Abstract
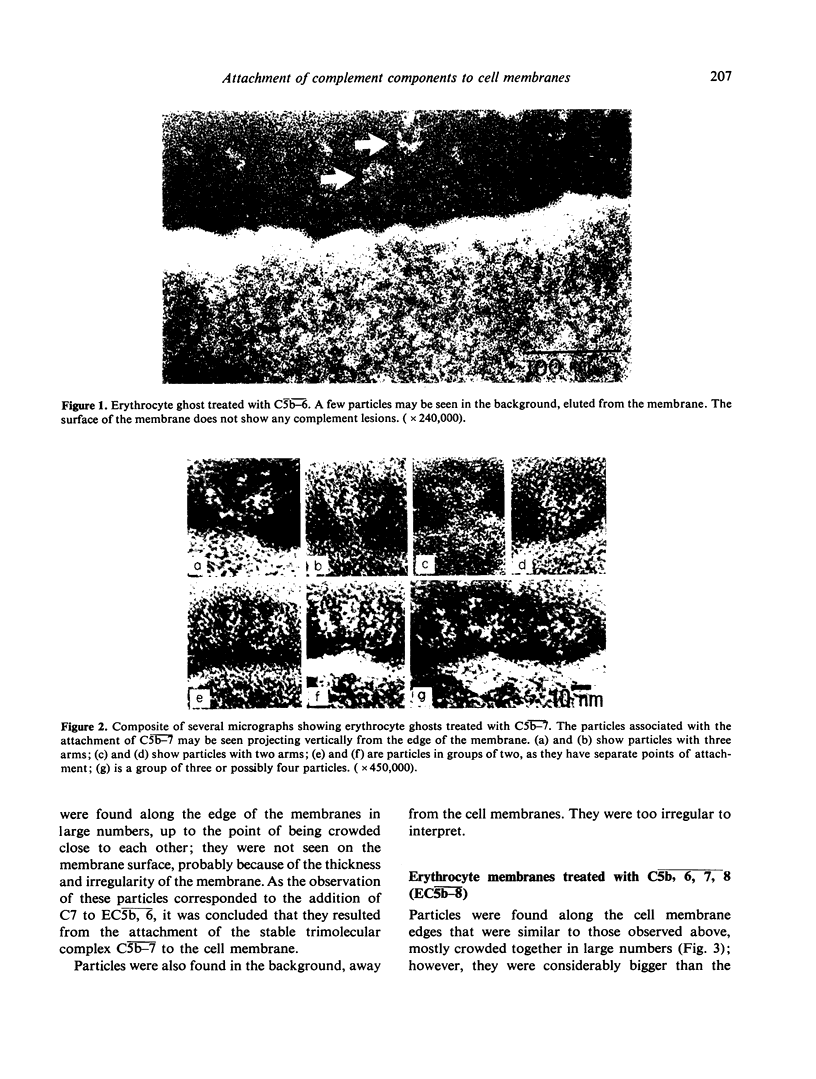
Electron microscopic study of the events occurring at the cell membrane during reactive lysis by complement, showed that a foliaceous particle was formed at the C5b-7 stage, that enlarged to a particle with a variable number of arms at the C5b-8 stage. Up to this point, no typical complement lesions were found. At the C5b-9 stages, the particles were completely converted to typical complement lesions, i.e. hollow cylinders projecting from the cell membrane and partly penetrating it. C5b-9 complexes assembled in the fluid phase did not show the typical structure of the lesions, but were amorphous masses of fibres.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Dourmashkin R. R., Humphrey J. H. Observations on the mechanism of immune hemolysis: importance of immunoglobulin class and source of complement on the extent of damage. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1502–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Nicholson A., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cytolysis by complement: evidence on insertion of C5b and C7 subunits of the C5b,6,7 complex into phospholipid bilayers of erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Shin M. L., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cell membrane damage by complement: evidence on insertion of polypeptide chains from C8 and C9 into the lipid bilayer of erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Dourmashkin R. R. The lesions in cell membranes caused by complement. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:75–115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H. The nature of complement-induced lesions in membranes. Haematologia (Budap) 1972;6(3):319–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Reversible interactions among the five native components in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):428–437. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Bowyer D. E., Nicol P., Dawson R. M., Munn E. A. Studies on the terminal stages of complement lysis. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):135–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Munn E. A., Weissmanng Complement-mediated lysis of liposomes produced by the reactive lysis procedure. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):983–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Weed R. I., Leddy J. P. Complement-induced ultrastructural membrane lesions: requirement for terminal components. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Feldman J. D. Production of ultrastructural membrane lesions by the fifth component of complement. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):53–62. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dourmashkin R., Humphrey J. H. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. 3. The membrane defects caused by complement lysis. J Exp Med. 1966 Jun 1;123(6):969–984. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by C: exposure of hydrophobic sites on activated C proteins. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirchia G., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of AET-treated normal red cells (PNH-like cells). Nature. 1967 Aug 12;215(5102):747–748. doi: 10.1038/215747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Lachmann P. J. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. I. The characterization of the indicator factor and its identification as C7. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):629–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








