., Hyman R., Kincade P. W. CD44 and its interaction with extracellular matrix. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:271–335. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Tarin D. Significance of CD44 gene products for cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93077-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Medina K. L., Hayashi S., Ono S., Hamaoka T., Kincade P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Pgp-1/CD44 block lympho-hemopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):477–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Underhill C. B., Lesley J., Kincade P. W. Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):69–75. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Underhill C. B., Lesley J., Kincade P. W. Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):69–75. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Argumedo L., Teixeira C., Preece G., Kirkham P. A., Parkhouse R. M. A B lymphocyte surface molecule mediating activation and protection from apoptosis via calcium channels. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3119–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Aruffo A., Amiot M., Seed B. The hematopoietic and epithelial forms of CD44 are distinct polypeptides with different adhesion potentials for hyaluronate-bearing cells. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):343–348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Guo Y. J., Stamenkovic I. Distinct effects of two CD44 isoforms on tumor growth in vivo. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):859–866. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres R. M., Law C. L., Santos-Argumedo L., Kirkham P. A., Grabstein K., Parkhouse R. M., Clark E. A. Identification and characterization of the murine homologue of CD22, a B lymphocyte-restricted adhesion molecule. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2641–2649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Oishi K., Sato N., Sagara J., Kawai A., Tsukita S. ERM family members as molecular linkers between the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 and actin-based cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):391–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahalka M. A., Okon E., Gosslar U., Holzmann B., Naor D. Lymph node (but not spleen) invasion by murine lymphoma is both CD44- and hyaluronate-dependent. J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5345–5355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]