Abstract
C57Bl mice are relatively resistant to a moderate subcutaneous infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium while BALB/c mice are much more susceptible. Cutaneous delayed hypersensitivity reactions which develop in the first 3 weeks of infection were compared in these two strains of mice. Both strains gave a peak of delayed hypersensitivity between 6 and 10 days after infection which was followed by a period of low reactivity before the development, in the third week, of a stable persistent delayed hypersensitivity reaction. There was no difference between the strains in the size at 24 h of the delayed hypersensitivity reaction but the reactions differed in their kinetics. The low resistance strain, BALB/c, gave a Jones-Mote-type of response while the high resistance strain gave a response which could be described as a tuberculin-type reaction.
Full text
PDF

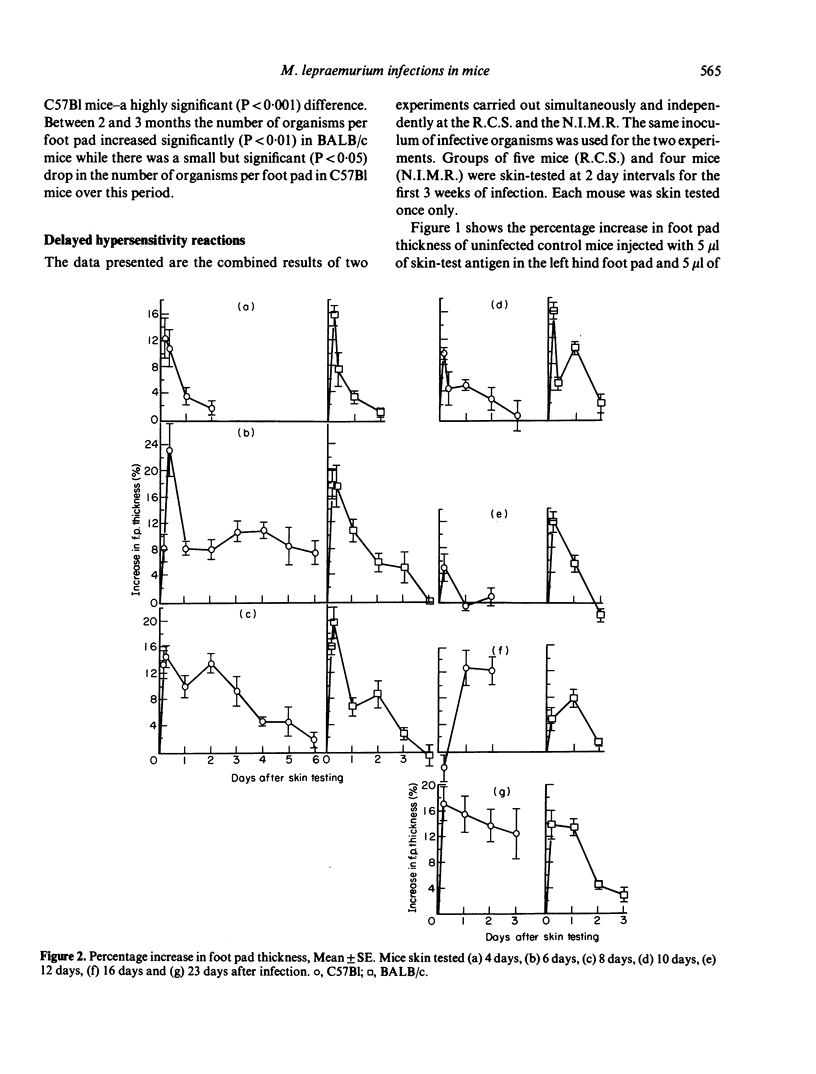
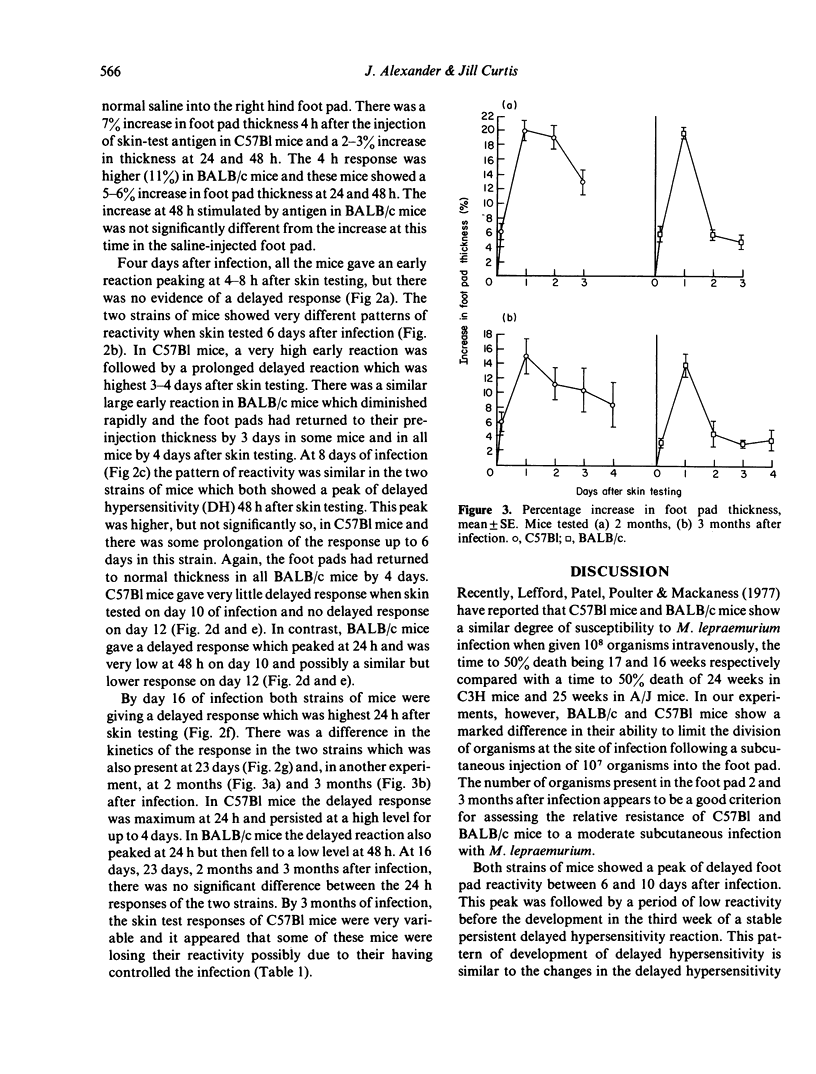

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Closs O. Experimental murine leprosy: growth of Mycobacterium lepraemurium in C3H and C57/BL mice after footpad inoculation. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):480–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.480-489.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Haugen O. A. Experimental murine leprosy. 2. Further evidence for varying susceptibility of outbred mice and evaluation of the response of 5 inbred mouse strains to infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1974 Jul;82(4):459–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P. The walls of Mycobacterium lepraemurium: chemistry and ultrastructure. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):313–324. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART P. D., REES R. J. Effect of macrocyclon in acute and chronic pulmonary tuberculous infection in mice as shown by viable and total bacterial counts. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:414–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J., Patel P. J., Poulter L. W., Mackaness G. B. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to Mycobacterium lepraemurium in susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.654-659.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzini L., Rottoli P., Rottoli L. The spectrum of human tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Feb;27(2):230–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Lefford M. J. Development of delayed-type hypersensitivity during Mycobacterium lepraemurium infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.439-446.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



