Abstract
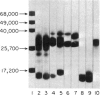
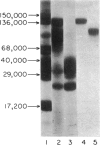
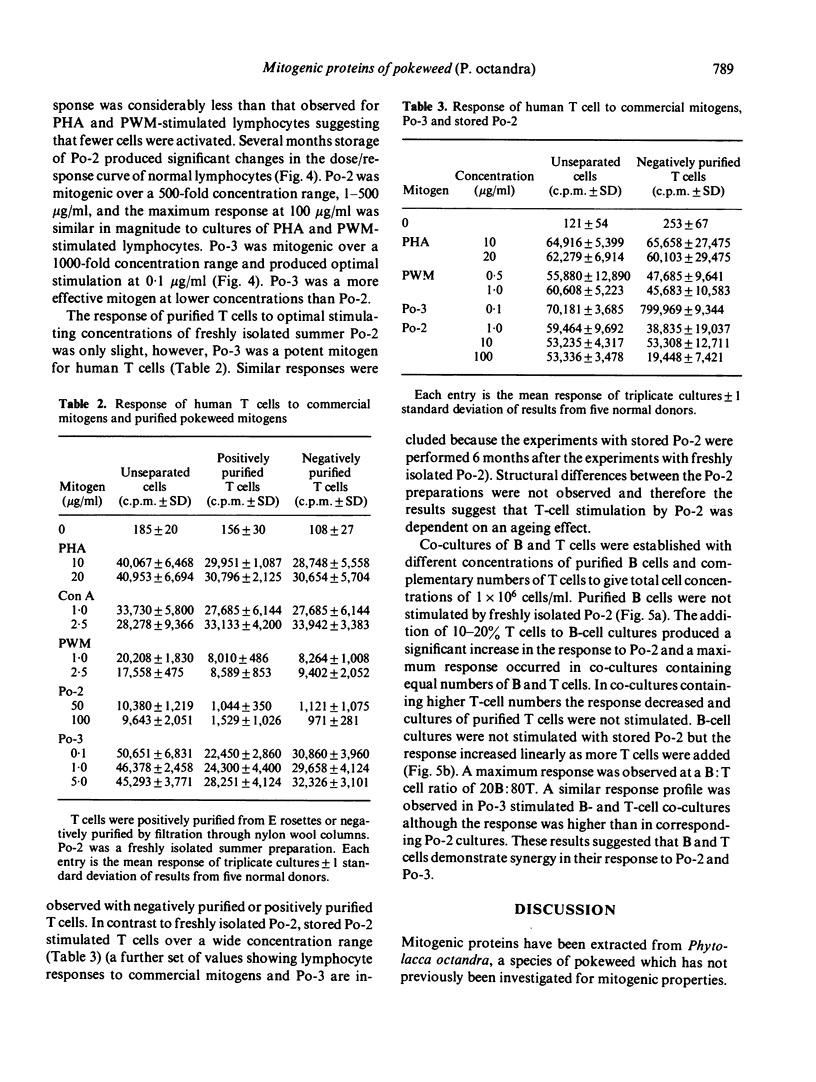
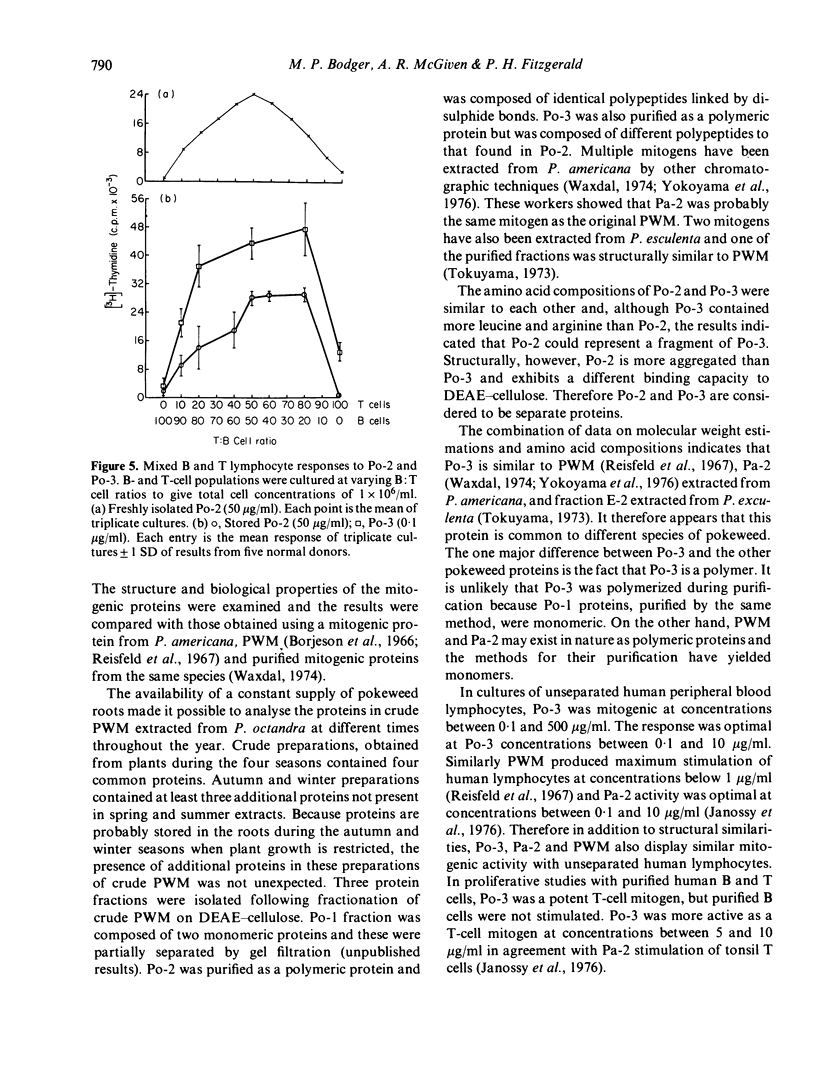
Saline extracts from the roots of the pokeweed species. Phytolacca octandra were separated by ion-exchange chromatography into three fractions, Po-1, Po-2 and Po-3. Po-1 contained two monomeric proteins with molecular weights of 36,000 and 29,000 and these were partially purified by gel filtration. Po-2 was purified as a single polymeric protein composed of approximately ten 14,000 mol. wt polypeptides and is a new pokeweed mitogen. Po-3 was purified as a single polymeric protein composed of approximately four 31,000 mol. wt subunits, and apart from its polymeric structure closely resembles commercial pokeweed mitogen (PWM). Po-2 and Po-3 were mitogenic for unseparated human peripheral blood lymphocytes but the degree of mitogenic activity in Po-2 preparations was dependent on storage following purification. Purified B cells were not stimulated by either mitogen. Po-3 was a potent mitogen for T cells but preparations of Po-2 required storage before they stimulated T cells. Higher responses were observed in co-cultures of B and T cells than in separated B and T cell cultures. It is suggested that human B and T lymphocytes show synergy in their responses to Po-2 and Po-3.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker B. E., Farnes P., LaMarche P. H. Peripheral blood plasmacytosis following systemic exposure to Phytolacca americana (pokweed). Pediatrics. 1966 Sep;38(3):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Börjeson J., Reisfeld R., Chessin L. N., Welsh P. D., Douglas S. D. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. I. Biological and physicochemical properties of the pokeweed mitogen. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):859–872. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Quantitative isolation of human T and B cells and response to mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessin L. N., Börjeson J., Welsh P. D., Douglas S. D., Cooper H. L. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. II. Morphological and biochemical studies on the transformation of lymphocytes by pokeweed mitogen. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):873–884. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clot J., Massip H., Mathieu O. In Vitro studies on human B and T cell purified populations. Stimulation by mitogens and allogeneic cells, and quantitative binding of phytomitogens. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):445–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Fudenberg H. H. In vitro development of plasma cells from lymphocytes following pokeweed mitogen stimulation: a fine structural study. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Feb;54(2):277–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARNES P., BARKER B. E., BROWNHILL L. E., FANGER H. MITOGENIC ACTIVITY IN PHYTOLACCA AMERICANA (POKEWEED). Lancet. 1964 Nov 21;2(7369):1100–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Purification of human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):420–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G., Doenhoff M. Selective triggering of human T and B lymphocytes in vitro by polyclonal mitogens. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Gomez De La Concha E., Waxdal M. J., Platts-Mills T. The effects of purified mitogenic proteins (Pa-1 and Pa-2) from pokeweed on human T and B lymphocytes in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):108–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. F. Lymphocyte activation. I. Response of T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Oct;9(4):483–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. Functional analysis of murine and human B lymphocyte subsets. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:177–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellstedt H. In vitro activation of human T and B lymphocytes by pokeweed mitogen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B., Roitt I. M. Evidence for transformation of human B lymphocytes by PHA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):254–256. doi: 10.1038/newbio241254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Börjeson J., Chessin L. N., Small P. A., Jr Isolation and characterization of a mitogen from pokeweek (Phytolacca americana). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2020–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Basham T. Y. B and T-cell stimulatory activities of multiple mitogens from pokeweed. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):163–164. doi: 10.1038/251163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J. Isolation, characterization, and biological activities of five mitogens from pokeweed. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3671–3677. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. T. Direct evidence for the response of B and T cells to pokeweed mitogen. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Yano O., Terao T., Osawa T. Purification and biological activities of pokeweek (Phytolacca americana) mitogens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]