Abstract
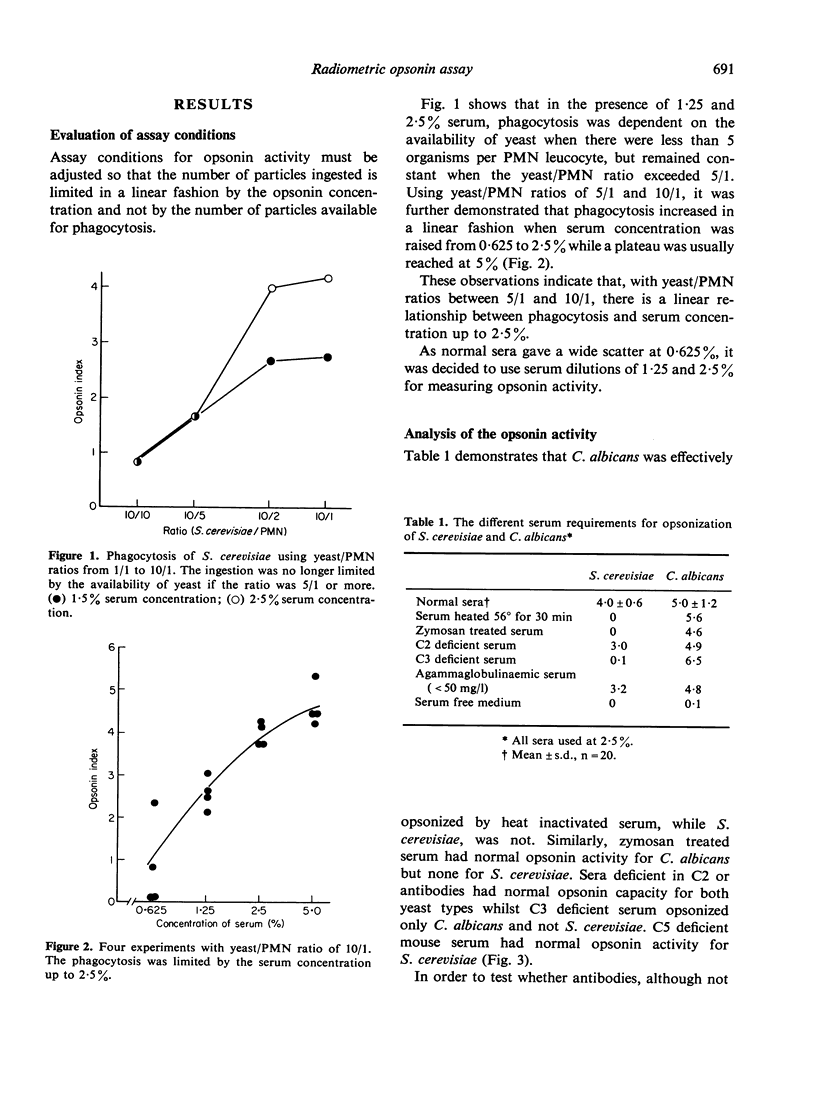
A new semiquantitative radiometric opsonin assay is described. It was found that the opsonin activity generated by incubating brewer's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in medium containing less than 5% human serum was exclusively complement dependent. In contrast, C. albicans was effectively opsonized in the absence of complement. Antibodies and the early classical complement pathway did not contribute to the opsonization of S. cerevisiae and neither did C5-9. The brewer's yeast assay can therefore be used for measuring selectively the opsonizing capacity of the alternative pathway. Sera from approximately 7% of apparently healthy adult controls consistently failed to generate significant opsonin activity while 8 out of 26 patients with suspected immune deficiency of unknown cause were defective in this assay. All opsonin deficient sera so far tested had haemolytically normal alternative pathway and Factor B activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Miller M. E., Nilsson U. R. A familial deficiency of the phagocytosis-enhancing activity of serum related to a dysfunction of the fifth component of complement (C5). N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 12;282(7):354–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002122820702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Harvey B. A. A defect of the alternative pathway of complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):30–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Harvey B. A. Defective opsonization. A common immunity deficiency. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Feb;51(2):91–99. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.2.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F. President's address. Some intrinsic and extrinsic factors predisposing to allergy. Proc R Soc Med. 1976 Jun;69(6):439–442. doi: 10.1177/003591577606900617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Evaluation of opsonic and leukocyte function with a spectrophotometric test in patients with infection and with phagocytic disorders. Blood. 1973 Jul;42(1):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


