Abstract
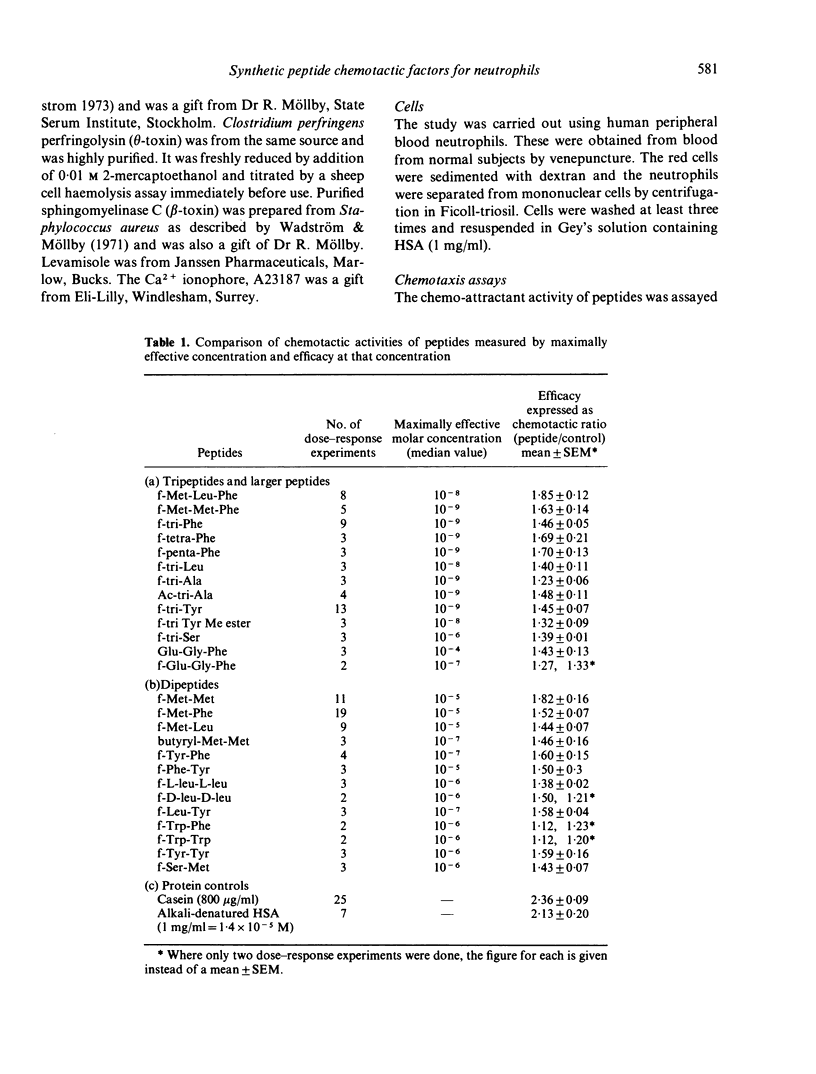
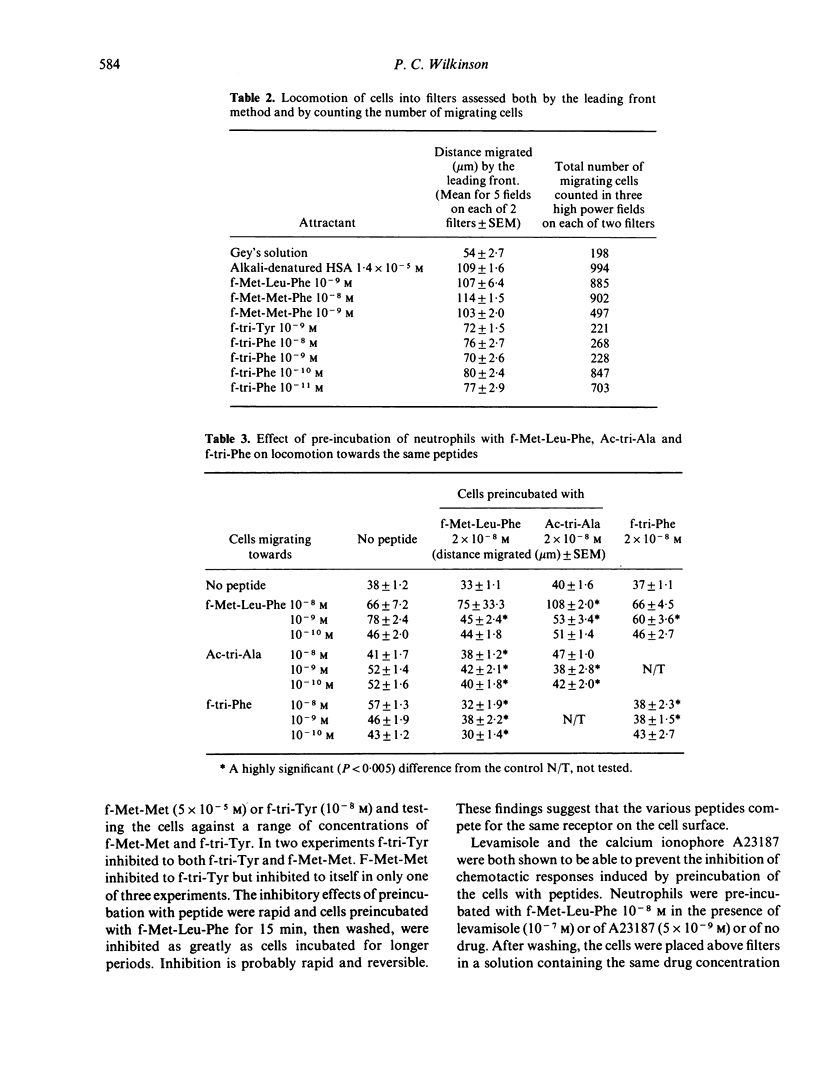
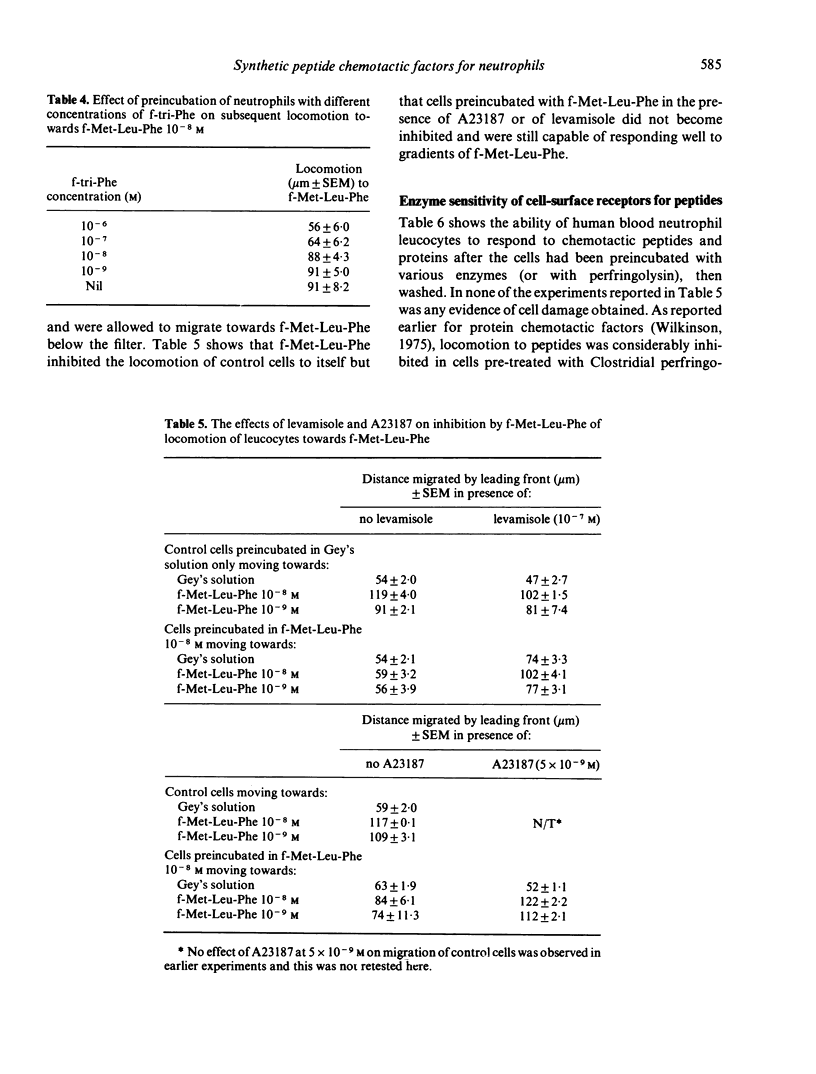
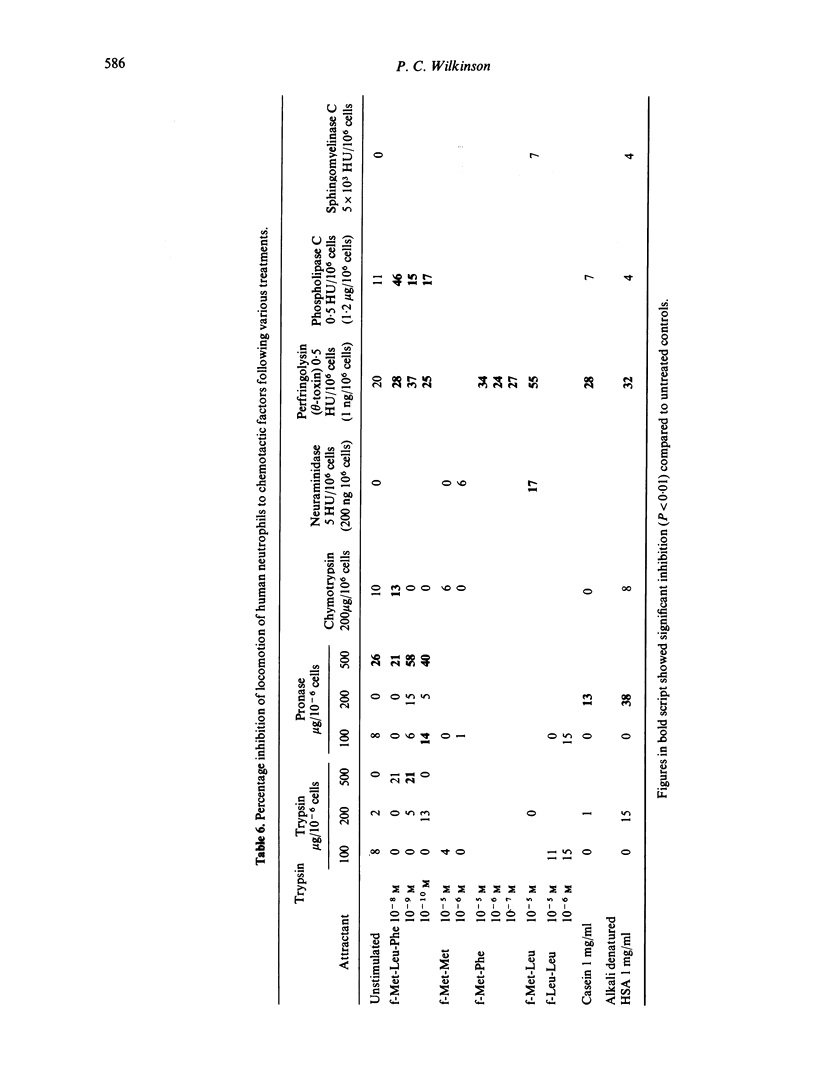
The chemotactic activity for neutrophil leucocytes of twenty-six peptides of varied sequence, of which the majority were N-formylated, was assessed by determining the concentration at which each was maximally active and the efficacy of each peptide at that concentration. These two measures of activity did not correlate with one another. Many formylated peptides with a wide variety of sequences were active. Of these, the formyl-methionyl peptides had highest efficacy, but many other peptides were active at concentrations as low as the formyl-methionyl tripeptides. Unrelated peptides, viz formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, acetyl-tri-alanine, formyl-tri--phenyla-lanine, cross-inhibit the cells' response to one another, and this inhibition is reversible. Inhibition is prevented if the cells are incubated throughout the experiment in levamisole or A23187. These experiments suggest that the leucocyte peptide receptor is capable of binding many ligands, and that activation of a response is not solely a function of binding affinity. They exclude a strict steric specificity for binding. Chemotactic responses to formylated peptides were shown to be reduced in cells pretreated with perfringolysin, a bacterial cholesterol-binding toxin, and with phospholipase C. Trypsin and pronase also reduced these responses when used at 500 micrograms per 10(6) cells but not at lower doses.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Gallin J., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: microtubule assembly and membrane fusion induced by a component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro neutrophil responses to chemotactic factors by a competitive antagonist. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. VI. Production and purification of -haemolysin in large scale. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):288–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Allan R. B. Binding of protein chemotactic factors to the surfaces of neutrophil leukocytes and its modification with lipid-specific bacterial toxins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;20(1):25–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00229452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Inhibition of leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis by lipid-specific bacterial toxins. Nature. 1975 Jun 5;255(5508):485–487. doi: 10.1038/255485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabucchi G., Soranzo M. R., Rossi F. Exocytosis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by A 23187 and calcium. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 1;54(1):44–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to orient in gradients of chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):606–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


