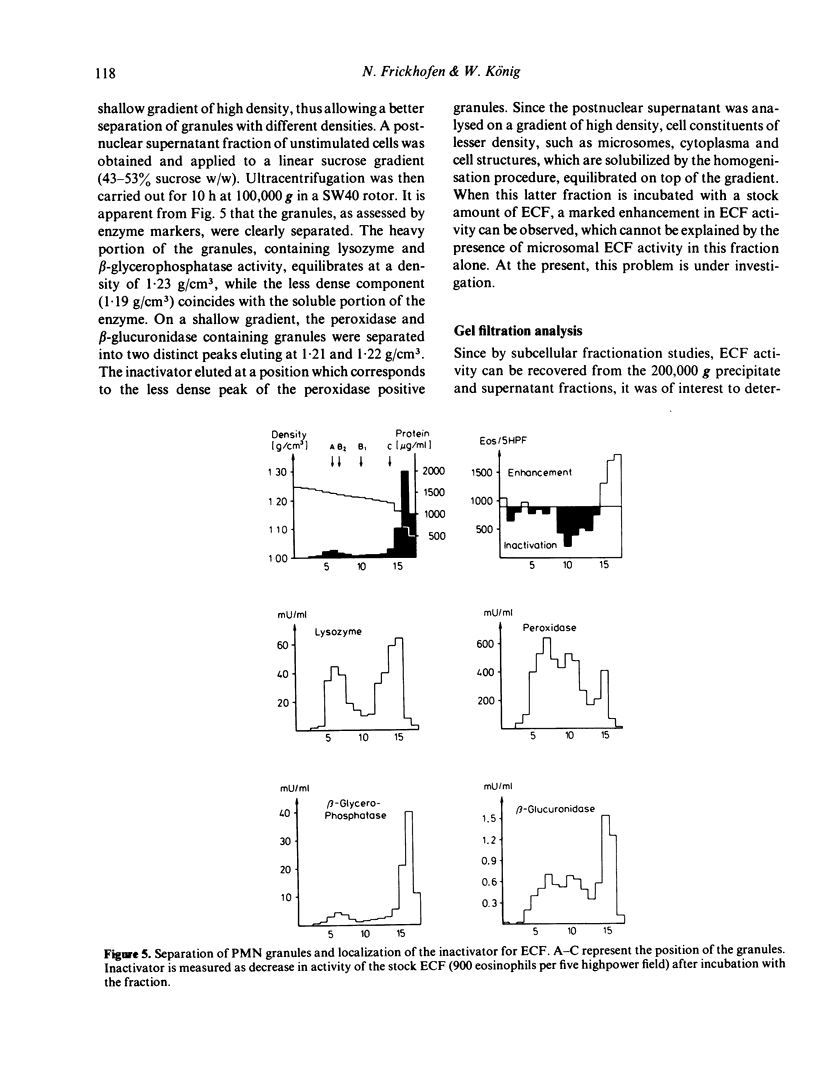
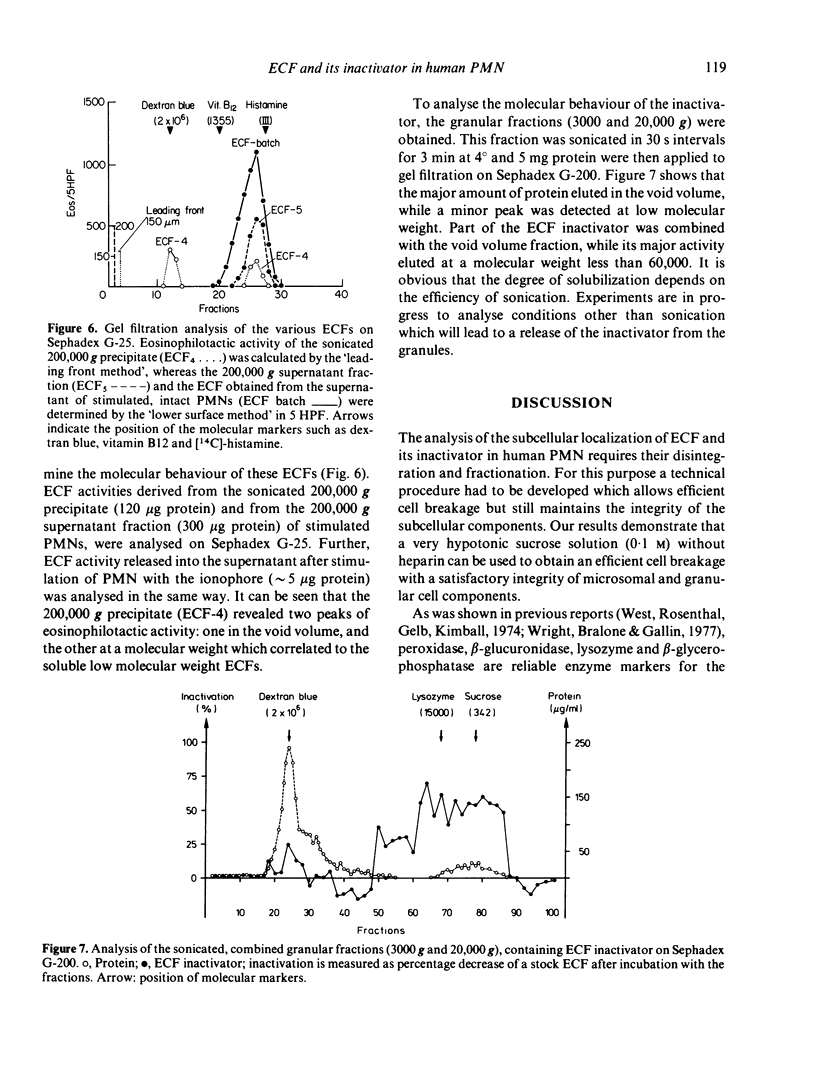
Abstract
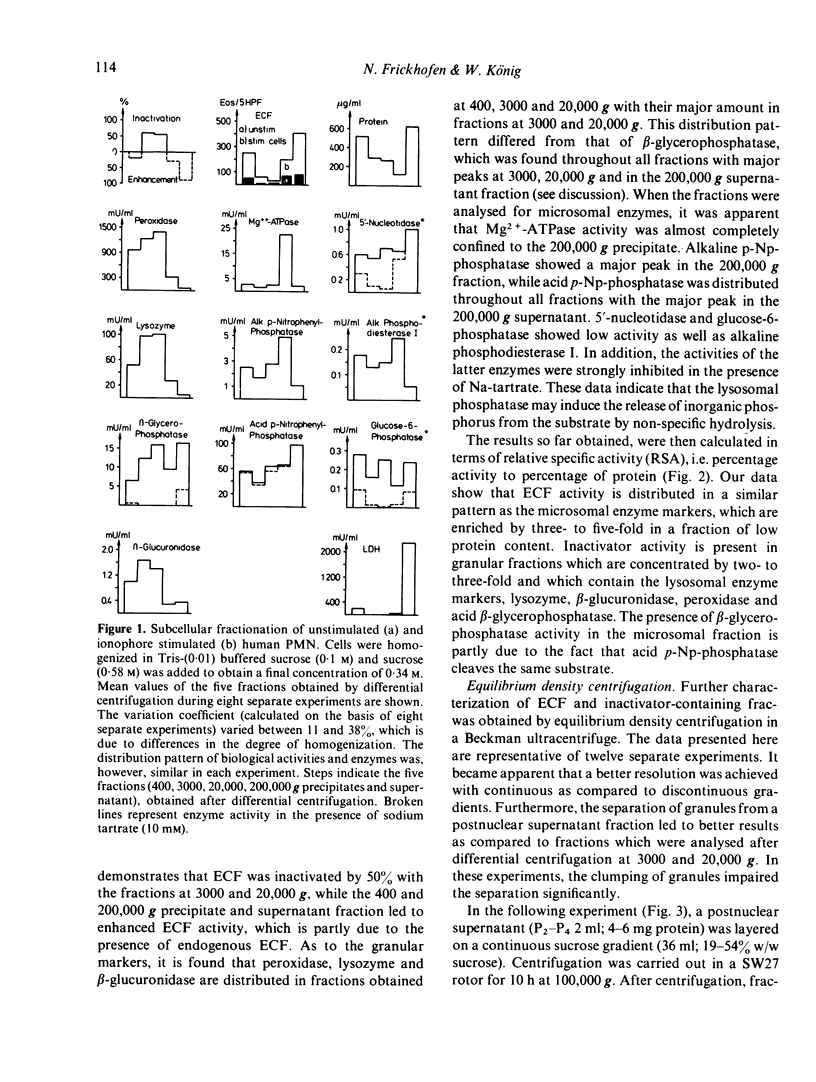
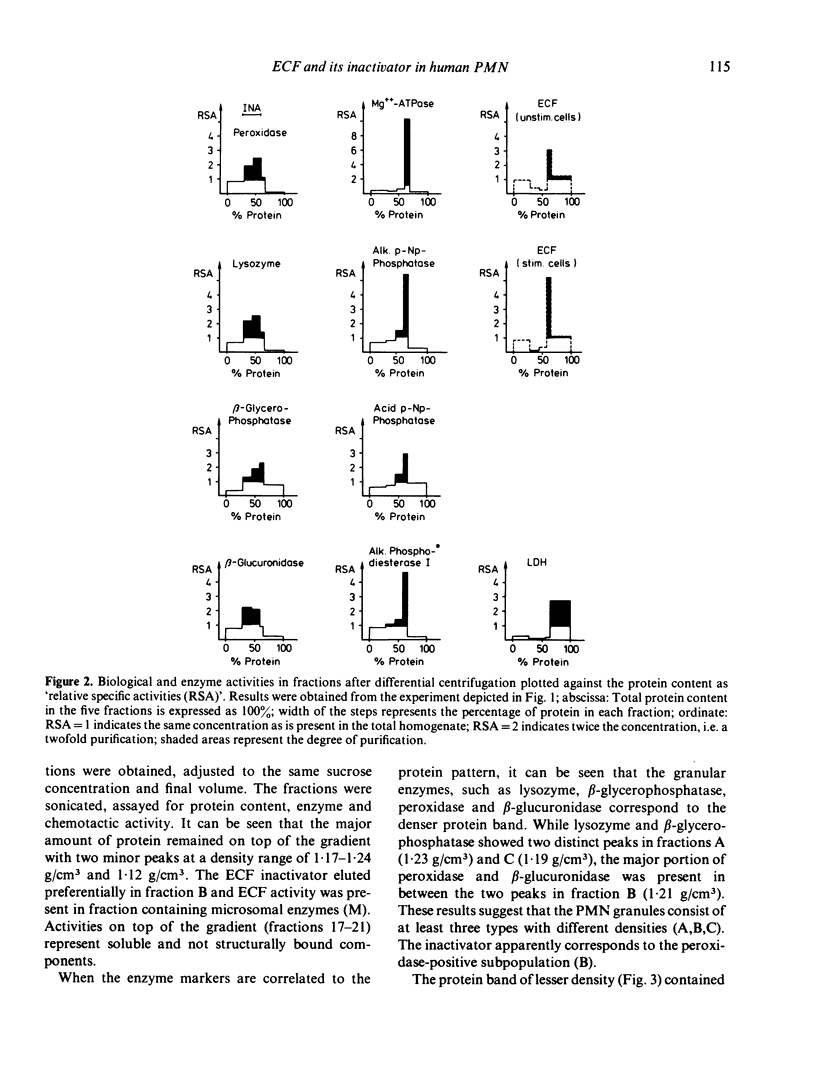
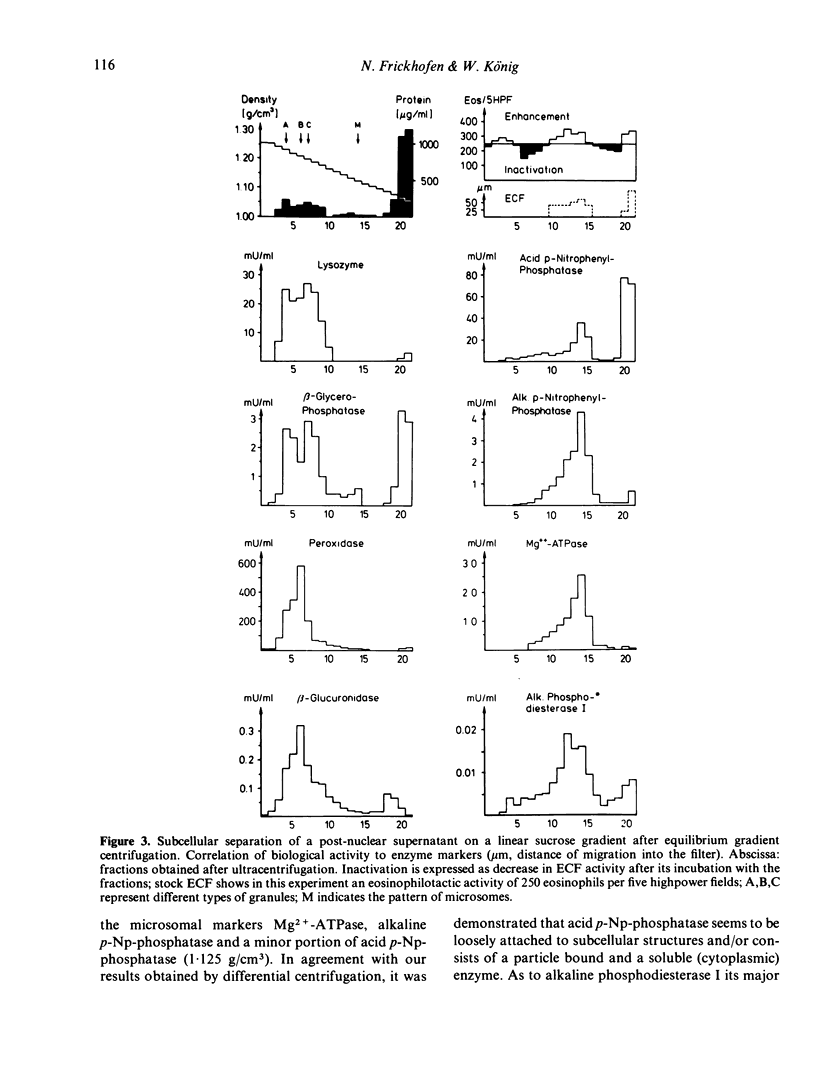
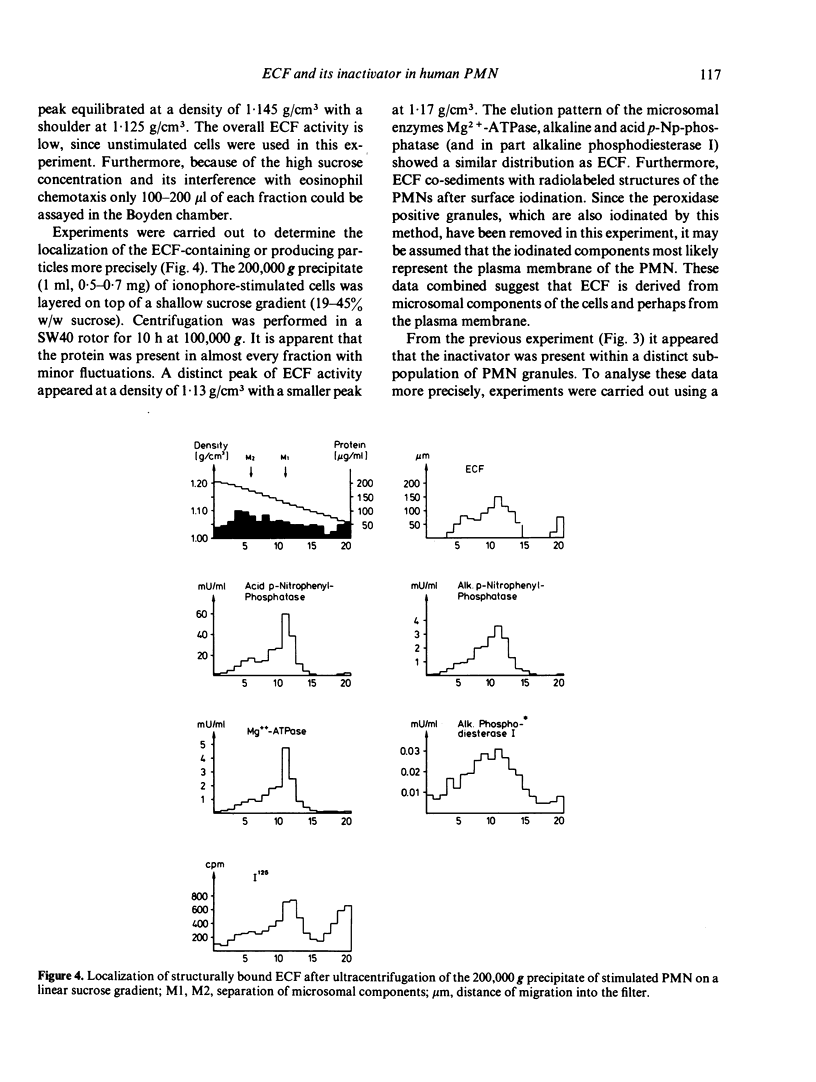
An eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF) of low MW can be released from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) on stimulation with the Ca-ionophore, arachidonic acid and during phagocytosis. After a rapid rise of ECF activity in the supernatant a steep fall of in its activity occurred at the later times of secretion suggesting a mechanism of ECF inactivation. ECF obtained at the later times of secretion represents a stable biological activity and does not decrease on further incubation. In addition, intact PMN and ECF combined do not lead to its inactivation, while incubation of homogenized PMN with ECF decreased its activity. These data suggest the presence of an inactivator for ECF within human PMN. The purpose of the study was to localize ECF and its inactivator within human PMN. After cell disruption, differential and equilibrium gradient centrifugation, subcellular components of human PMN can be obtained which reveal eosinophilotactic (ECF) or ECF-inactivating activity. ECF activity can be recovered (in a structurally bound state) from the microsomal fraction of unstimulated and stimulated PMNs, while another portion is obtainable as a soluble, low mol. wt ECF. The PMN-derived ECF inactivator can be recovered from the peroxidase positive (azurophilic) granules and has a mol. wt of 60,000 and less. We suggest that low mol. wt ECF is derived from the plasma membrane of PMN which can be inactivated by components of the azurophilic granules. The mechanism of inactivation is still unresolved.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretz U., Baggiolini M. Biochemical and morphological characterization of azurophil and specific granules of human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):251–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. M., König W., Lichtenstein L. M. Eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF). I. Release from polymorphonuclear leukocytes by the calcium ionophore A23187. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. M., König W. Modulation of eosinophil chemotaxis and eosinophil chemotactic factor release by concanavalin A. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;56(6):551–557. doi: 10.1159/000232071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J., DeChatelet L. R., Iverson D. B., McCall C. E. Magnesium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase as a marker enzyme for the plasma membrane of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):436–443. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.436-443.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Czarnetzki B. M., Lichtenstein L. M. Eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF). II. Release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Czarnetzki B. M., Lichtenstein L. M. Eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF). III. Generation in human peripheral leukocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;56(4):364–375. doi: 10.1159/000232043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Frickhofen N., Tesch H. Generation and secretion of eosinophilotactic activity from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by various mechanisms of cell activation. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):733–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Ishizaka K. Binding of rat IgE with the subcellular components of normal rat mast cells. Immunochemistry. 1976 Apr;13(4):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Tesch H., Frickhofen N. Generation and release of eosinophil chemotactic factor from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by arachidonic acid. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jun;8(6):434–437. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Nonrespiratory functions of pulmonary cells: the mast cell. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2676–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Dalldorf F. G., Leffell M. S., Folds J. D., Welsh I. R., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E. Character of azurophil and specific granules purified from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):774–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C., Rosenthal A. S., Gelb N. A., Kimball H. R. Separation and characterization of human neutrophil granules. Am J Pathol. 1974 Oct;77(1):41–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


