Abstract
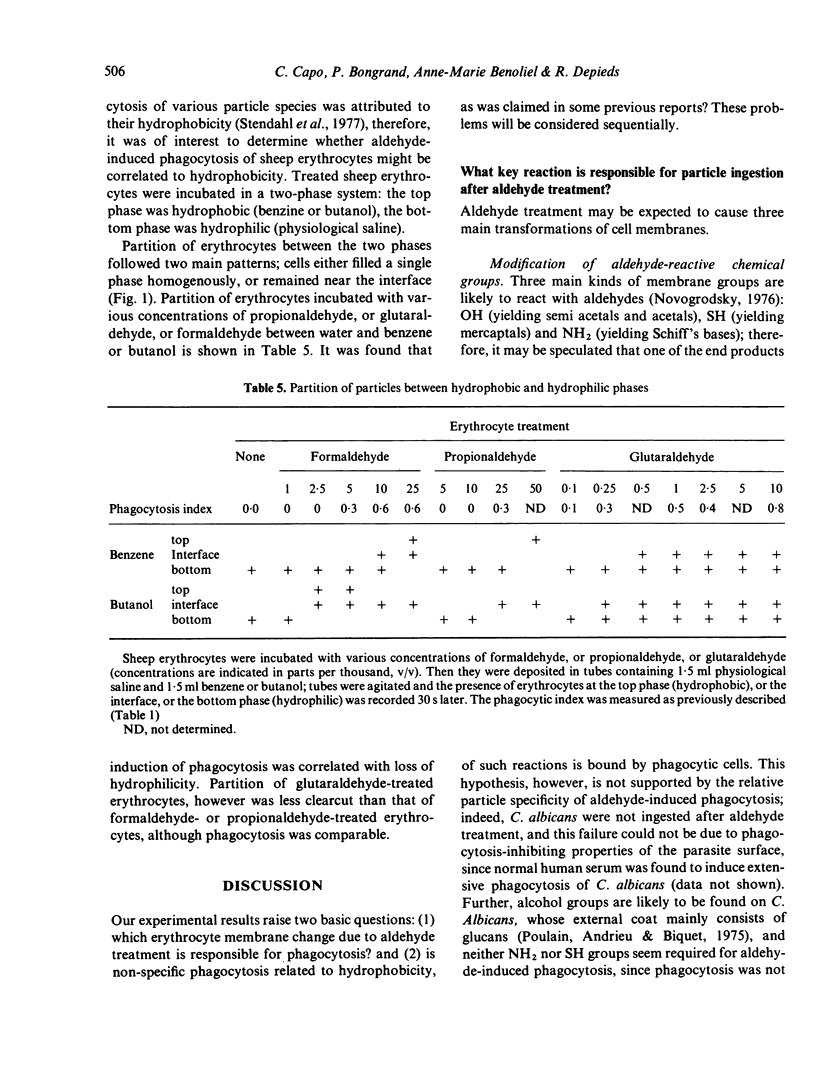
Particles were chemically modified with aldehydes and incubated with rat peritoneal cells for phagocytosis. All dialdehydes and lower monaldehydes tested (methanal, ethanal and propanal) made sheep erythrocytes phagocytosable. Failure of higher monaldehydes to induce phagocytosis of treated erythrocytes was not due to lack of reactivity with red cell membranes. All erythrocytes tested (bird and mammal red cells were used) and rat thymocytes were phagocytosed by rat macrophages after incubation with aldehyde. Treatment of Candida albicans did not induce phagocytosis: this failure was not due to lack of aldehyde binding (as demonstrated with [14C]-methanal) nor to anti-phagocytic properties of the parasite membrane. Sheep erythrocytes were submitted to enzymatic treatment (pronase, trypsin, neuraminidase) or incubated with succinic anhydride (to block free NH2 groups) or iodacetamide (to block free SH groups) before aldehyde treatment: phagocytosis was not decreased, which suggested that aldehydes did not act by altering some definite surface structure of the treated particles. Treatment of erythrocytes with cross-linking compounds such as tetraazotized o-dianisidine (coupling occurs mainly on tyrosine and histidine residues) or l-ethyl(3-dimethyl aminopropyl) carbodiimide (a bivalent reagent binding free COOH groups) did not induce any substantial phagocytosis of erythrocytes. Phagocytosis of aldehyde treated erythrocytes was partly correlated with hydrophobicity of these cells, as measured with a two-phase partition system. It is concluded that aldehyde-mediated phagocytosis of erythrocytes is mainly due to cross-linking of red cell membrane structures, probably involving free OH groups, which must increase local rigidity and thereby modify hydrophobicity of the red cell surface.
Full text
PDF

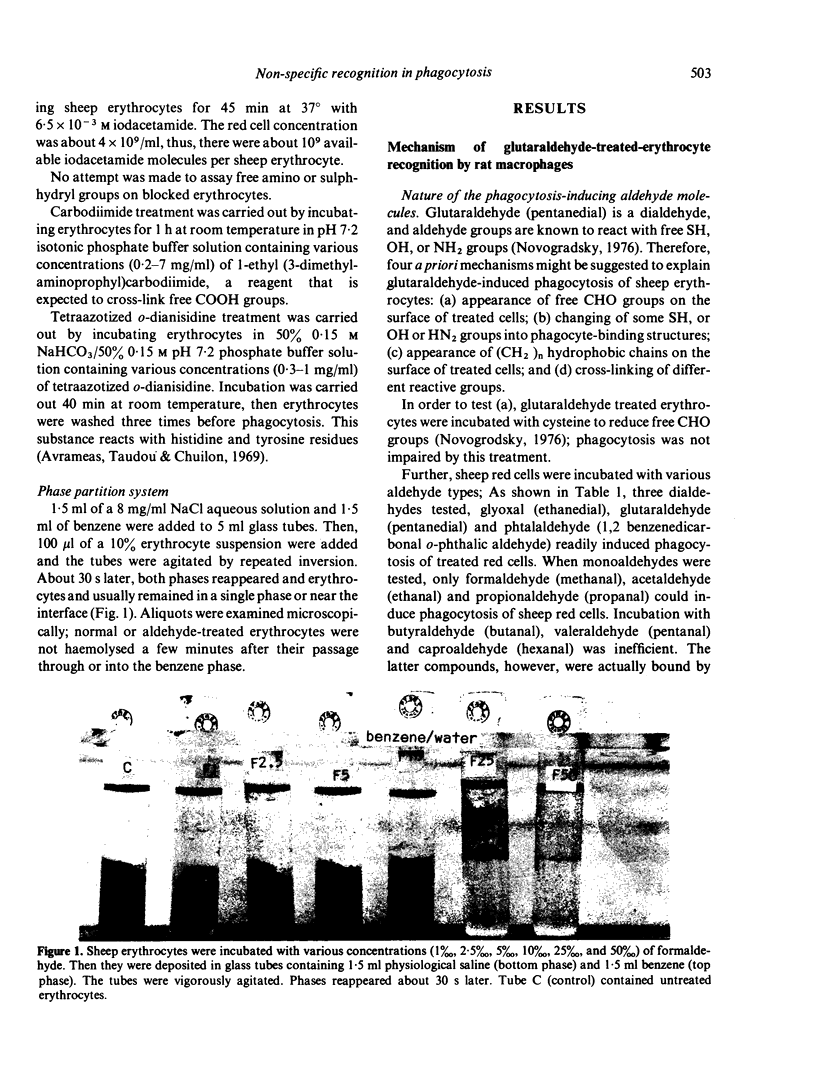
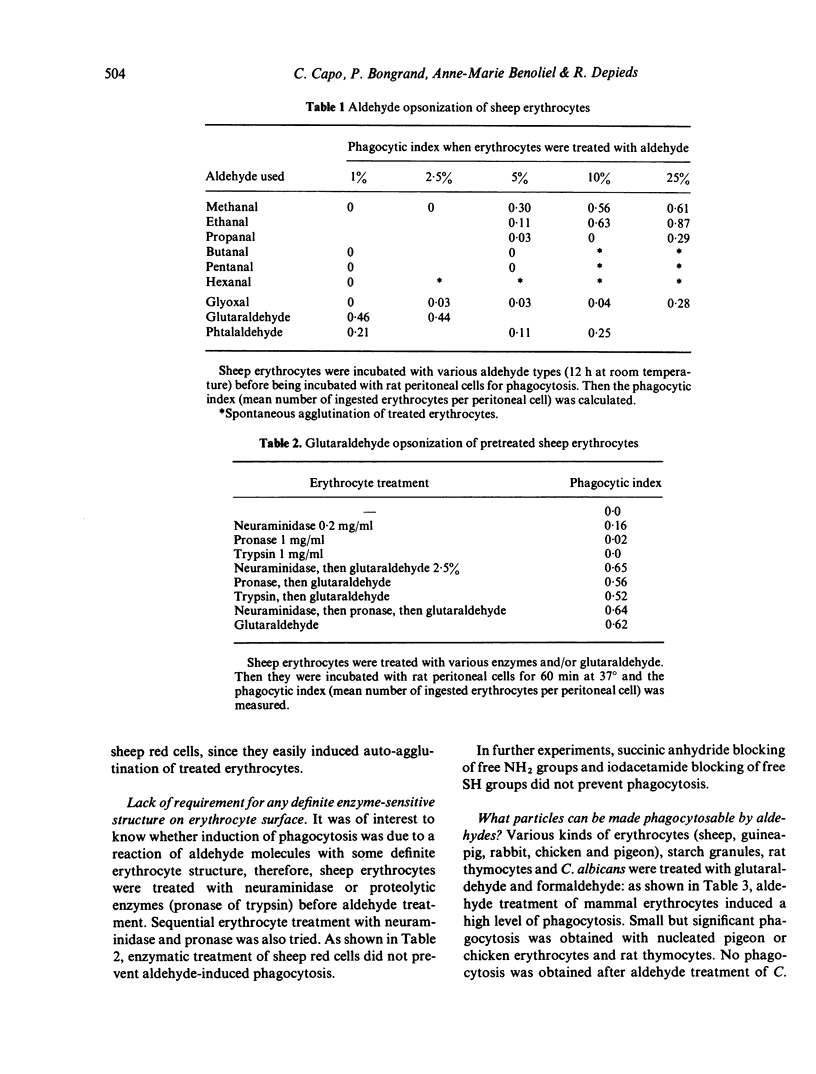
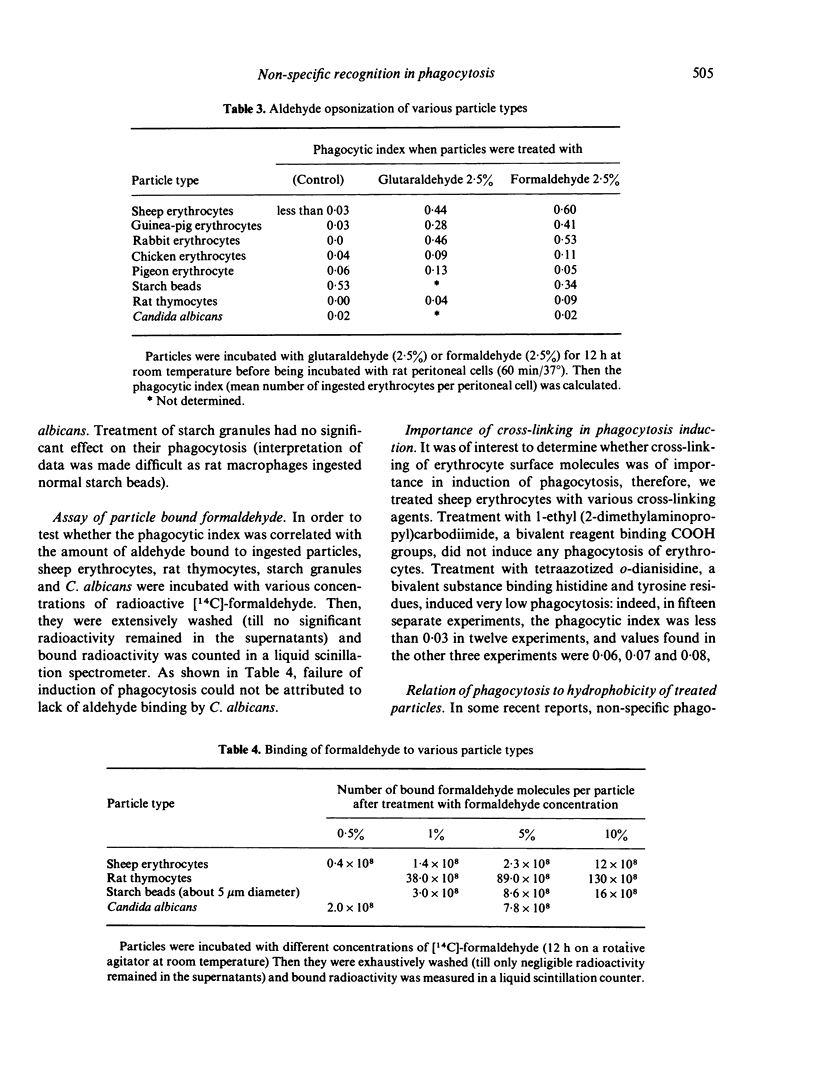


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIOZZI G., STIFFEL C., HALPERN B. N., MOUTON D. Lack of action of serum opsonins in phagocytosis of inert particles by cells of reticuloendothelial system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Apr;112:1017–1020. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzri S., Korn E. D. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cells. Endocytosis and fusion as alternate mechanisms for the uptake of lipid-soluble and water-soluble molecules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):621–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Sulica A., Dumitrescu M., Vranialici D. Recognition of altered autologous constituents as foreign by phagocytic cells. Nature. 1967 Feb 25;213(5078):824–825. doi: 10.1038/213824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guri C. D., Bernstein D. S. Rat epiphyseal cartilage. V. Glucose-C14 metabolism as related to growth and to various anatomical areas, in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):386–391. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEEB A. F., CASSIDY H. G., SINGER S. J. Molecular structural effects produced in proteins by reaction with succinic anhydride. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. The action of lower aldehydes on the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:366–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90448-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M., Sachs L. Rotational relaxation time of concanavalin A bound to the surface membrane of normal and malignant transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUTON D., BIOZZI G., BOUTHILLIER Y., STIFFEL C. Phagocytosis of Salmonellae by reticuloendothelial cells of newborn piglets lacking natural antibody. Nature. 1963 Feb 16;197:706–706. doi: 10.1038/197706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrasher S. G., Yoshida T., Van Oss C. J., Cohen S., Rose N. R. Alteration of macrophage interfacial tension by supernatants of antigen-activated lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K. G., Kelley R. O. Cell surface glycosaminoglycans: identification and organization in cultured human embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Sep;92(3):469–480. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]