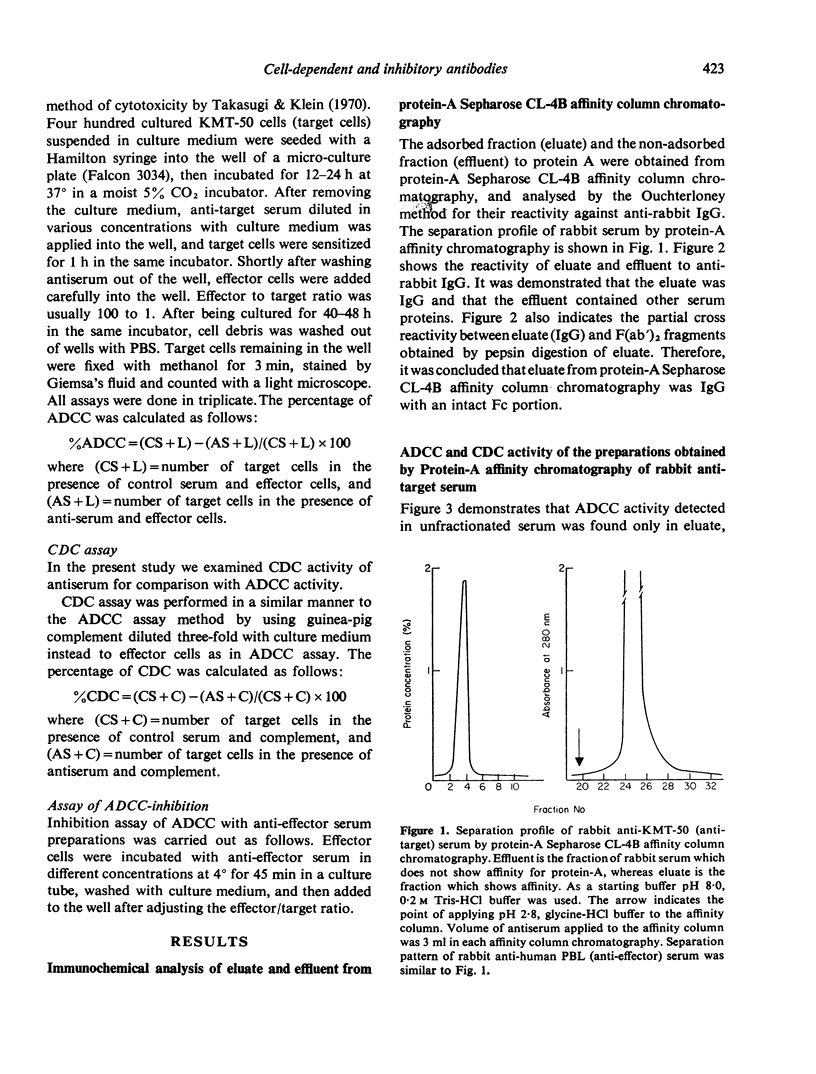
Abstract
The nature of cell-dependent antibody (CDA) and the mechanism of inhibition of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) were studied in the ADCC assay system in which culture cells of methylcholanthrene-induced rat fibrosarcoma (KMT-50) were used as target cells, xenogeneic antiserum (rabbit anti-KMT-50) as the CDA, and human peripheral blood leucocytes (PBL) as effector cells, respectively. By using protein-A Sepharose CL-4B affinity column chromatography of rabbit anti-KMT-50 serum, CDA was shown to bind protein A. Complement dependent-cytotoxicity (CDC), however, was demonstrated in both the adsorbed fraction (eluate) and the non-adsorbed fraction (effluent) to protein A from the same affinity column chromatography. These data confirmed that CDA was IgG with an intact Fc portion. Inhibition of ADCC occurred by pretreatment of effector cells with rabbit anti-effector (human PBL) serum even with extremely small amounts of antiserum. Such inhibition was demonstrated with the eluate but not with the effluent from protein-A Sepharose CL-4B affinity column chromatography of rabbit anti-effector serum. F(ab')2 fragments of the same eluate (IgG) did not inhibit the ADCC activity. These data showed that the inhibition of ADCC was induced by the blocking of Fc receptors of effector cells with the Fc portions of IgG in anti-effector serum. The data obtained indicate the usefulness of protein A in separation and analysis of CDA and in investigation of the inhibitory mechanisms of ADCC.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Studies of the human lymphocyte receptor for heat-aggregated or antigen-complexed immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill J. S. ADCC effector cells in a murine adenocarcinoma. I. Evidence for blood-borne bone-marrow-derived monocytes. Int J Cancer. 1977 Sep 15;20(3):432–440. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayami M., Ito M., Yoshikawa Y., Yamanouchi K. Temporal analysis of cellular cytotoxicity and humoral factors during progession and regression of Rous sarcomas in Japanese quails. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1976 Feb;29(1):11–24. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.29.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Koshiba H., Ueno H., Maeyama I., Takami T. Characterization of human B lymphocyte specific antigens. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Neauport-Sautes C., Ellerson J. R., Fridman W. H. Binding site of human IgG subclasses and their domains for Fc receptors of activated murine T cells. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1077–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Frommel D. Definition of staphylococcal protein A reactivity for human immunoglobulin G fragments. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):124–127. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon E. W., Whitten H. D., Skurzak H. M., Andersson B., Lidin B. IgM antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the Moloney sarcoma virus system: the involvement of T and B lymphocytes as effector cells. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1288–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H. Contactual lysis of antibody-coated chicken erythrocytes by purified lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):300–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cytolytic lymphocytic cells with complement receptor in human blood. Induction of cytolysis by IgG antibody but not by target cell-bound C3. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):287–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perper R. J., Zee T. W., Mickelson M. M. Purification of lymphocytes and platelets by gradient centrifugation. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Nov;72(5):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski W. K. Cytodestructive mechanisms provoked by lymphocytes. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. B., Nelson K. Evidence for two factors in sera of tumor-immunized mice which induce specific lymphoid cell-dependent cytotoxicity: IgG2 and a rapidly appearing factor not associated with IgG or IgM. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prather S. O., Lausch R. N. Kinetics of serum factors mediating blocking, unblocking and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in hamsters given isografts of para-7 tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1976 Mar 15;17(3):380–388. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmacher V., Halloran P., David C. S. Interactions of Fc receptors with antibodies against Ia antigens and other cell surface components. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1201–1209. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Klein E. A microassay for cell-mediated immunity. Transplantation. 1970 Mar;9(3):219–227. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197003000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S. Mediation of macrophage cytolytic and phagocytic activities by antibodies of different classes and class-specific Fc-receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Michaelsen T. E., Froland S. S. Inhibition of antibody-dependent human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity by immunoglobulin classes, IgG subclasses, and IgG fragments. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y. Immunologic responses to a murine mammary adenocarcinoma. II. Monocyte effector activation by humoral factors. Int J Cancer. 1977 May 15;19(5):717–724. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]