Abstract
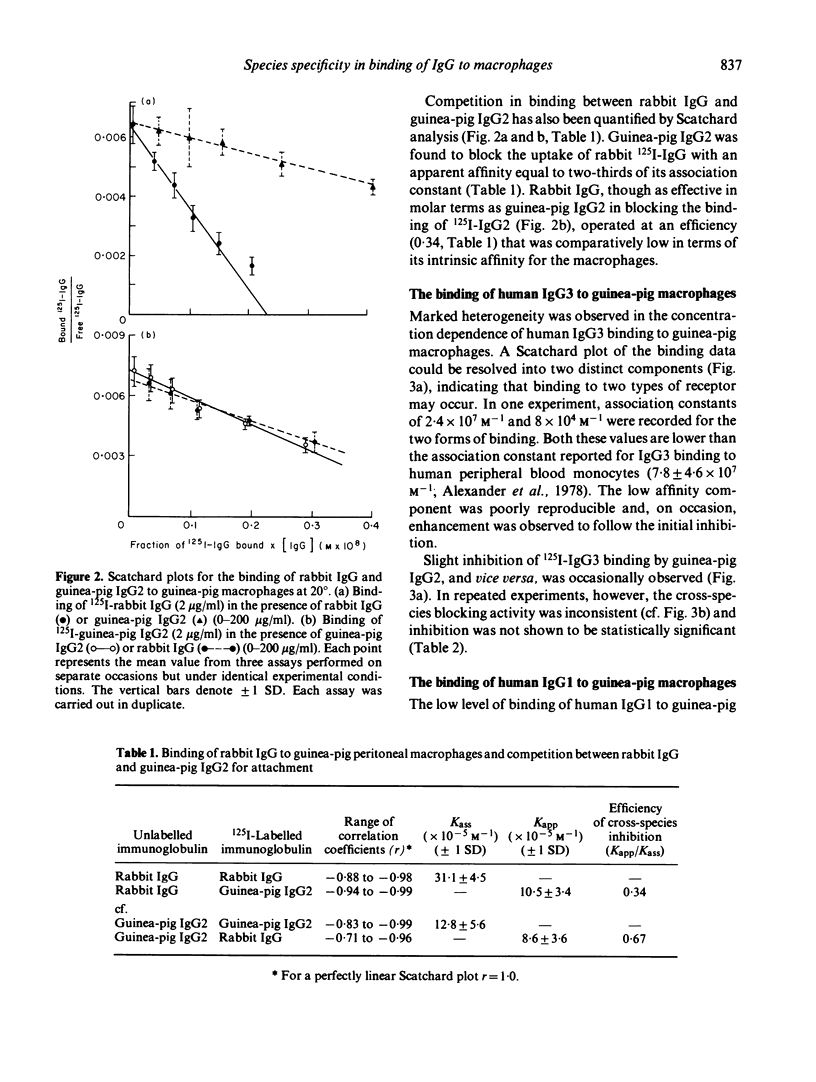
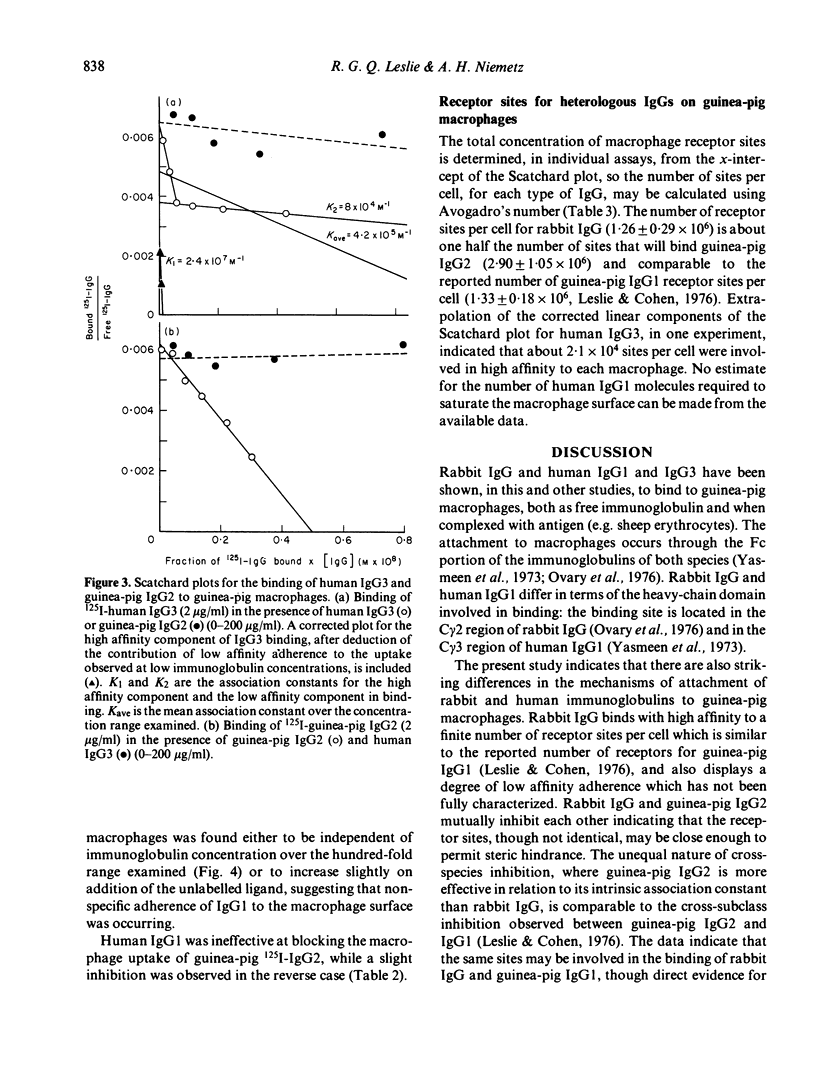
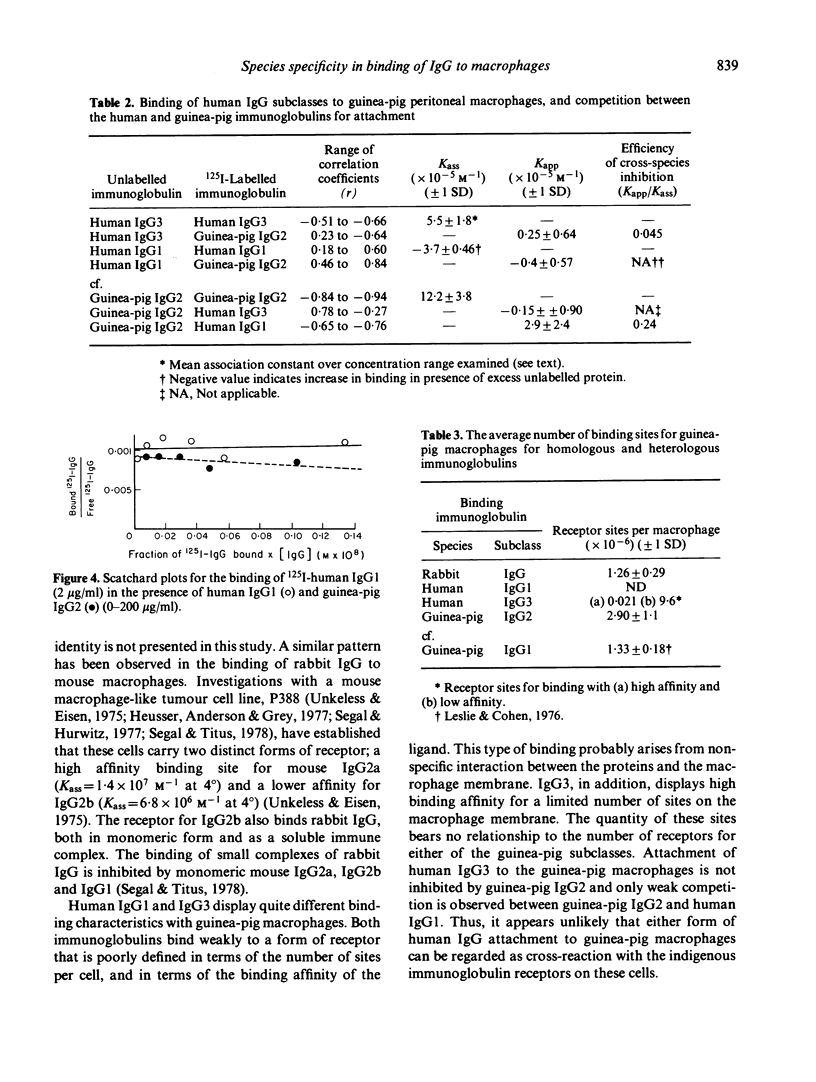
The binding of human IgG1 and IgG3 and rabbit IgG to guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages was examined, and differences between the species, in terms of their binding mechanisms, were characterized. Rabbit IgG bound with high affinity (Kass = 3.11 +/- 0.45 x 10(6) M-1) to a finite number of receptor sites per cell (1.26 +/- 0.29 x 10(6)) and competitively inhibited the binding of guinea-pig IgG2. Heterogeneity in binding, with distinct high and low affinity components, was observed when human IgG3 was reacted with guinea-pig macrophages, while human IgG1 exhibited only low affinity binding. Neither human IgG subclass competed effectively with guinea-pig IgG2 for its cell receptor. Thus, rabbit IgG appeared to cross-react with a macrophage receptor for guinea-pig immunoglobulin, whereas the human IgG subclasses bound to macrophage membrane components that remained undefined.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. D., Andrews J. A., Leslie R. G., Wood N. J. The binding of human and guinea-pig IgG subclasses to homologous macrophage and monocyte Fc receptors. Immunology. 1978 Jul;35(1):115–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaafar H. A., Doyle J. Specificity of macrophage receptors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):121–123. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganczakowski M., Leslie R. G. The binding of rabbit IgG and its enzymatically derived fragments to homologous peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):487–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C. H., Anderson C. L., Grey H. M. Receptors for IgG: subclass specificity of receptors on different mouse cell types and the definition of two distinct receptors on a macrophage cell line. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1316–1327. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Cohen S. Chemical properties of guinea-pig immunoglobulins gamma-1 G, gamma-2 G and gamma M. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):787–795. doi: 10.1042/bj1200787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Cohen S. Cytophilic activity of IgG2 from sera of unimmunized guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):577–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onyewotu I. I., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. Detection and radioassay of soluble circulating immune complexes using guinea pig peritoneal exudate cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 8;248(5444):156–159. doi: 10.1038/248156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovary Z., Saluk P. H., Quijada L., Lamm M. E. Biologic activities of rabbit immunoglobulin G in relation to domains of the Fc region. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1265–1271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., Coe J. E. The immune response in the hamster. VII. Studies on cytophilic immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Titus J. A. The subclass specificity for the binding of murine myeloma proteins to macrophage and lymphocyte cell lines and to normal spleen cells. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1395–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Eisen H. N. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulins to Fc receptors of mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1520–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. The presence of two Fc receptors on mouse macrophages: evidence from a variant cell line and differential trypsin sensitivity. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):931–945. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


